- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

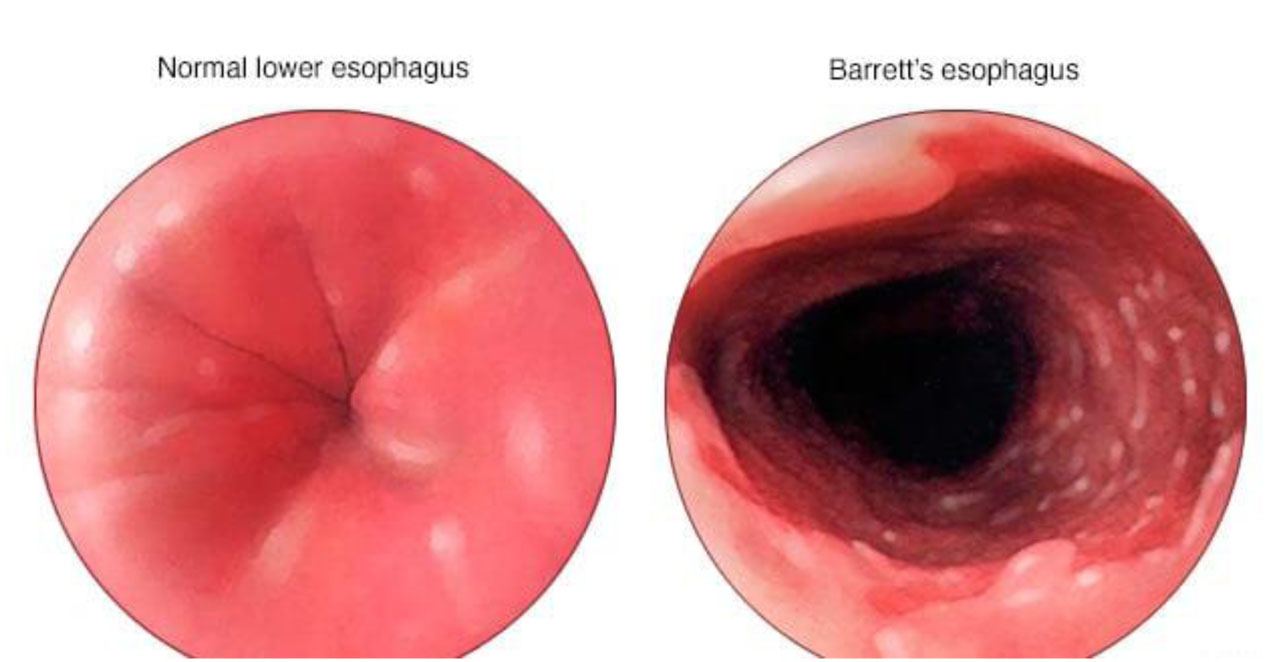
1. Barrett’s esophagus shows (AIIMS May 2010)
- Intestinal dysplasia
- Intestinal metaplasia
- Columnar cell metaplasia
- Columnar cell dysplasia
ANSWER b
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which tissue that is similar to the lining of your intestine replaces the tissue lining your esophagus. People with Barrett's esophagus may develop a rare cancer called esophageal adenocarcinoma.
2. Predisposing factor for esophageal cancer is all except (AIIMS May 2009)
- Mediastinal fibrosis
- Diverticula
- Caustic alkali burn
- HPV
ANSWER a
External beam irradiation but not mediastinal fibrosis is a risk factor for esophageal cancer.
HPV DNA is found frequently in esophageal squmaous cell carcinoma in high incidence regions.
Caustic ingestion, achalasia, bulimia, tylosis (an inherited autosomal dominant trait), Plummer-Vinson syndrome, external-beam radiation, and esophageal diverticula all have known associations with squamous cell carcinoma.
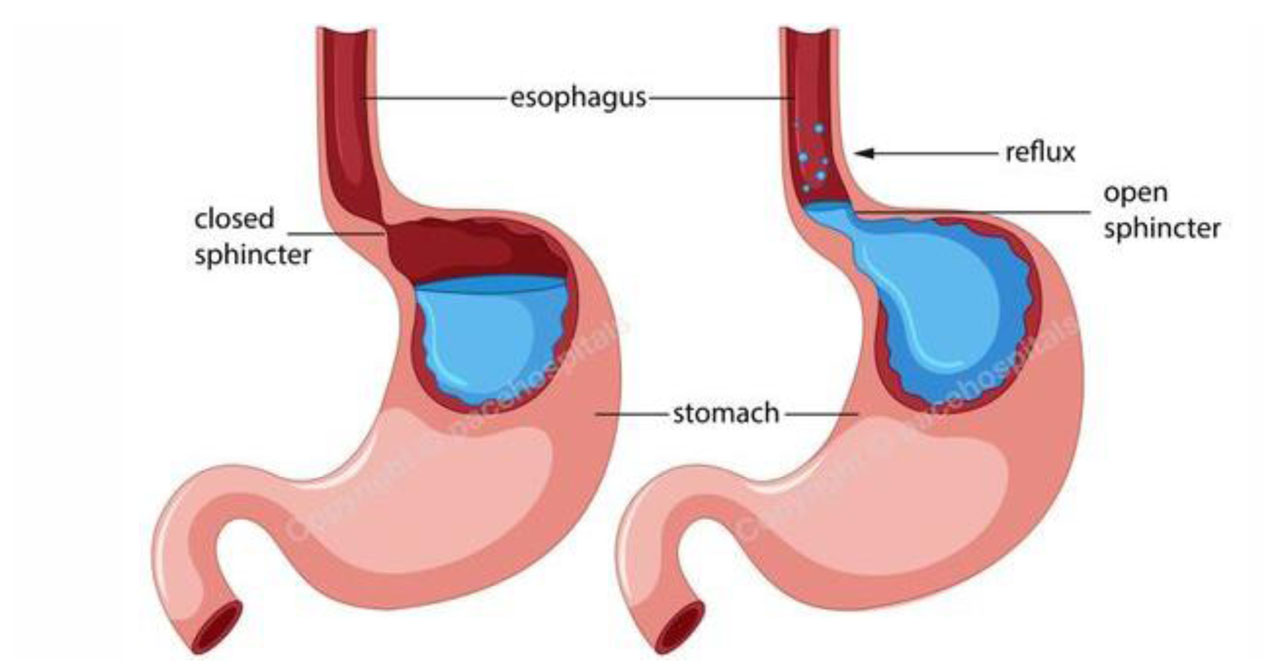
3. Most common cause of esophagitis is (AIIMS May 2009)
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Reflux disease
- Increased intake of spices
ANSWER c
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid repeatedly flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of your esophagus.
4. Best site for taking biopsy for viral esophagitis is (AIIMS Nov 2001)
- Edge of ulcer
- Base of ulcer
- Adjacent indurated area around ulcer
- Surrounding normal mucosa
ANSWER a
Herpes viruses typically cause punched-out ulcers; the nuclear inclusions of herpes virus are found in a narrow rim of degenerating epithelial cells at the margin of the ulcer.
CMV causes linear ulceration of the esophageal mucosa; the histologic findings of CMV-associated change with both intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions are found in capillary endothelium and stromal cells in the base of the ulcer.
5. Which of the following viruses does not produce viral esophagitis?
- Herpes
- Adenovirus
- Varicella
- Cytomegalovirus
ANSWER b
Viruses that can cause esophagitis are: HSV-1, HSV-2, Varicella zoster virus, Cytomegalovirus and HIV For diagnosis, the biopsy should be taken from edge of ulcer in HSV and base of ulcer in CMV. Findings in biopsy of edge of ulcer in HSV are:
- Ballooning degeneration
- Ground glass changes in nuclei
- Cowdry type A intranuclear inclusion bodies




