- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Pain can be defined as the feeling of distress or suffering or agony caused by the stimulation of receptors for pain. It is an unpleasant sensation.
The chemicals which are thought to stimulate pain receptors are as follows:
- Pain-producing substance (PPS): It is a polypeptide produced from plasma proteins by the action of proteolytic enzymes released from the damaged tissue.
- Other chemicals such as bradykinin, prosta and cyclic AMP (adenosine monophosphate) also act as PPS.
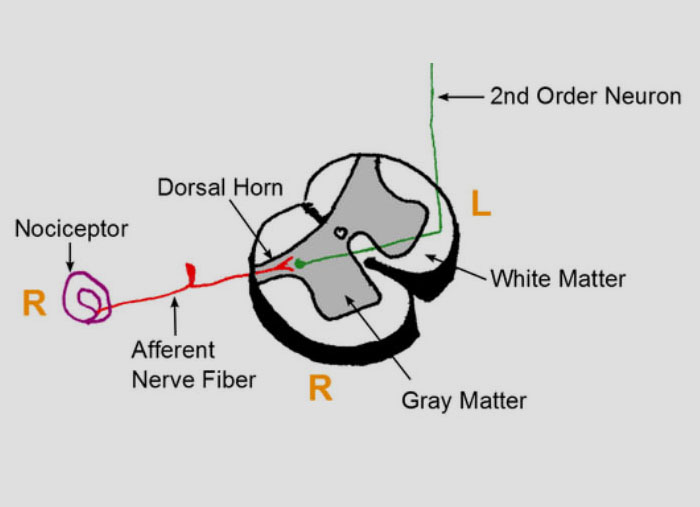
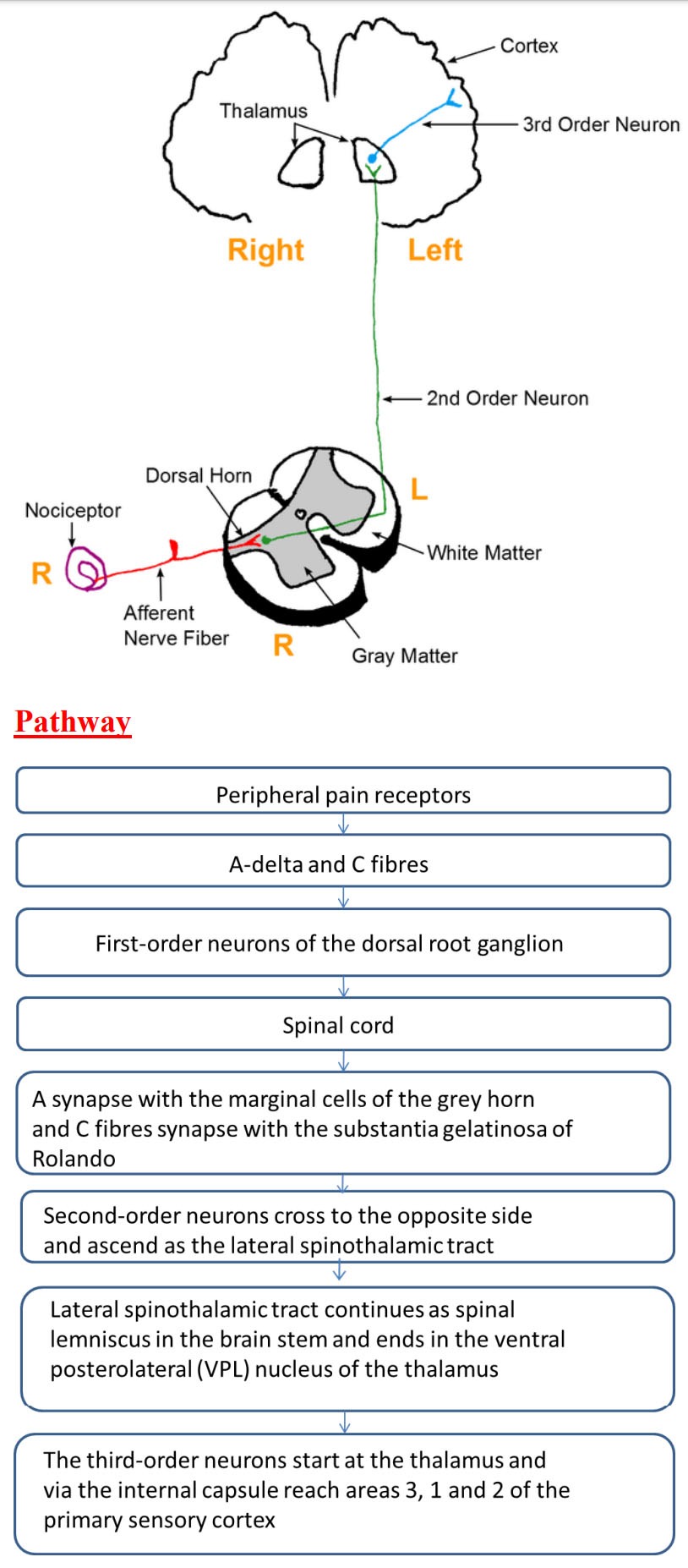
Pathway of pain
Within the pain pathway there are 3 orders of neurones that carry action potentials signalling pain:
- First-order neurones – These are pseudounipolar neurones which have cells bodies within the dorsal root ganglion. They have one axon which splits into two branches, a peripheral branch (which extends towards the peripheries) and a central branch (which extends centrally into the spinal cord/brainstem).
- Second-order neurones – The cell bodies of these neurones are found in the Rexed laminae of the spinal cord, or in the nuclei of the cranial nerves within the brain stem. These neurones then decussate in the anterior white commissure of the spinal cord and ascend cranially in the spinothalamic tract to the ventral posterolateral (VPL) nucleus of the thalamus.
- Third-order neurones – The cell bodies of third-order neurones lie within the VPL of the thalamus. They project via the posterior limb of the internal capsule to terminate in the ipsilateral postcentral gyrus (primary somatosensory cortex). The postcentral gyrus is somatotopically organised. Therefore, pain signals initiated in the hand will terminate in the area of the cortex dedicated to sensations of the hand.
Applied anatomy
Acute Pain- It is a protective mechanism that alerts the individual to a condition or experience that is immediately harmful to the body.
Chronic Pain- It is persistent or intermittent and usually lasts for at least 6 months.
Hyperalgesia- Excessive sensitiveness to pain is called hyperalgesia. It is noticed around an injury or inflammation due to the release of certain chemicals which decrease the threshold of pain receptors and increase pain sensitivity.
Pain in Thalamic Syndrome- A patient suffers from acute attacks of pain without any obvious stimulus. This type of pain is due to lesions anywhere in the pathway of pain.
Phantom Pain- Pain in the area of non-existing tissue or organ.
Allodynia- Painful sensations provoked by non-noxious stimuli are known as allodynia.
Referred Pain- Pain in the area remote from the region of origin of pain. This occurs since the area of referred pain is supplied by the same spinal segment as the region of origin of pain. For example, myocardial pain can be referred to the lower jaw.
Somatic Pain- Pain arising from the skin or in areas which are in proximity to the surface of the body.
Visceral Pain- Pain arising in the internal organs. Hemiagnosia-Inability to perceive pain in one side of the body.This is commonly associated with stroke.
Trigeminal Neuralgia- It is one-sided facial pain occurring along the distribution of any one of the branches of trigeminal nerve.




