- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. UREA CYCLE
This cycle is known as Krebs-Henseleit urea cycle. As ornithine is the first member of the reaction sequences, it is also called as Ornithine cycle. The 2 nitrogen atoms of urea are derived from two nitrogen atoms of urea are derived from two different sources, one from ammonia and the other directly from aspartic acid
Step 1: Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate
One molecule of ammonia condenses with Co2 in the presence of 2 molecules of ATP to form carbamoyl phosphate. The reaction is catalyzed by the mitichondrial enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)
Step 2: Formation of Citrulline
The carbamoyl group is transferred to the NH2 group of ornithine. Citrulline is neither present in tissue proteins nor in blood, but it is present in milk
Step 3: Formation of Argininosuccinate
One molecule of aspartic acid is added, which provide the 2nd nitrogen atom of urea. This needs hydrolysis of ATP to AMP level, so two high energy phosphate bonds are utilized.
Step 4: Formation of Arginine
Argininosuccinate is cleaved to arginine and fumarate. The 3rd and 4th steps taken together may be summarized as:
Citrulline + aspartate >> arginine + fumarate
Step 5: Formation of urea
The final reaction of the cycle is the hydrolysis of arginine to urea and ornithine by arginase. Ornithine may be consideredas a catalyst which enters the reaction and is regenerated.
Regulation of urea cycle:
1. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism
2. The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS I where the positive effector is N acetyl glutamate(NAG)
Disorders of urea cycle:
| DISEASES | ENZYME DEFICIT |
| Hyperammonemia type I | CPS I |
| Hyperammonemia type II | Ornithine transcarbamoylase |
| Hyperornithinemia | Defective ornithine transporter protein |
| Citrullinemia | Argininosuccinate synthetase |
| Argininosuccinic aciduria | Argininosuccinate lyase |
| Hyperargininemia | Arginase |
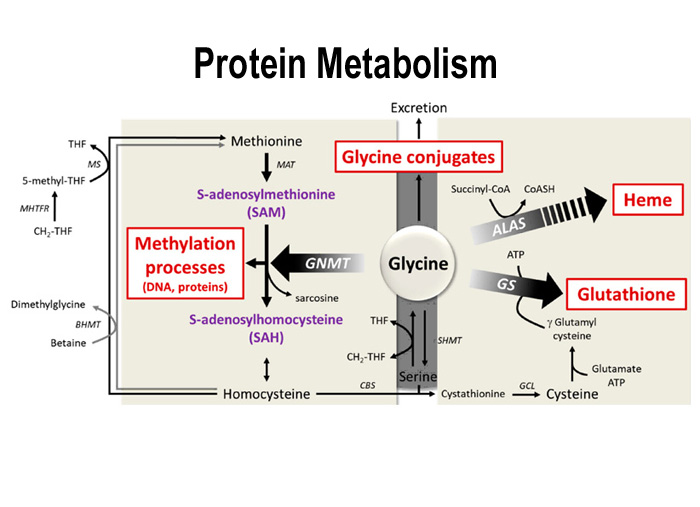
2. GLYCINE:
Glycine undergoes oxidative deaminationto form NH3, CO2, and the one carbon unit methylene THFA. It needs the coenzymes, NAD, lipoamide, tetrahydrofolic acid and pyridoxal phosphate.
Glycine may be used for the biosynthesis of the following compounds
1. Creatine, creatine phosphate and creatinine
2. Heme
3. Purine nucleotides
4. Glutatione
5. Conjugating agent
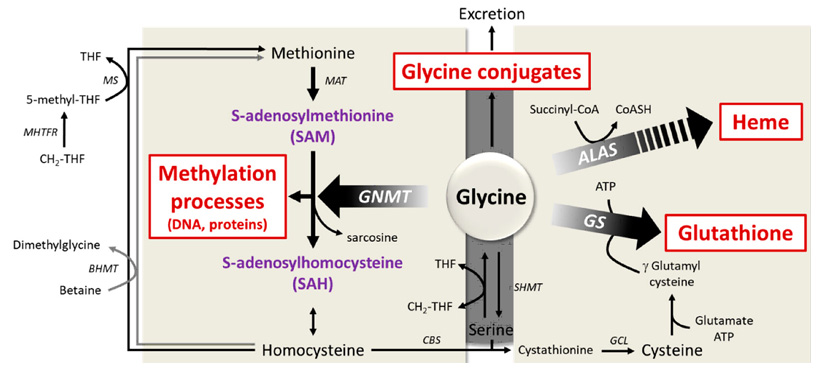
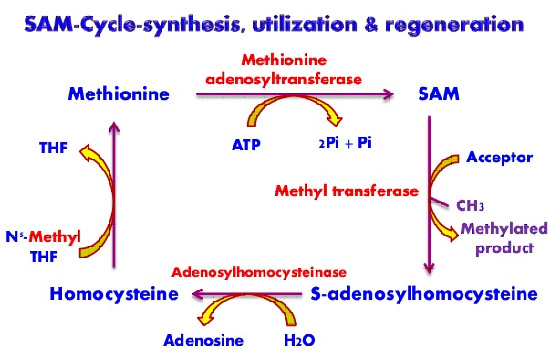
3. METHIONINE
It is sulfur containing, essential glucogenic amino acid. Methionine is activated to active methionine or S- adenosylmethionine(SAM). The adenosyl group is transferred to the sulfur atom
4. PHENYLALANINE
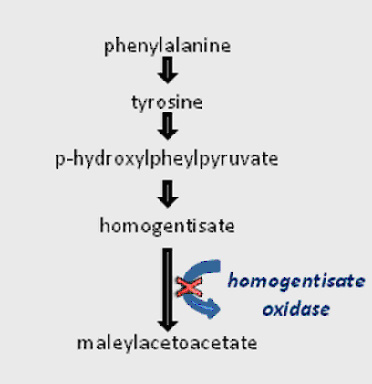
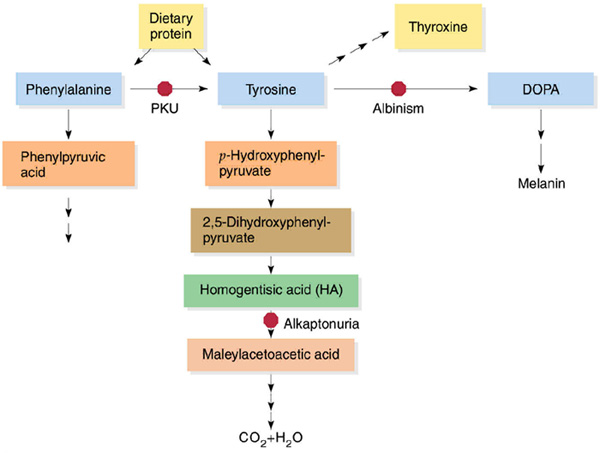
Phenylalanine to tyrosine, the reaction involves addition of hydroxyl group to the aromatic ring, by phenylalanine hydroxylase. It needs NADPH,NADH and tetrahydrobiopterin as coenzymes
Important specialised products from Tyrosine
1. Melanin
2. Catecholamines
3. Thyroxine
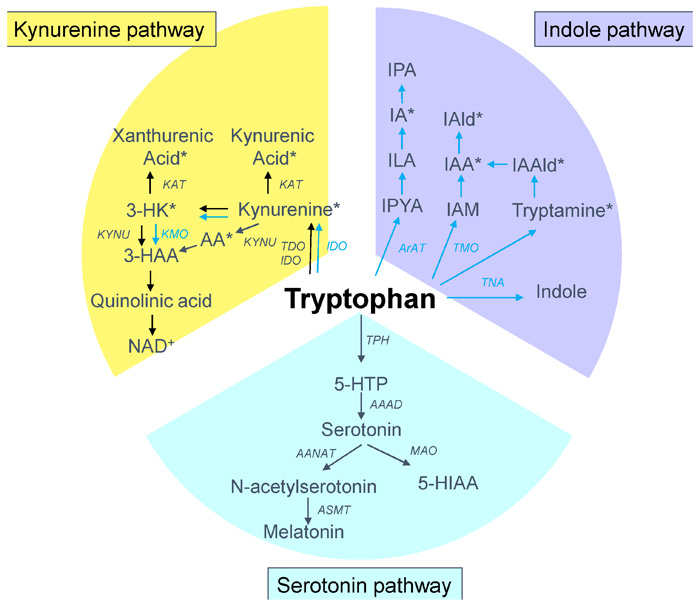
5. TRYPTOPHAN
Tryptophan is an aromatic essential amino acid with an indole ring. Tryptophan is both glucogenic abd ketogenic. Im the major pathway, kynureninase is an enzyme dependent on pyridoxal phosphate. Therefore, in vitamin B6 deficiency, the pathway at this level is blocked. This leads to niacin deficiency and manifestations of pellagra.