- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

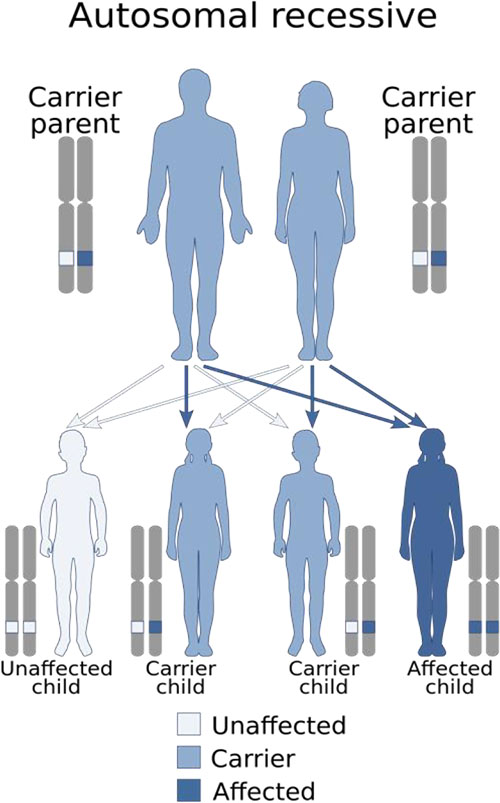
1. Chediak- Higashi syndrome is inherited as
A. X-linked dominant trait
B. Autosomal dominant
C. Autosomal recessive
D. X-linked recessive
ANSWER C
- Chédiak-Higashi syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency disorder that involves phagocytic cell defects.
- The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the LYST (lysosomal trafficking regulator; also known as CHS1) gene.
- Giant lysosomal granules develop in neutrophils and other cells (eg, melanocytes, neural Schwann cells).
- The abnormal lysosomes cannot fuse with phagosomes, so ingested bacteria cannot be lysed normally.
2. Which of the following blood disease has a racial predilection ?
A. Purpura
B. Hemophilia
C. Polycythemia
D. Thalassemia
ANSWER D
- Thalassemia is a blood disorder passed down through families (inherited) in which the body makes an abnormal form or inadequate amount of hemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
- The disorder results in large numbers of red blood cells being destroyed, which leads to anemia.
- Two types
| Alpha thalassemia | Beta thalassemia |
| Occurs when a gene or genes related to the alpha globin protein are missing or changed (mutated). | Occurs when similar gene defects affect production of the beta globin protein |
There are many forms of thalassemia. Each type has many different subtypes. Both alpha and beta thalassemia include the following two forms:
- Thalassemia major
- Thalassemia minor
Certain ethnic groups are at greater risk:
- Alpha thalassemia most often affects people who are of Southeast Asian, Indian, Chinese, or Filipino descent.
- Beta thalassemia most often affects people who are of Mediterranean (Greek, Italian and Middle Eastern), Asian, or African descent.
3. Deficiency of all the three components of coagulation factor VIII result in
A. Von willebrand’s disease
B. Haemophilia- A
C. Parahemophilia
D. Haemophilia – B
ANSWER A
- Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a blood disorder in which the blood does not clot properly.
- Von Willebrand factor (factor VIII-related antigen) is a large glycoprotein that is present in the plasma and endothelium and binds to other proteins, particularly factor VIII, preventing its rapid degradation.
- It is absent in von Willebrand's disease.
- Von Willebrand factor/factor VIII concentrates play a key role in the treatment of patients with von Willebrand disease.
- The von Willebrand factor multimer fraction is very effective in achieving hemostasis.
4. A hair on end appearance of the skull is seen in all of the following except
A. Thalassemia
B. Sickle anemia
C. Cooley’s anaemia
D. Pagets disease
ANSWER D

- The hair on end sign refers to a radiographic appearance of the diploic space of the skull vault which results from a thickening of trabeculae as the diploic space expands.
- These trabeculae are perpendicular in orientation, interspersed by radiolucent marrow hyperplasia along with skull vault
- It is classically described with plain skull radiographs although can also be appreciated on CT or MRI
- Causes include:
- Thalassemia major
- Sickle cell disease
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Iron deficiency anemia
5. Hemophilia is associated with
A. Normal bleeding time normal clotting time
B. Normal bleeding time prolonged clotting time
C. Prolonged bleeding time normal clotting time
D. Prolonged bleeding time prolonged clotting time




