- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Salivary Glands And Thyroid Glands
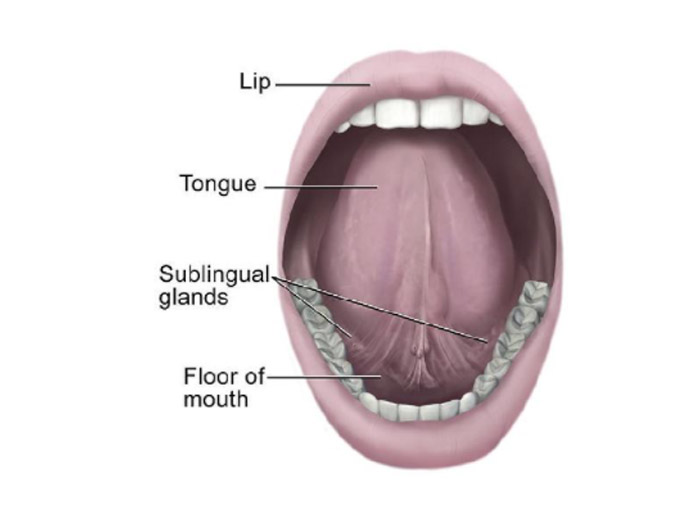
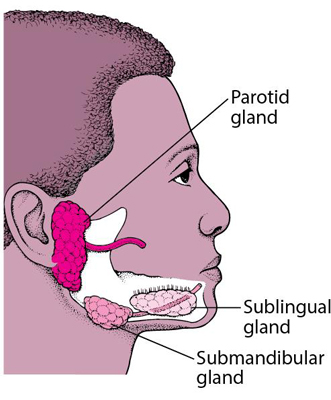
There are 3 pairs of large salivary glands- the parotid, submandibular and sublingual. In addition, there are numerous small glands in the tongue, the palate, the cheek and the lips. These glands produce saliva which keeps the oral cavity moist, and helps in chewing and swallowing. The saliva also contains enzymes that aid digestion.
1. PAROTID GLAND:
- The parotid is the largest of the salivary glands. It weighs about 15g.
- It is situated below the external acoustic meatus, between the ramus of the mandible and the sternocleidomastoid.
- Anteriorly, the gland overlaps the masseter muscle. A part of this forward extension is often detached, and is known as the accessory parotid. And it lies between the zygomatic arch and the parotid duct.
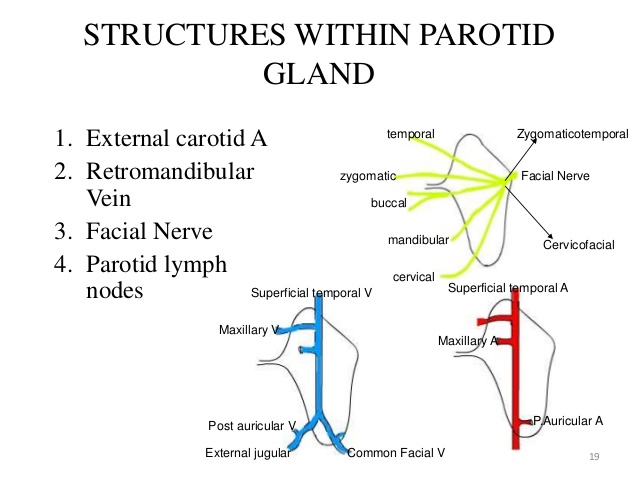
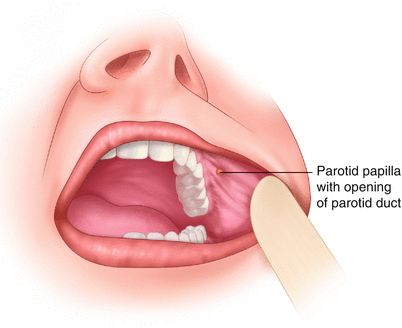
PAROTID DUCT:
It is thick walled and about 5cm long. It emerges from the middle of the anterior border of the gland. It runs forward and slightly downwards on the masseter. Its reations are:Superiorly
- Accessory parotid gland
- Transverse facial nerve
- Upper buccal branch of facial nerve
BLOOD SUPPLY: External carotid artery
NERVE SUPPY:
A) Parasympathetic:
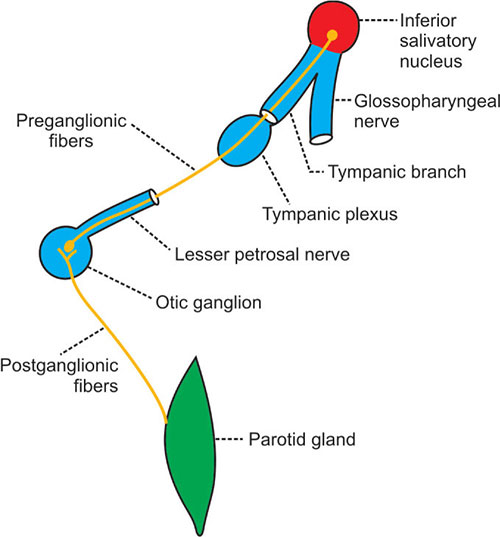
B) Sympathetic nerves are vasomotor, and are derived from the plexus around the middle meningeal artery
C) Sensory nerves to the gland come from the auriculotemporal nerve.
C) Sensory nerves to the gland come from the auriculotemporal nerve.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE:
Lymph drains first to the parotid nodes and from there to the upper deep cervical nodes2. SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND
This is a large salivary gland situated in the anterior part of the digastric triangle. The gland is about the size of a walnut.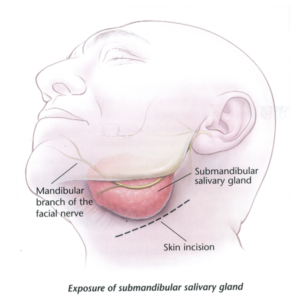
SUBMANDIBULAR DUCT;
It is thin walled and about 5cm long. It emerges at the anterior end of the deep part of the gland and runs forward on the hyoglossus between the lingual and hypoglossal nerves.BLOOD SUPPLY: FACIAL ARTERY
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE: SUBMANDIBULAR LYMPH NODES
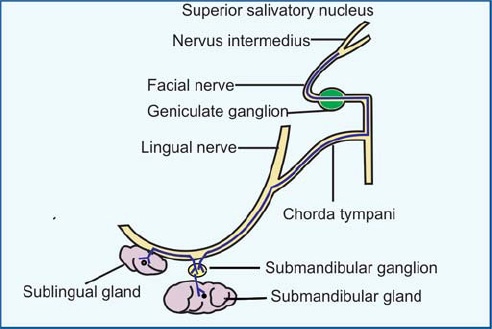
NERVE SUPPLY: SUBMANDIBULAR GANGLION
- SENSORY FIBRES: LINGUAL NERVE
- SYMPATHETIC FIBRES: PLEXUS ON THE FACIAL ARTERY
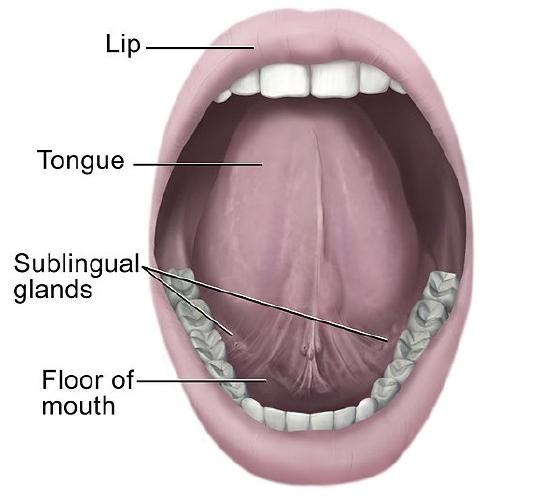
3. SUBLINGUAL SALIVARY GLAND:
This is smallest of the three salivary glands. It is almond shaped and weighs about 3 to 4 g. It lies above the mylohyoid below the mucosa of the floor of the mouth, medial to the sublingual fossa of the mandible and lateral to the genioglossus.About 15 ducts emerge from the gland. Most of them open directly into the floor of the mouth on the summit of the sublingual fold. A few of them join the submandibular duct. The gland receives its blood supply from the lingual and submental arteries. The nerve supply is similar to the submandibular gland.
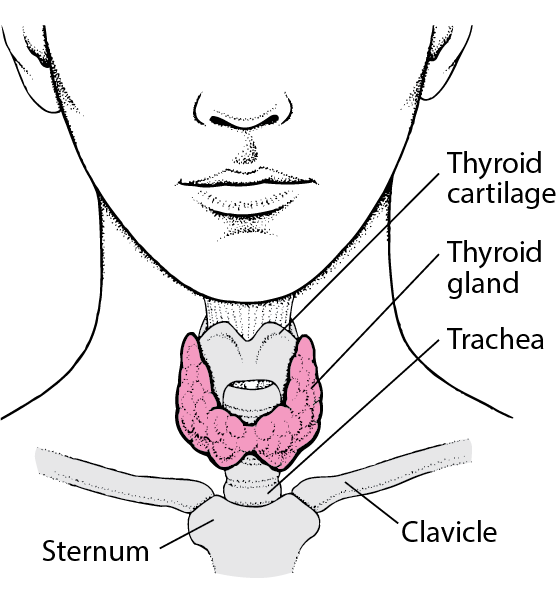
4. THYROID GLAND:
It is an endocrine gland situated in the lower part of the front and sides of the neck. It regulates the basal metabolic rate, stimulates somatic and psychic growth and plays an important role in calcium metabolism.The gland consists of right and left lobes that are joined to each other by the isthmus. A third pyramidal lobe may project upwards from the isthmus. Sometimes a fibrous and fibromuscular band descends from the body of the hyoid bone to the isthmus or to the pyramidal lobe.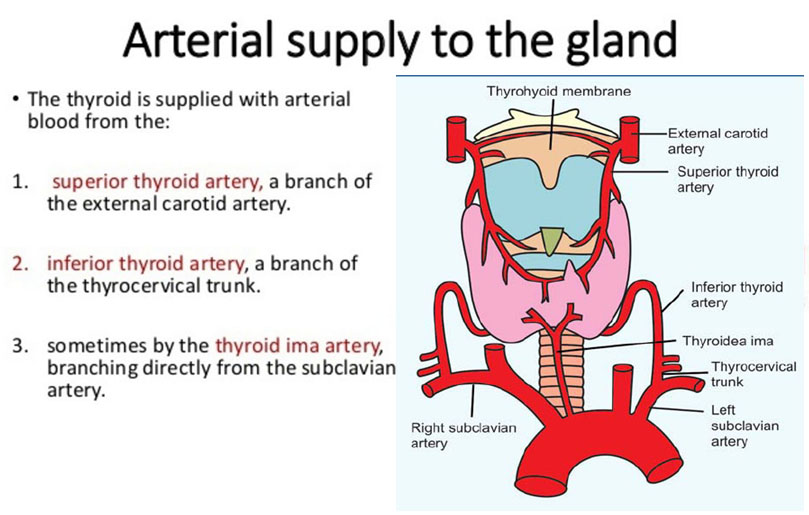
VENOUS DRAINAGE:
- Superior thyroid vein
- Middle thyroid vein
- Inferior thyroid vein
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE:
Upper part of the gland: Prelaryngeal nodesLower part of the gland: Pretracheal and paratracheal nodes
NERVE SUPPLY:
- Middle cervical ganglion
- Superior and inferior cervical ganglion
Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




