- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

A. Emphysema
B. Asthma
C. Pulmonary artery thrombosis
D. Skeletal abnormalities of the chest
Ans. A
2. Which of the following causes some degree of temporary alkalosis
A. Hyperventilation
B. High fluid intake
C. Excessive smoking
D. Severe muscular effort
Ans. A
Hyperventilation exists when there is a decrease in the ratio of carbon dioxide production to alveolar ventilation. Hyperventilation refers to a situation where the elimination of carbom dioxide exceeds CO2 produced. Thus there is a decrease in arterial pCO2 leading to hypocapnia. It results in a decrease in blood H+ and an increase in blood pH. This is called respiratory alkalosis. An increased breathing frequency is called tachypnoea and is not simply synonymous with hyperventilation.
3. The major sign of hypoventilation is
A. Cyanosis
B. Dyspnoea
C. Hypercapnia
D. Hypoxia
Ans. B
In hypoventilation the amount of air moving in and out of lungs is reduced. Hypoventilation results in hypoxia (reduced oxygen availability to cells) , hypercapnia(increased CO2 content of blood), dyspnoea(difficulty in breathing) and death.
4. The oxygen tension of the mixed venous blood is
A. 25mmHg
B. 40mmHg
C. 55mmHg
D. 70mmHg
Ans. B
5. Which of the following increases with increase in arterial CO2
A. Tidal volume
B. Respiratory rate
C. Alveolar ventilation
D. All of the above
Ans. D
6. Which of the following is least stable compound of haemoglobin
A. Oxyhaemoglobin
B. Carboxy haemoglobin
C. Methaemoglobin
D. Carbohaemoglobin
Ans. A
Methaemoglobin is most stable form
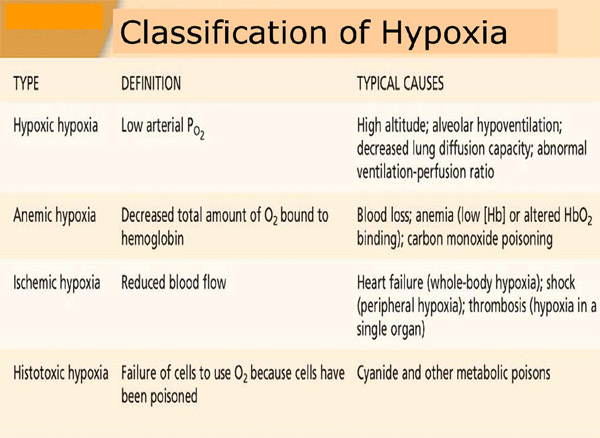
7. The most common form of hypoxia is
A. Hypoxic
B. Stagnant
C. Anaemic
D. Histotoxic
Ans. A
8. For which of the following organs continous supply of oxygen is most critical
A. Spleen
B. Brain
C. Kidneys
D. Liver
Ans. B
Brain is very sensitive to oxugen demand. Arrest of circulation for 5 sec leads.to unconsiousness and irrepairable damage to brain if more than 2 minutes
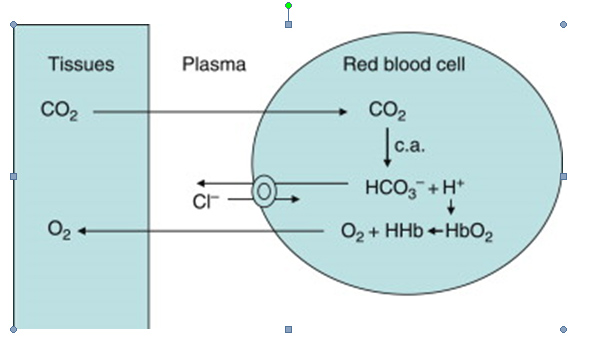
9. Bicarbonate ions diffuse out of erythrocyte into plasma in exchange of
A. Potassium
B. Phosphate
C. Carbonic acid
D. Chloride ion
Ans. D
10. Cheyne stokes breathing is seen in
A. Congestive heart failure
B. Uraemic patients
C. Brain diseases
D. All of the above
Ans. D




