- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
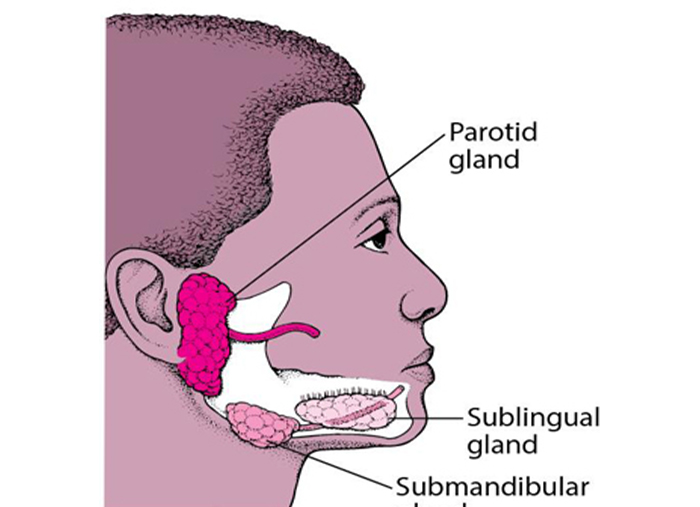
1. Which of the following is predominantly mucous
A) Parotid gland
B) Submandibular gland
C) Sublingual gland
D) Von Ebner’s gland
Ans: C
Sublingual gland is mixed and predominantly mucous.
Parotid is purely serous.
Submandibular is mixed and predominantly serous.
2. Stenson’s duct drains
A) Submandibular gland
B) Sublingual gland
C) Parotid gland
D) Minor salivary gland
Ans: C
Parotid duct (Stensen’s duct): A 5 cm long duct obliquely through buccinator.
This prevents the inflation of duct during blowing and opens on the buccal mucosa, opposite the second molar tooth.
Submandibular gland– Warthin’s duct
Sublingual gland– Bartholin duct or duct of rivinus
3. Which one of the following structures pierces the buccinator muscle
A) Deep facial vein
B) sublingual artery
C) Parotid duct
D) Auriculotemporal nerve
Ans: C
Parotid or stensen’s duct pierces buccal pad of fat, buccopharyngeal fascia and buccinator muscle.
4. Submandibular gland is located in
A) Digastric triangle
B) Carotid triangle
C) Muscular triangle
D) Deep to hyoglossus muscle
Ans: A
5. The opening of submandibular gland duct into oral cavity is at
A) Maxillary second molar
B) Mandibular third molar
C) Dorsum of tongue
D) Sublingual caruncle
Ans: D
Warthin’ s duct is 5cm long emerges from submandibular gland and in its course runs on the hyoglossus between lingual and hypoglossal nerve and opens at the sublingual papilla at the side of frenum of tongue.
6. Sublingual gland is situated between
A) Hyoglossus and genioglossus
B) Hyoglossus and styloglossus
C) Genioglossus and mandible
D) Geniohyoid and genioglossus
Ans: C
sublingual gland is situated medial to the sublingual fossa of the mandible and lateral to genioglossus
7. Sublingual salivary gland is located superior to
A) Genioglossus
B) Hyoglossus
C) Mylohyoid
D) None of the above
Ans: C
Sublingual gland lies superior to mylohyoid and lateral to the genioglossus muscle. Its duct opens directly into floor of mouth on the summit of sublingual fold.
8. Isthmus of thyroid gland is at the level of
A) 2nd to 3rd tracheal rings
B) 3rd to 5th tracheal rings
C) 5th to 6th tracheal rings
D) 6th tracheal rings only
Ans: A
Thyroidae descends from body of hyoid bone to the isthmus or pyramidal lobe
9. The structure between two lobes of thyroid gland may be
A) Pyramidal lob
B) Remnant of thyroglossal duct
C) Muscular slip
D) Any of the above
Ans: D
10. The suspensory ligament of Berry of the thyroid gland is a derivative of
A) Pretracheal fascia
B) Prevertebral fascia
C) Condensation of the stroma of the gland
D) Thyrohyoid membrane
Ans: A




