- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

1. Many congenital abnormalities occur due to interaction between genetic
factor and environment influences this type of association is known as
multifactorial inheritance
All are true regarding multifactorial inheritance except
- Risk is high in close relatives
- Incidence of abnormally is high in relatives of severely affected patients
- Female affects more than males in some condition
- Consanguinity is commonly seen
ANSWER d
Multifactorial inheritance refers to disorders caused by multiple genes and environmental factors.
This group of disorders includes a broad range of medical (cardiac disease and diabetes), congenital (birth defects including cardiac malformations, neural tube defects, and cleft lip and/or palate), and neuropsychiatric (ASD, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder) diseases.
These traits include the following:
The disease can occur in isolation, with affected children born to unaffected parents. Although familial aggregation is also common (i.e., there may be multiple cases in the same family), there is no clear Mendelian pattern of inheritance.
Environmental influences can increase or decrease the risk of the disease.
The disease occurs more frequently in one gender than in the other, but it is not a sex-limited trait.
In addition, first-degree relatives of individuals belonging to the more rarely affected gender have a higher risk of bearing the disease.
The concordance rates in monozygotic and dizygotic twins contradict. Mendelian proportions. A concordance rate is a measure of the rate at which both twins bear a specific disease.
The disease occurs more frequently in a specific ethnic group.
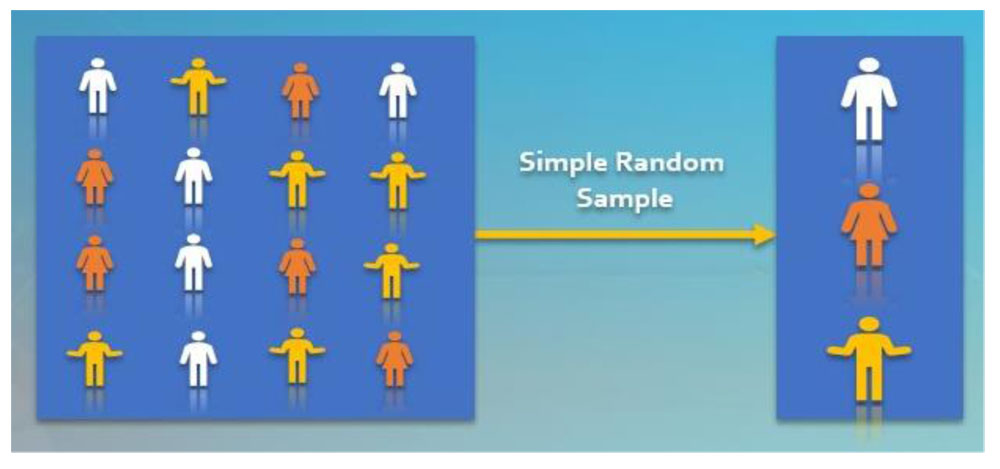
2. About simple random sampling true to
- Each member has equal chances of being selected
- Adjacent member must not be chosen
- Likely error cannot be estimated
- Depends on subject densities
ANSWER a
Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling in which the researcher randomly selects a subset of participants from a population. Each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
3. Which of the following is true
- Both incidence and prevalence are rates
- Incidence is rate and prevalence is not
- Prevalence is rate and incidence is not rate
- Both incidence and prevalence are not rate
ANSWER b
Incidence
Incidence = the rate of new cases of a disease occurring in a specific population over a particular period of time.
Two types of incidence are commonly used: „incidence proportion‟ and „incidence rate‟.
Prevalence differs from incidence proportion as prevalence includes all cases (new and pre-existing cases) in the population at the specified time whereas incidence is limited to new cases only.
Prevalence is sometimes referred as the prevalence rate, but prevalence is actually a proportion.
4. Yearly increases in carious lesion in mouth is called
- Caries incidence
- Caries prevalence
- Cumulative caries experience
- Caries increment
ANSWER a
Caries incidence
The number/proportion of individuals with new or progressing caries at a specified threshold in a given population, detected during a given period.
5. The type of study when subjects and investigator both are unaware of experimental group is called
- Single blind
- Double blind
- Triple blind
- Randomized trial
ANSWER b
Blinding, or “masking”, is the process by which information that has the potential to influence study results is withheld from one or more parties involved in a research study.
Types
| Unblinded or open label- All parties are aware of the treatment the participant receives. |
| Single blind or single-masked- Only the participant is unaware of the treatment they receive. |
| Double blind or double-masked -The participant and the clinicians / data collectors are unaware of the treatment the participant receives. |
| Triple blind - Participant, clinicians / data collectors and outcome adjudicators / data analysts are all unaware of the treatment the participant receives. |
Placebo effect
The placebo effect is the measure or observed effect on a person or group that has been given a placebo treatment.
A placebo is an inert substance, or "fake" surgery or therapy, used as a control in an experiment or given to a patient for its possible or probable beneficial effect. Why an inert substance, a so-called "sugar pill," or a fake surgery or therapy would be effective, is not yet completely known.




