- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. A hemophilia B patient needs a major surgery. Factor replacement should be
done at what rate?
a) 80-100 units/kg every 12 hours
b) 80-100 units/kg every 24 hours
c) 60units/kg every 12 hours
d) 80-100 units/kg every 6 hours
ANSWER b
- Hemophilia B is an inherited disease, mainly caused by the deficiency of factor IX.
- It mostly affects males, but carrier females may show some signs of bleeding.
- It has an X-linked recessive inherited mode of inheritance, but someacquired form has also been reported due to the development of autoantibodies toward factor IX.
- Replacement of factor IX remains the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia B patients.
- The dose is calculated according to the desired percentage of the factor with a goal of 30% in patients with mild hemorrhages, 50% in patients with severe bleed after trauma or prophylaxis of major dental surgery or major surgery, and 80% to 100% in patients with life-threatening conditions.
- It is calculated with this formula : Initial dose = body weight (kg) x desired factor IX increase (% or IU/dL) x reciprocal of observed recovery (IU/dL per IU/kg).
- It there is no available factor IX then prothrombin complex concentrate can be given at a dose of IU/kg.
2. In a polytrauma patient, chest tube insertion caused sudden drainage of 1500 ml blood from left side. Oxygen saturation is 92%. What should be the immediate next step?
a) Transfer to trauma center
b) Prepare for immediate open thoracotomy
c) Auscultate for left chest breath sounds and wait for saturation to rise
d) Clamp the chest tube
ANSWER d
3. When isoflurane is used as a general anaesthetic agent, what is the maximum dose of adrenaline that can be given?
a) 3.4 mug/kg
b) 6.7 mug/kg
c) 2.1 mug/kg
d) 10.9 mug/kg
ANSWER b
- Isoflurane is a general inhalation anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. It induces muscle relaxation and reduces pains sensitivity by altering tissue excitability.
- Dose of adrenaline should be limited to 1micrograms/kg/30 min in presence of halothane 3 micrograms/kg/30 min in presence of isoflurane to prevent ventricular arrythmias
- In adults, the epinephrine dose required to produce three premature ventricular contractions in 50% of patients (ED50) at 1.25 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) was 2.1 μg/kg for halothane, 6.7 μg/kg for isoflurane, and 10.9 μg/kg for enflurane.
- Children tolerate larger doses than do adults
- Hypocapnia potentiates this drug interaction.
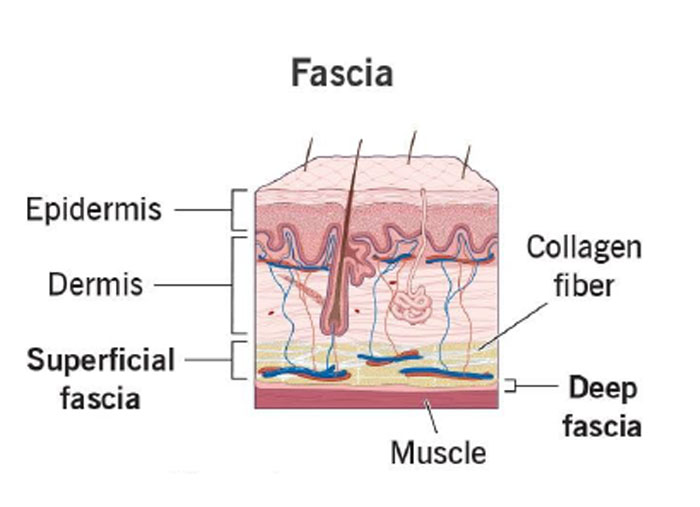
4. Which of these is the maximum content of fascia space?
a) Fibrous tissue
b) Loose connective tissue
c) Water
d) Air
ANSWER b
Fascia is a sheath of stringy connective tissue that surrounds every part of your body. It provides support to your muscles, tendons, ligaments, tissues, organs, nerves, joints and bones. When your fascia is healthy, it’s flexible and stretches with you. When your fascia tightens up, it can restrict movement and cause painful health conditions.
Fascia is located throughout the inside of your body

5. Which of these is a strong in
a) 20 degree displacement
b) Lateral displacement
c) Stump dislocation
d) 5mm shortening of ramus
ANSWER b