- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
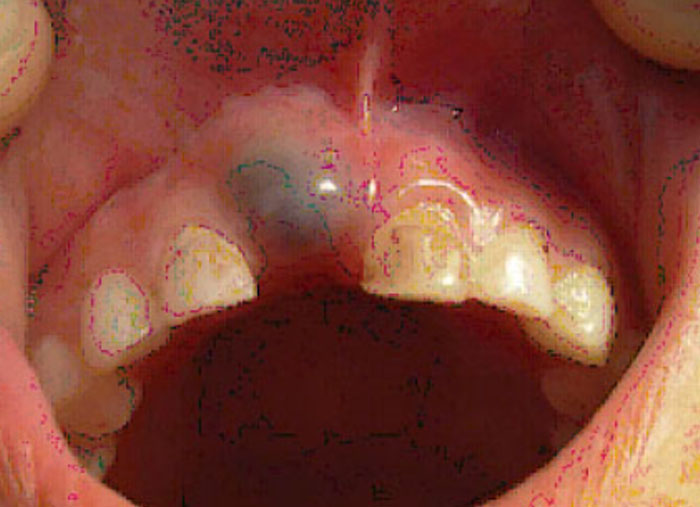
1. Eruptive cysts are best treated by
A. Incision and Drainage
B. Curettage
C. Excision
D. No treatment, only observation
2. Head shape in Down’s syndrome is typically
A. Mesocephalic
B. Dolichocephalic
C. Brachycephalic
D. Acephalic
3. Which type of malocclusion is generally observed in patients with spastic type of cerebral palsy
A) class I
B) class II div 1
C) class II div 2
D) class III
4. Tetracycline administration causes primary tooth staining
A) At birth
B) Up to 3rd month of life
C) Up to 6th month of life
D) Up to 9th month of life
5. All are seen in a child with cerebral palsy except:
A) Flurosis
B) Increased caries
C) Increased salivation
D) Trauma
ANSWERS AND DESCRIPTION:
1. D
2. C
Dolicocephalic head shape is seen in case of Marfan’s syndrome
3. C
some studies have reported class II div 1 malocclusion to be common in spastic CP children, many have reported that these children usually exhibit a class II div 2 malocclusion with unilateral or bilateral cross bite.
4. D
Tetracycline administration causes statining during:
● 4 months in utero to 3 months postpartum for primary max and man incisors
● 5 months in utero to 9 months postpartum for primary max and mand canines
● In permanent dentition, max and mand incisors and canines get affected when administered between 3 to 5 month postpartum to about 8 year.
The maxillary lateral incisors are an exception because they begin to calcify at 10- 12 months postpartum
5. A
Oral features of cerebral palsy are:
1. Poor oral hygiene, increased periodontal disease, and drug induced gingival enlargement
2. Malocclusion( increased prevalence to skeletal class II with anterior openbite)
3. A tendency to bruxism
4. Tongue thrust and mouth breathing
5. An increase in caries prevalence
6. Increased prevalence of anterior trauma
7. Enamel hypoplasia
8. Gag reflex and peri oral sensitivity
9. Drooling
10. Decreased parotid flow rate




