- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. Which stage of Plasmodium Vivax is infectious to Mosquito ?
a. Gametocyte
b. Trophozytes
c. Merozoite
d. Sporozoite
ANSWER: d
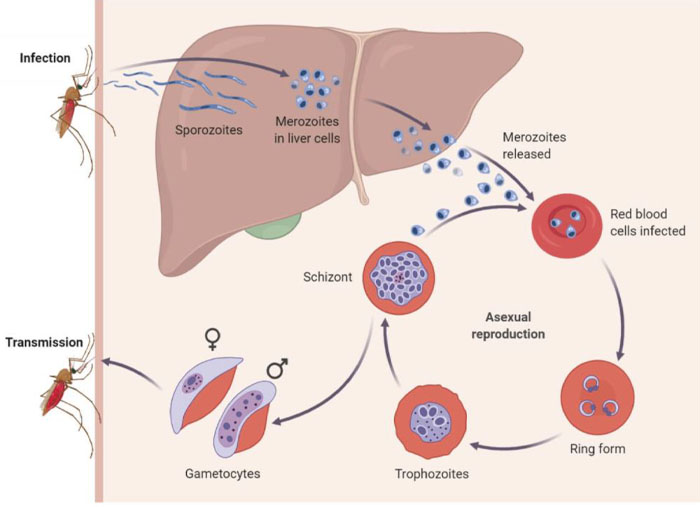
The P. vivax lifecycle is complex, including more than ten stages of cellular differentiation, with the parasite invading at least four types of cells within two different hosts.
The life cycle of Plasmodium vivax is divided into:
- Asexual life cycle or schizogony in man
- Sexual life cycle or sporogony in female Anopheles mosquito
Asexual Stage
- Sporozoite is the asexual stage of the Plasmodium.
- It is the infectious stage that infects humans.
- Sporozoites get transmitted from the female Anopheles to humans when the infected mosquito bites.
- The sporozoites reach the human liver cells and mature into schizonts.
- The cells burst and it releases merozoites into the blood. The initial multiplication in the liver is called exo-erythrocytic schizogony.
- In Plasmodium vivax, a dormant stage may persist for weeks to even years, if remain untreated. It is known as hypnozoites.
- Merozoites attack RBCs and multiply asexually leading to the rupture of RBCs.
- The asexual multiplication in the erythrocytes is known as erythrocytic schizogony.
- The merozoites change into the ring-stage immature trophozoites, which mature into schizonts.
- Schizoints rupture and release merozoites.
- They release a toxic substance known as haemozoin.
- Haemozoin is responsible for recurring chills and high fever during malaria.
Sexual Stage
- The male and female gametocytes are produced in the RBCs of humans.
- Some of the trophozoites in erythrocytes differentiate into gametocytes, which is the sexual stage. It forms microgametocytes (male) and megagametocytes (female).
- When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected human, it takes up the gametocytes with blood.
- Further fertilisation and development take place in the gut of the female mosquitoes.
- The multiplication in mosquitoes is known as the sporogonic cycle.
- The male gametocytes penetrate the female gametocytes leading to the formation of zygotes in the stomach of mosquitoes.
- Zygotes develop into ookinetes as they become motile and elongated.
- Ookinetes enter the midgut wall and develop into oocysts.
- Oocysts rupture and release sporozoites, which is the infective stage for humans.
- The sporozoites migrate to salivary glands and are stored there. When an infected mosquito bites a human, these sporozoites enter the human blood and the cycle continues.

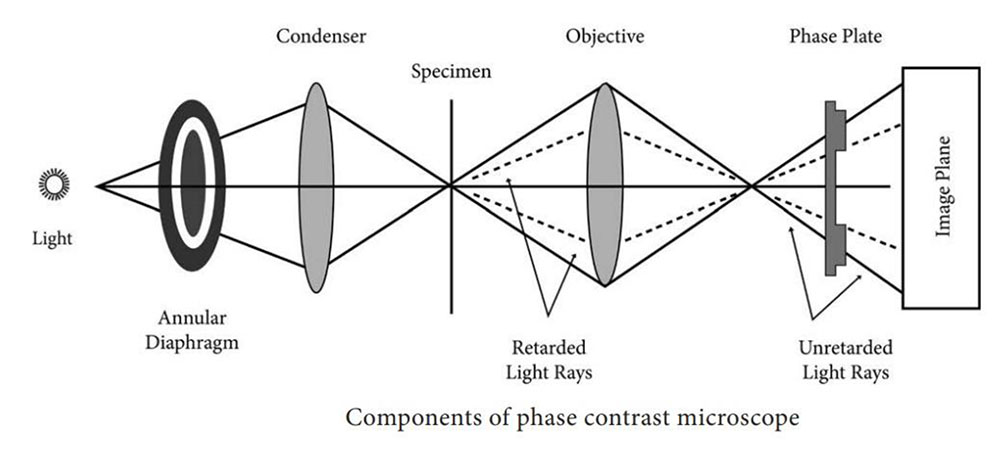
2. Mechanism of Phase contrast microscope is?
a. Light scatter
b. Refraction of Light
c. Difference in refractive index of objects
d. Difference in reflective index of objects
ANSWER: c
The phase contrast microscopy is based on the principle that small phase changes in the light rays, induced by differences in the thickness and refractive index of the different parts of an object, can be transformed into differences in brightness or light intensity.
3. A Dental surgeon has recovered from Hepatitis B by 3 months rest. His laboratory findings are normal but he is not allowed to attend to patients as per medical board as he is?
a. Healthy carrier
b. Active Carrier
c. Convalescent carrier
d. Paradoxical carrier
ANSWER: c
Convalescent carriers are those who have recovered from their illness but remain capable of transmitting to others.
Chronic carriers are those who continue to harbor a pathogen such as hepatitis B virus or Salmonella Typhi, the causative agent of typhoid fever, for months or even years after their initial infection.
4. In Pseudomonas aeraginosa all are true except?
a. Strict Aerobes
b. Children with cystic fibrosis commonly affected
c. Infection mostly due to endogenous source
d. Can grow in disinfectants in hospital
ANSWER: c
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a bacteria that's commonly found in the environment, for example in soil and water. It can be spread to people in health care settings through contaminated surfaces, hands, and equipment.
Risk Factors
- It can grow on fruits and vegetables, so you could get sick from eating contaminated food.
- It also thrives in moist areas like pools, hot tubs, bathrooms, kitchens, and sinks.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa can easily grow in humidifiers and types of medical equipment -- catheters, for instance -- that aren’t properly cleaned
- Risk increases when patient have a wound from surgery
- Patient being treated for burns
- Use of a breathing machine, catheter, or other medical device
- Those having diabetes or cystic fibrosis
- Or a disorder that weakens your immune system, such as HIV
5. About N.gonorrhoeae, all are true except?
a. Most common cause of male urethritis
b. Present mainly in mixed infections
c. All strains are susceptible to Pencillins
d. Found only in human beings




