- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Respiratory System
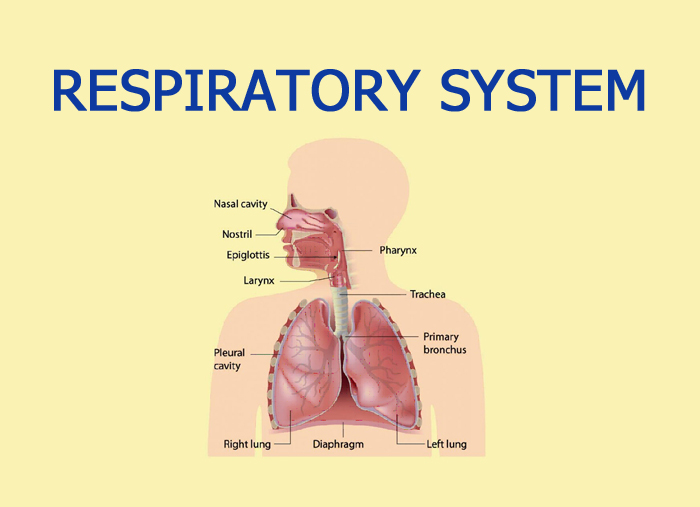
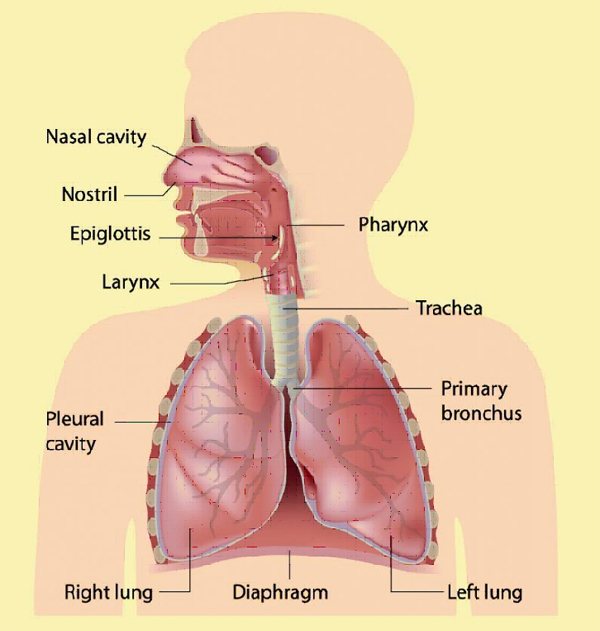
Respiration is the process by which oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is given out. The normal respiratory rate in adults is 12 to 16 per minute
Respiration is often classified as 2 types:
- External respiration that involves exchange of respiratory gases ie, oxygen and carbon dioxide between lungs and blood.
- Internal respiration which involves exchange of gases between blood and tissues
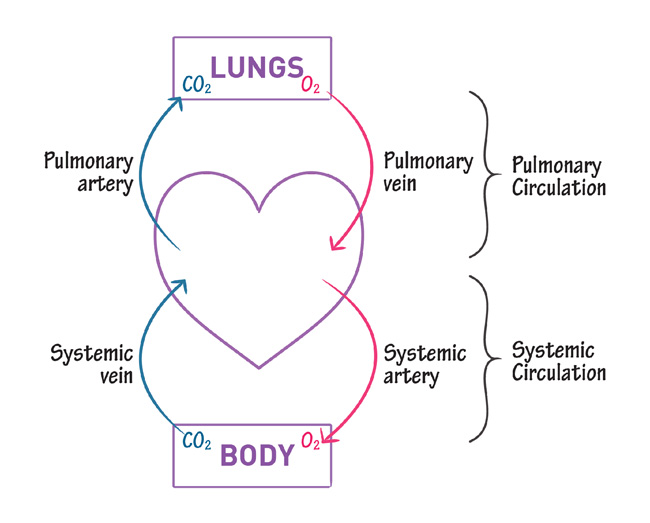
PULMONARY CIRCULATION:
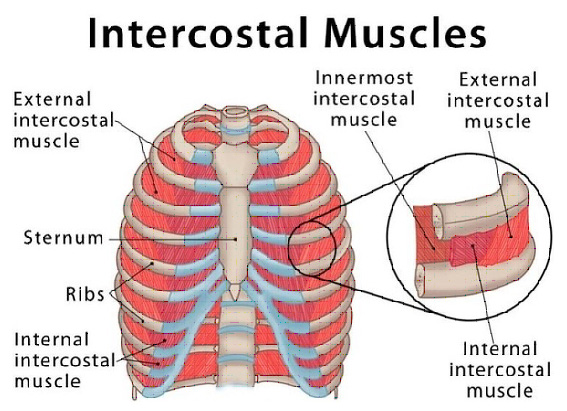
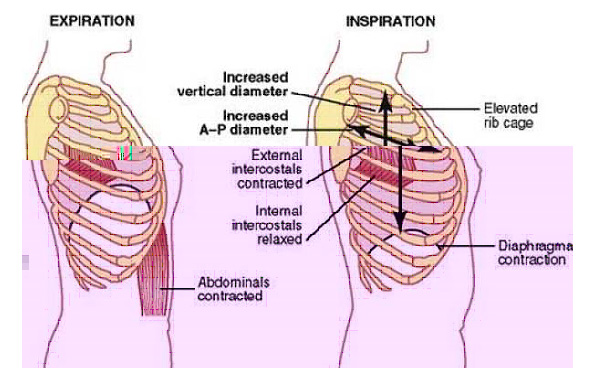
MUSCLES OF RESPIRATION
- Primary or major respiratory muscles which are responsible for change in size of thoracic cage during normal quiet breathing
- Accessory respiratory muscles that help primary respiratory muscles during forced respiration
Expiratory muscles: Primary expiratory muscles are the internal intercoastal muscles. Accessory expiratory muscles are the abdominal muscles.
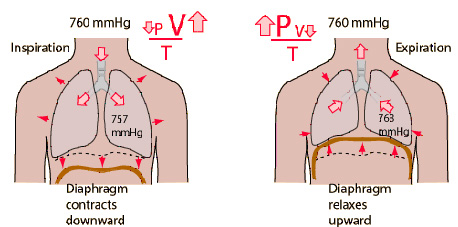
RESPIRATORY PRESSURES
1. Intrapleural pressure: The intrapleural pressure is the pressure existing in pleural cavity, that is, in between the visceral and parietal layers of pleura. It is exerted by the suction of the fluid that lines the pleural cavity. It is also called intrathoracic pressure since it is exerted in the whole of thoracic cavity. The normal values are:- At the end of normal inspiration: -6mmHg
- At the end of normal expiration: -2mmHg
- At the end of forced inspiration: -30mmHg
Intra alveolar pressure is the pressure existing in the alveoli to the lungs. It is also known as intrapulmonary pressure
The normal values are:
1. During normal inspiration: -1mmHg
2. During normal expiration: +1mmHg
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST
Pulmonary function tests or lung function tests are useful in assessing the functional status of the respiratory system. These tests involve measurement of lung volumes and capacities. The air in lung is classified into 2 divisions:- Lung volumes
- Lung capacities
PULMONARY VENTILATION
Pulmonary ventilation is the volume of air moving in and out of lungs per minute in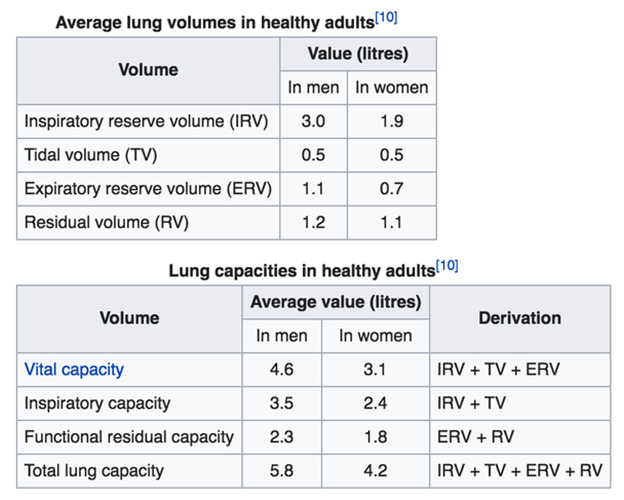
quiet breathing. It is also called respiratory minute volume (RMV)
Pulmonary volume= Tidal volume× Respiratory rate
= 500ml×12/minute
=6000ml=6L
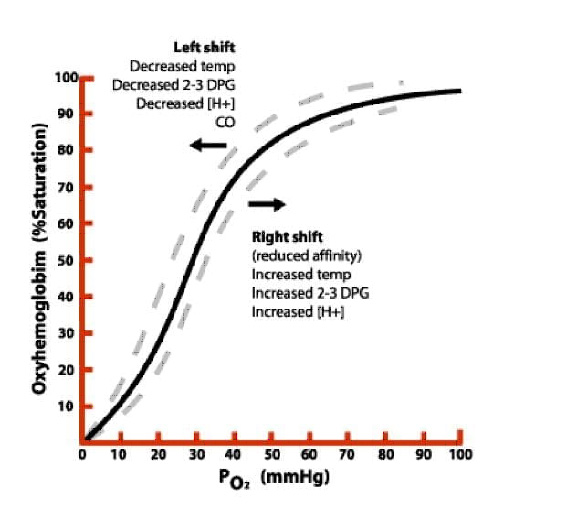
OXYGEN HAEMOGLOBIN DISSOCIATION CURVE
Pulmonary volume= Tidal volume× Respiratory rate
= 500ml×12/minute
=6000ml=6L

OXYGEN HAEMOGLOBIN DISSOCIATION CURVE

Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




