- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
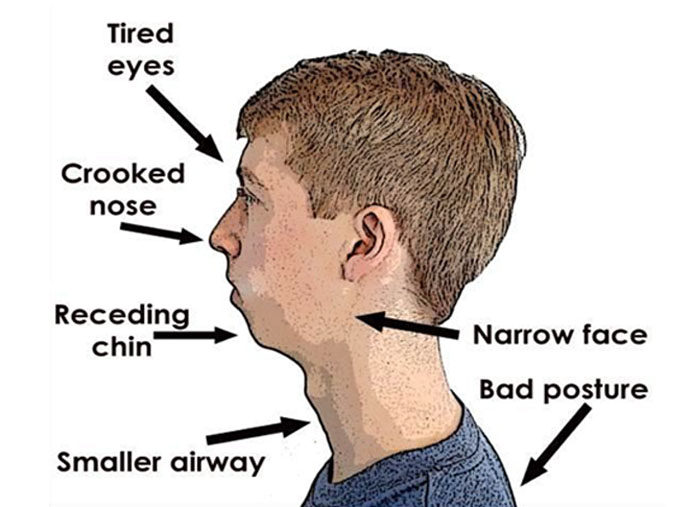
1. The importance of proximal caries in deciduous 1st molar for an orthodontist is
a. Reduction in arch length due to growth of mandible
b. Loss of arch length
c. Class I occlusion
d. Flush terminal plane malocclusion
ANSWER b
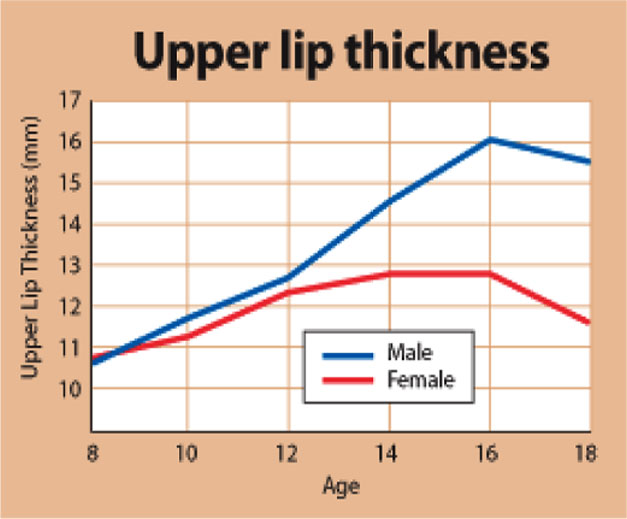
2. Maximum upper lip thickness is seen at what age in males
a. 10 year
b. 16 year
c. 18 year
d. 21 year
ANSWER b
The upper lip in girls reaches its maximum thickness by age 14 and remains that way until age 16; whereas in males it does not reach maximum thickness until 16. Thereafter the lips of both sexes begin the slow and inexorable process of thinning throughout the rest of the lifespan
3. A 3year old child suffered traumatic lateral luxation injury to his upper central incisor the tooth is not mobile and does not interfere in occlusion what and does not interfere un occlusion what should be done
a. Reposition the tooth and splint
b. Reduce the affected tooth
c. Reduce both the affected and the opposite tooth
d. Wait and watch
ANSWER d
4. In a mouth breather tonicity of upper lips is
a. Increased
b. Decreased
c. Slightly affected
d. No chance
ANSWER b
Some characteristics are commonly found in mouth breathers, such as
- Habitual semi-opened lips position,
- Low-lying tongue position,
- Hyper function of the mental muscle during lip occlusion,
- Eversion of the lower lip,
- Cheek symmetry,
- Possibility of lip occlusion,
- Altered dental occlusion, and altered hard palate
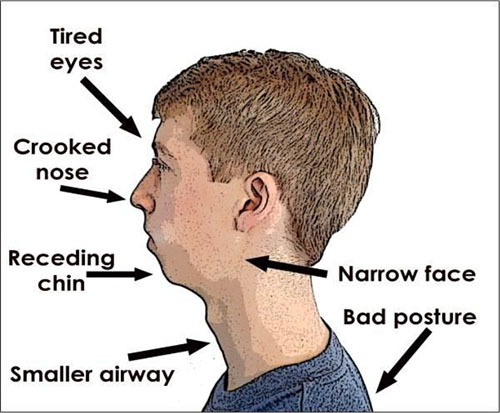
5. Facial profile of a child with a habit of thumb sucking
a. Convex and long face
b. Convex and short face
c. Convex and short face
d. Concave and long face
ANSWER a
Effect of thumb sucking
Clinical finding effects on maxilla
|
Effects on mandible on interarch relationship
|
Effects on tongue placement and function other effects
|
Dentoalveolar structures
|
Extra oral examination digits
|
LIPS
|
Facial form
|




