- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Tongue is a muscular organ – Situated in the floor of the mouth
FUNCTION
- Taste
- Speech
- Mastication
- Deglutition
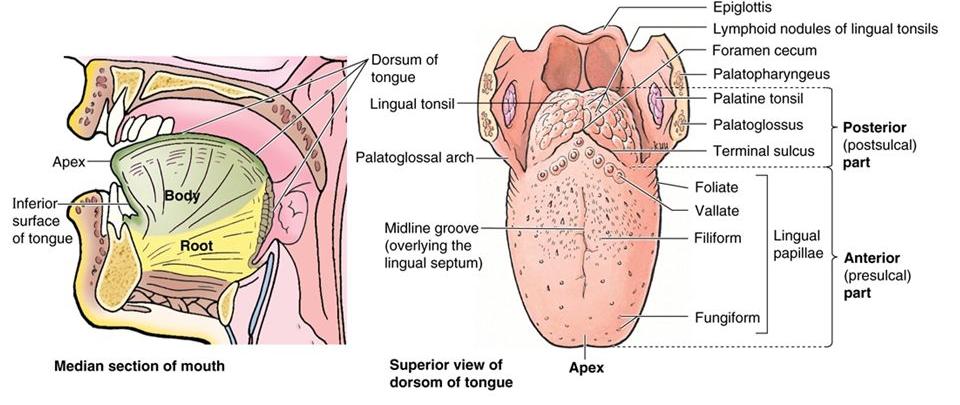
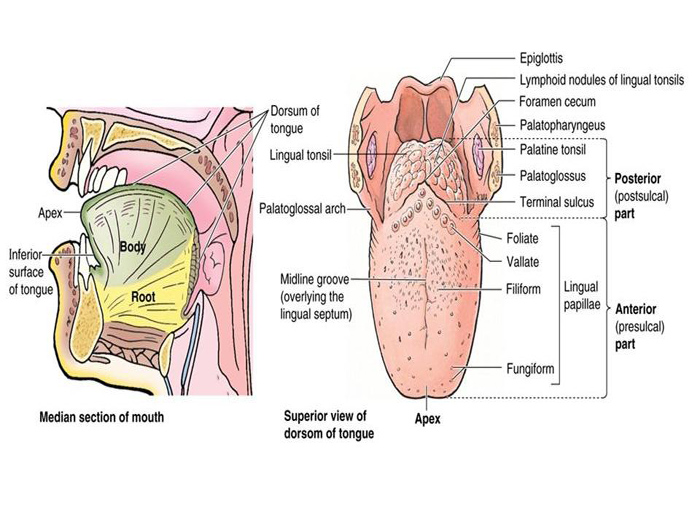
EXTERNAL FEATURES
Tongue has
- A Root
- A tip
- A body
ROOT
- Is attached to the mandible and soft palate above and hyoid bone below.
- These attachments prevent the swallowing of the tongue.
- In between the 2 bones it is related to the geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles.
TIP
- Of the tongue forms the anterior free end which lies behind the upper incisor teeth
BODY – Has
- A curved upper surface or dorsum
- An inferior or ventral surface
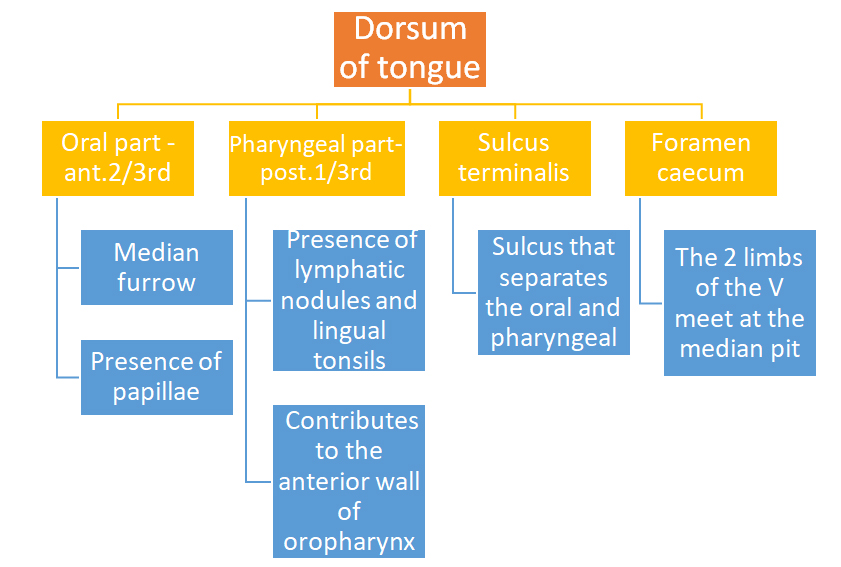
DORSUM
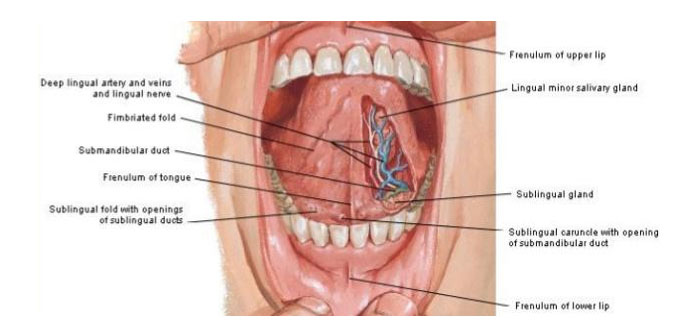
Ventral surface
- Is confined to the oral part only
- a smooth mucous membrane, which shows a median fold called frenulum linguae.
- On either side of the frenulum there is a prominence produced by the deep lingual veins.
- More laterally there is a fold called the plica fimbriata that is directed forwards and medially towards the tip of the tongue .
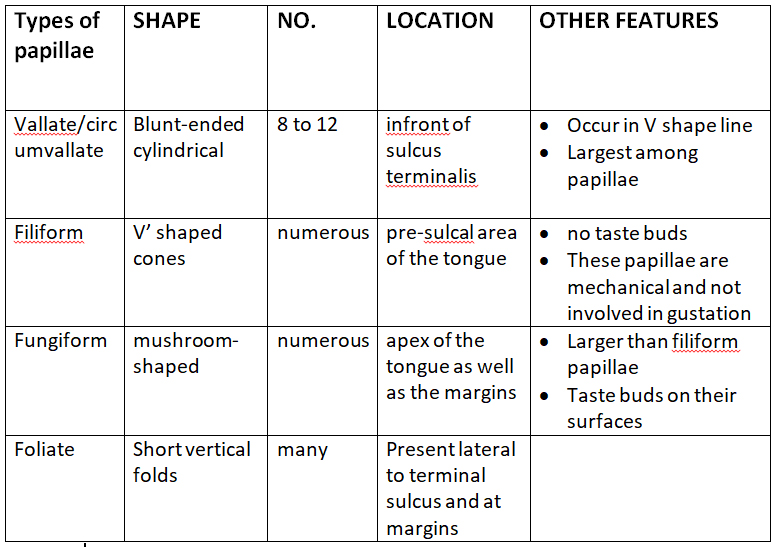
PAPILLAE
Indentation of any structure in the overlying epithelium is called papillae Superior surface of tongue
Taste Buds
- Sensory receptors for taste
- The sensation of taste is called gustation
- Taste buds are located on the surfaces of papillae except filiform papillae
- Four taste sensations, recently a fifth basic taste has been added: sour, sweet, salty, bitter and the recently added umami UMAMI
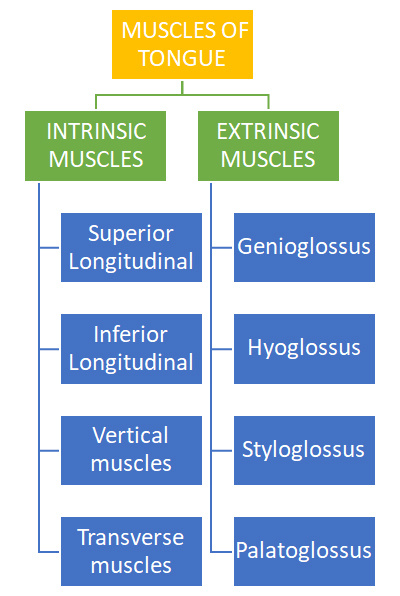
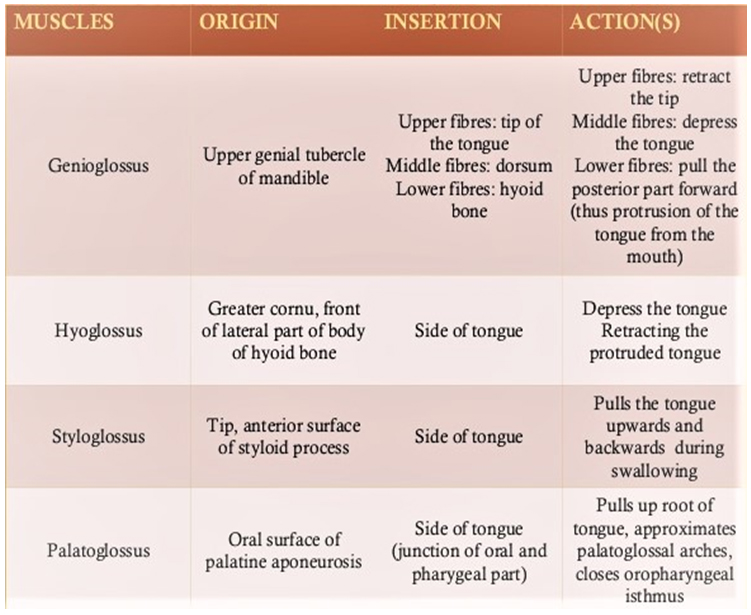
INTRINSIC MUSCLES
- These muscles are confined to the tongue
- They originate and inserts within the tongue
- No bony attachments
- FUNCTION: They alter the shape of tongue
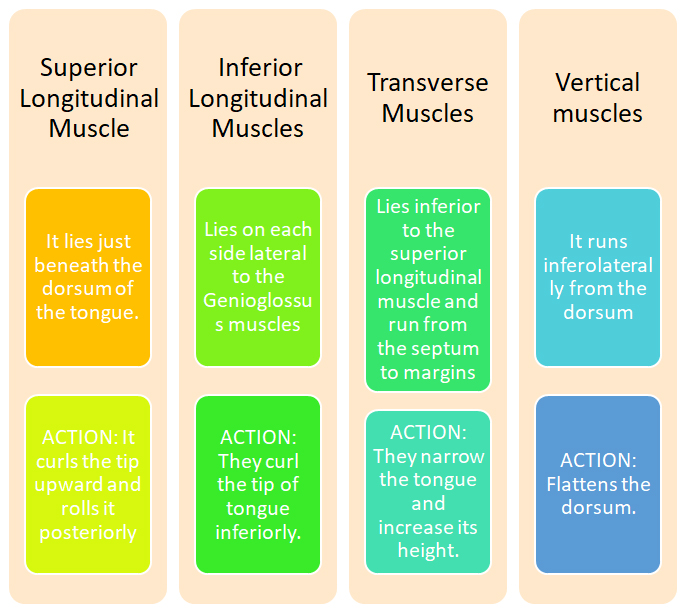
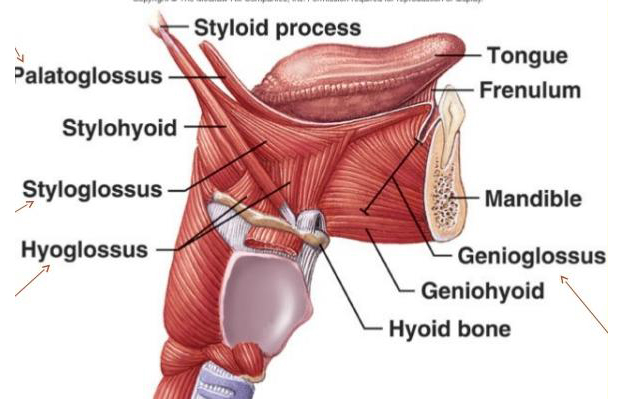
EXTRINSIC MUSCLES
These muscles take origin from parts outside the tongue, therefore move the tongue as well as alter the shape
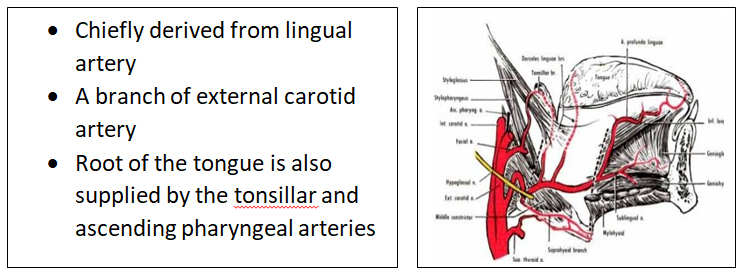
ARTERIAL SUPPLY
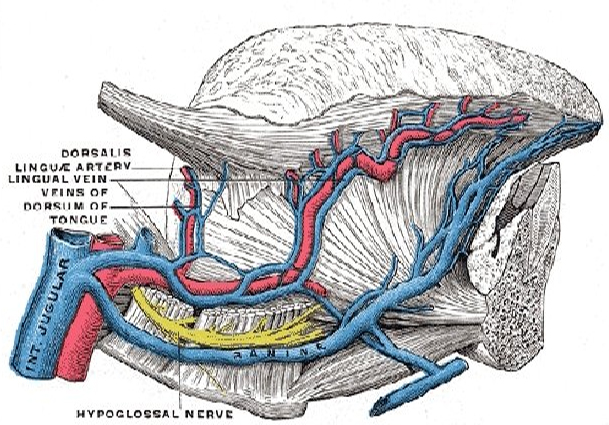
VENOUS DRAINAGE
- Veins of the tongue are called vena comitantes.
- The arrangement of vena comitantes is variable.
- 2 vena comitantes accompany the lingual artery and 1 vena comitantes accompanies the hypoglossal nerve.
- The deep lingual vein is the largest and the principal vein of the tongue.
- It is visible on the inferior surface of the tongue.
- It runs backwards and crosses the genioglossus and the hyoglossus below the hypoglossal nerve.
- These veins unite at the posterior borders of the hyoglossus to form lingual vein which ends either in the common facial vein or in the internal jugular vein.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
- Tip of the tongue drains bilaterally to the submental nodes
- Right and left halves of the remaining part of the anterior 2/3rd of the tongue drains unilaterally to the submandibular nodes.
- Few central lymphatics drain bilaterally to the same nodes.
- Posterior 1/3rd of the tongue drains bilaterally to the jugulo-omohyoid nodes, these are known as the lymph nodes of the tongue.
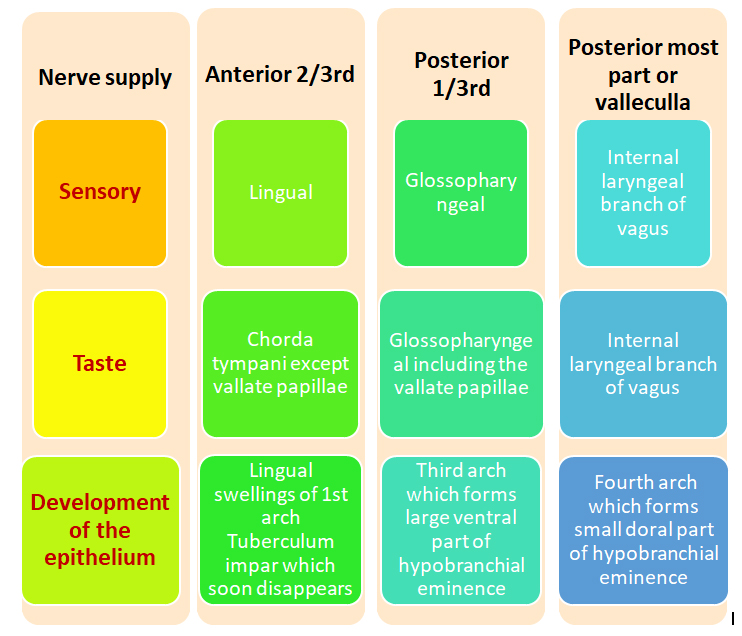
NERVE SUPPLY OF THE TONGUE
Innervation is complex and consists of three different supplies
- Motor supply
- General sensory supply
- Special sensory supply(taste)
Motor Supply
- All extrinsic and intrinsic muscles are supplied by HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE except PALATOGLOSSUS muscle which is supplied by VAGUS NERVE.
HISTOLOGY
- Bulk of the muscle is made up of striated muscles
- Mucous membrane consists of a layer of CT (corium), lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
- Oral part of dorsum : is thin, forms papillae and is adherent to the muscles.
- Pharyngeal part of the dorsum:is very rich in lymphoid follicles.
- Inferior surface :is thin and smooth. Numerous glands, both mucous and serous lie deep to the mucous membrane.
DEVELOPMENT OF TONGUE
I EPITHELIUM
Anterior 2/3rd
• From 2 lingual swellings and one tuberculum impar ,which arise from the first branchial arch
• Tuberculum impar :soon disappears
• Therefore supplied by lingual nerve (post trematic) and chorda tympani (pretrematic)
Posterior 1/3rd
• From cranial large part of the hypobranchial eminence, i.e. from the third arch.
• Therefore supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Posterior most part
• From 4th arch
• Therefore, supplied by vagus nerve
II MUSCLES
• Muscles develop from the occipital myotomes which are supplied by the hypoglossal nerve
III CONNECTIVE TISSUE CT
• develops from the local mesenchyme
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
MCQS
1 Hypoglossal nerve supplies to all of the following muscles EXCEPT;
A Palatoglossus
B Genioglossus
C Hyoglossus
D Styloglossus
Answer: A
2 The lymphatic drainage from the tip of tongue first passes to;
A Submental nodes
B Supra clavicular nodes
C Sub mandibular nodes
D Superior deep cervical nodes
Answer : A