- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
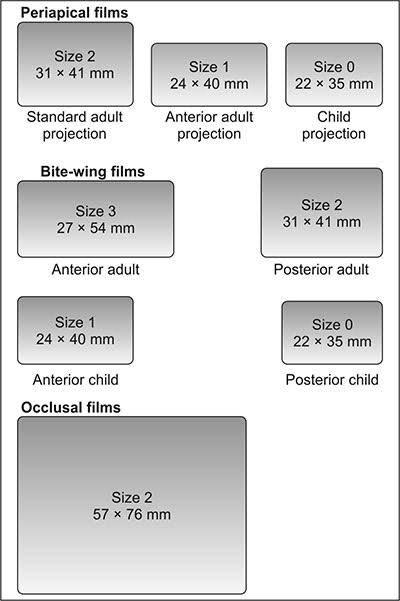
1. Standard film size for bitewing radiograph
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
ANSWER c
Bitewing View
- They are useful for detecting interproximal caries and evaluating the height of alveolar bone.
- Size 2 film is normally used in adults; the smaller size 1 is preferred in children. In small children, size 0 may be used
Bitewing films:
- This film is slightly bigger in size when compared to the regular Periapical radiographic film and it helps in recording both the upper and lower teeth in a bite position and hence the name – Bitewing radiograph.
- Bitewing radiograph helps in identifying any Interdental caries, caries under existing restorations or crowns, bone loss between teeth etc.
| Size 0: 22 x 35 mm Anterior. Children |
| Size 1: 24 x 40 mm Posterior, Children Anterior,Adults |
| Size 2: 31 x 41 mm Posterior, Adults (Standard size) |
| Size 3: 27 x 54 mm Posterior, Adults (All posterior teeth are seen in 1 film) |
There are four sizes of Bitewing radiographic films based on the position and the age of the patient it is used in.
2. Difference between conventional and digital radiograph is
a. Sensor difference mode of capturing of the radiographic signals
b. X-ray are not used
c. Hard copy is not available in digital x-ray
d. No radiation hazard to patient
ANSWER: a
DR uses flat panel detectors based on direct or indirect conversion of X-rays to charge, which is then processed to produce a digital image.
CR uses cassette-based phosphor storage plates (PSP), which are then scanned by the computerized system into a digital format for image processing, archiving, and presentation.
3. Speeds of X-rays film recommended in dentistry are
a. D&E
b. C&E
c. C&D
d. B&D
ANSWER a
FILM SPEED D,E,F
- American academy of oral and maxillofacial radiology recommends E or F speed film to be used
- E - film- twice fast than D film.
- F-film reduces radiation exposure 20% compared to E and 70% compared to D speed film.
- D (ultra speed)
- E (ekta speed)
- F (ultra ekta speed)
SPEED SLOW SPEED FILMS – A, B, C.
- Small grain,
- Better definition,
- More exposure time
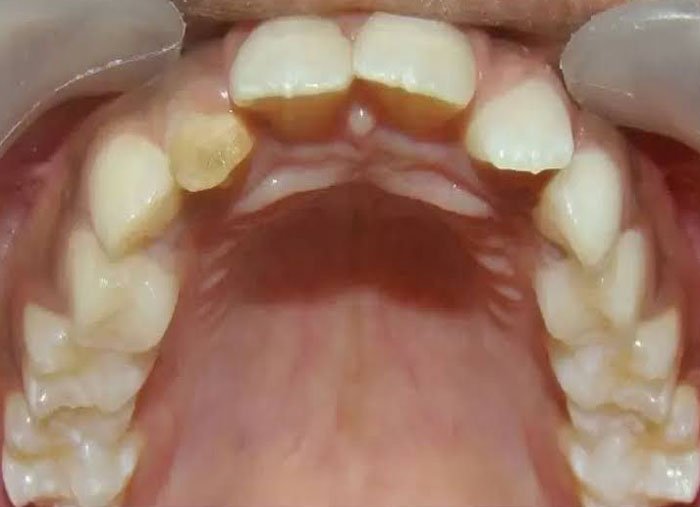
4. A mother comes to office with her son who has a yellow spot on newly erupted central incisor she gives history of trauma deciduous tooth 3 year back with the subsequent infection and recurrent pus discharge the possible etiology of the spot is
a. Fluorosis
b. Turner hypoplasia
c. Tetracycline stains
d. Pulpal trauma
ANSWER b
- Turner”s Tooth, also called Enamel Hypoplasia
- An enamel defect in the permanent teeth caused by periapical inflammatory disease in the overlying primary tooth is referred to as Turner”s tooth
- Also known as Turner’s hypoplasia
- Turner’s hypoplasia usually manifests as a portion of missing or diminished enamel, which affects one or more than one permanent tooth in the oral cavity.
- It commonly affects single permanent tooth because of infection of the corresponding deciduous tooth.

5. Bacteria are normally most populated in which area of teeth
a. Occlusal
b. Lingual
c. Buccal
d. Proximal




