- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

A. Infrabony pocket
B. Periodontal pocket
C. True pocket
D. Pseudo pocket
Ans. D
2. Pseudo pocket is seen in the
A. Base of the pocket lies on cementum
B. Chronic gingivitis
C. Periodontitis
D. Base of the pocket and lies on alveolar bone
Ans. B
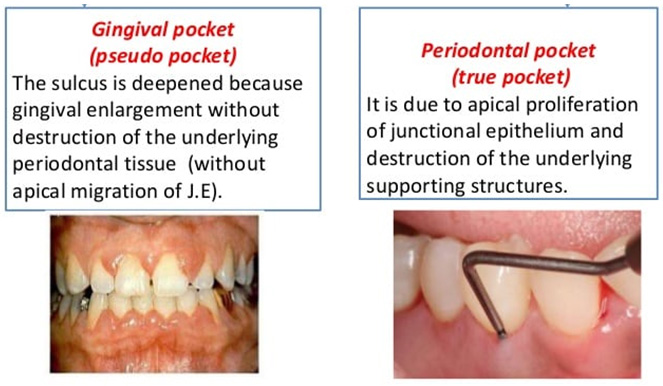
Pseudo pocket forms when there is deepening of the sulcus due to gingival growth rather than the displacement of junctional epithelium apically. There may be gingival enlargement in gingivitis.
3. Which of the following is most appropriate for pseudo pocket
A. Is a feature of periodontitis
B. Is assosciated with attachment loss
C. Is assosciated with trans septal fibres loss
D. May have a depth of more than 3 mm
Ans. D
Pseudopockets are usually seen in gingival enlargements
4. If the pocket depth is 5mm and gingival recession is 3mm then the total loss of attachment is
A. 8mm
B. 3mm
C. 5mm
D. 2mm
Ans. A
In the above question there is gingival recession that is, gingival margin is apical to CEJ then total loss of attachment= 5+3mm = 8mm
5. In a patient without gingival recession , the distance between base of pocket and cementoenamel junction is 4mm and that of free gingival margin to cementoenamel junction is 3mm. Total depth of the pocket
A. 7mm
B. 3mm
C. 4mm
D. 10mm
Ans. A
6. Apical migration of epithelial attachment with corresponding recession of marginal gingiva results in
A. Shallow sulcus
B. Gingival pocket formation
C. Infrabony pocket formatiom
D. Periodontal pocket formation
Ans. D
Pocket depth is distance between gingival margin to the base of the pocket (or coronal end of junctional epithelium) . Periodontal or true pocket can be definedas deepiening of the gingival sulcus with loss of attachment.( so option D is appropriate and option B is wrong)
If there is loss of attachment of more than 3mm a sulcus is technicallycalled as pocket. Depending upon the relation of the base of the pocket to the crest of alveolar bone, it may be supra alveolar or infra alveolar.
In supra alveolar bone loss is horizontal whereas in infra alveolar it is vertical, which can be diagnosed on radiographs. In this question this does not arise( option C may not be considered). Coronal migration of the marginal gingiva gives rise to gingival pocket or pseudo pocket formation.( so option B can be eliminated).
7. In which of the following true pocket formation cannot occur
A. ANUG
B. Adult periodontitis
C. Rapidly progressing periodontitis
D. Juvenile periodontitis
Ans. A
This is because in ANUG cells become necrotic
8. Periodontal pocket wall between tooth and bone is
A. Suprabony pocket
B. Infrabony pocket
C. Gingival pocket
D. Pseudo pocket
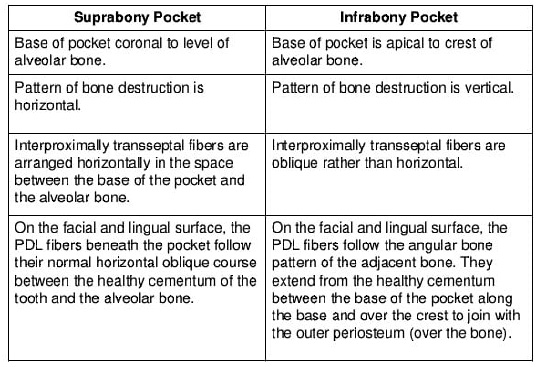
Ans. B
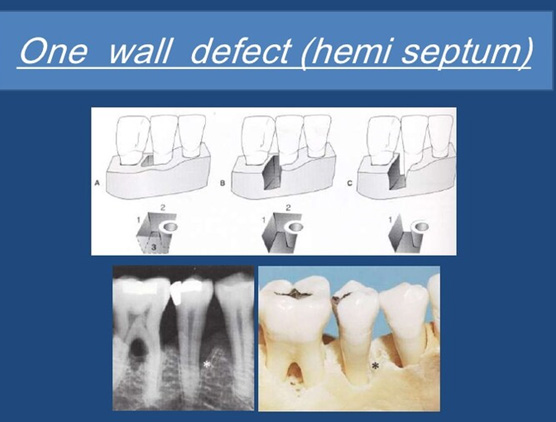
9. How many osseous walls are present in one walled vertical defect
A. One wall present
B. Two walls present
C. Three walls present
D. Four walls present
Ans. A
10. Vertical or angular defects are found in
A. Suprabony pockets
B. Infrabony pockets
C. Intrabony pockets
D. Both B and C
Ans. D





