- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
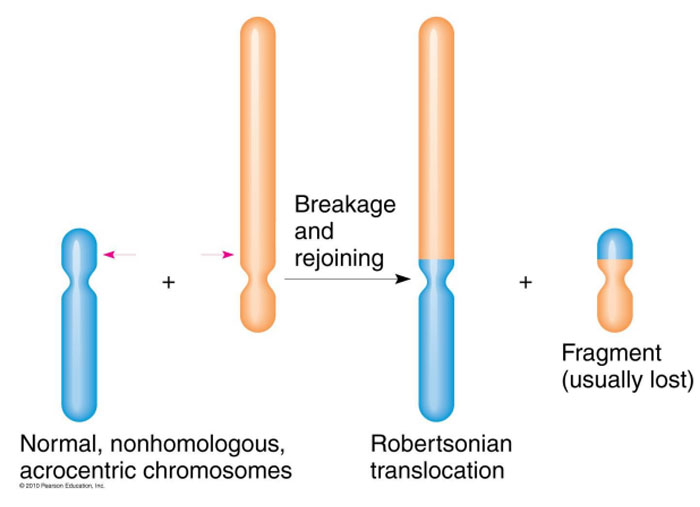
1. Down syndrome associated with mental retarding is seen in all of the following genotypes except
a. Trisomy 21
b. Delete 21
c. Robersonian translocation
d. Mosaicism
ANSWER c
A Robertsonian translocation is one in which, effectively, the whole of a chromosome is joined end to end with another. This type of translocation involves only chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21 and 22, because the ends of their short arms have similar repetitive DNA sequences that predispose to their fusion.

2. All are mediator inflammation except
a. TNF
b. Interferon
c. Prostaglandin
d. Myeloperoxidase
ANSWER d
Inflammatory mediators includes
- Bradykinin,
- Eicosanoids (prostaglandins and leukotriens),
- Adenosine triphosphate (atp),
- Histamin,
- Pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor, tnf,
- Interleukin-1b and ifny),
- Chemokines (chemotactic cytokine ligant 2, ccl2; fractalkine),
- Neurotrophins (nerve growth factor, ngf; brain neurotrophic factor, bdnf)
- And oxygen reactive species.
3. Cardiovascular effects seen in AIDS are all except
a. Pericardial effusion
b. Cardiac tamponade
c. Dilated cardiomyopathy
d. Aortic aneurysm
ANSWER d
- Individuals infected with HIV have a significantly increased risk for a variety of cardiovascular complications like
- Acute myocardial infarction,
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Coronary heart disease
- Systemic arterial hypertension
- Pericardial effusion
- Heart failure with both reduced and preserved ejection fraction,
- Sudden cardiac death
- peripheral arterial disease,
- Stroke.
4. In scurvy bones are affected because of
a. Decreased mineralization
b. Increased osteoclastic activity
c. Decreased osteoid matrix formation
d. Altered calcium and phosphate metabolism
ANSWER c
- Scurvy is disease caused by severe Vitamin
- C deficiency
Vitamin C deficiency symptoms can appear after 8-12 weeks Early signs include a loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, irritability, and lethargy. Within 1-3 months, there may be signs of: - Anemia
- Myalgia, or pain, including bone pain
- Swelling, or edema
- Petechiae, or small red spots resulting from bleeding under the skin
- Corkscrew hairs
- Gum disease and loss of teeth
- Poor wound healing
- Shortness of breath
- Mood changes, and depression
In time, the person will show signs of generalized edema, severe jaundice, destruction of red blood cells, known as hemolysis, sudden and spontaneous bleeding, neuropathy, fever, and convulsions. It can be fatal.
SCURVY AND BONE
- The manifestations of scurvy include musculoskeletal symptoms consisting of arthralgia, myalgia, hemarthrosis, and muscular hematomas.
- Vitamin C depletion is responsible for structural collagen alterations, defective osteoid matrix formation, and increased bone resorption.
- Imaging studies may show osteolysis, joint space loss, osteonecrosis, osteopenia, and/or periosteal proliferation.
- Trabecular and cortical osteoporosis is common.
- Children experience severe lower limb pain related to subperiosteal bleeding.
- Laboratory tests show nonspecific abnormalities including anemia and low levels of cholesterol and albumin
5.Measurement of HbA1c is required for
a. Screening controlled diabetes
b. Screening uncontrolled diabetes
c. Monitoring diabetes
d. Confirmation of diabetes
ANSWER c
A hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) test is a blood test that shows what your average blood sugar (glucose) level was over the past two to three months.
An HbA1C test may be used to screen for or diagnose:
- Type 2 diabetes. With type 2 diabetes your blood glucose gets too high because your body doesn’t make enough insulin to move blood sugar from your bloodstream into your cells, or because your cells stop responding to insulin.
- Prediabetes. Prediabetes means that your blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to diagnosed as diabetes.
Lifestyle
changes, such as healthy eating and exercise, may help delay or prevent prediabetes from becoming type 2 diabetes.
To diagnose diabetes or prediabetes, the percentages commonly used are:
- Normal: A1C below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: A1C between 5.7% and 6.4%
- Diabetes: A1C of 6.5% or higher




