- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
PHYSIOLOGICAL ANATOMY OF SKELETAL MUSCLES
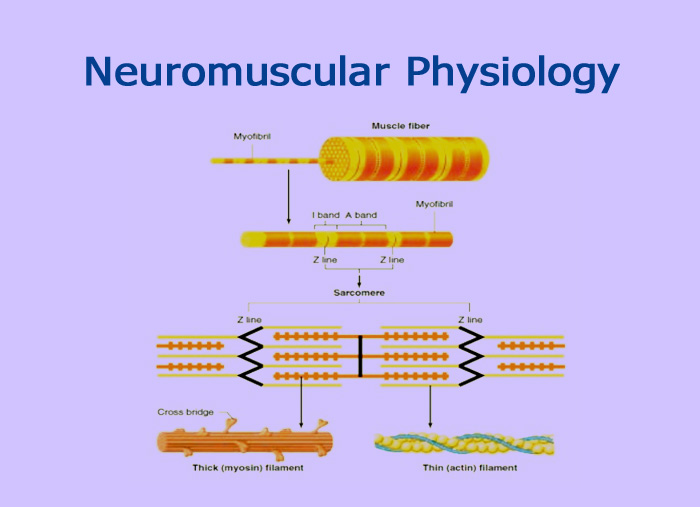
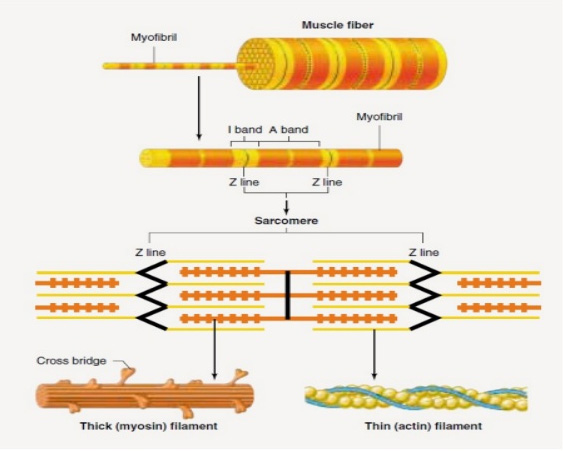
- Muscle consists a number of muscle fibers lying parallel to one another and held together by connective tissue
- Single skeletal muscle cell is known as a muscle fiber
- Each Muscle Fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called SARCOLEMMA.
- Individual MF is enveloped by layer of connective tissue called ENDOMYSIUM ( which lies outside Sarcolemma)
- Several MF are enveloped together by another connective tissue called PERIMYSIUM
- The entire Muscle is covered all round by EPIMYSIUM.
• Actin
two forms
• G-Actin (Globular monomer)
– Each molecule contains one molecule of ATP
– Molecular weight of about 43000.
• F-Actin ( Globular monomer)
– Fibrous, thickness of 6-7 nm, polymerized G-Actin, contains ADP.
– Polymerization occurs in presence of Calcium or Magnesium ions.
• Myosin –II
– Found in Thick Filaments
– Mol Weight of about 460,000.
– Chief Actin Binding Constituent.
– Hexamer containing two identical heavy chains and 4 light chains.
• Troponin
⇒ Troponin –C
– Can bind an release Calcium Ions.
⇒ Troponin-I
– Exerts an inhibitory action over Actin-Myocin interaction when Troponin C is without Calcium.
⇒Troponin T
– Serves to bind Troponin C and Troponin I subunits with Tropomyosin-Actin Complex.
(Troponin complex is found only in Striated Muscle)
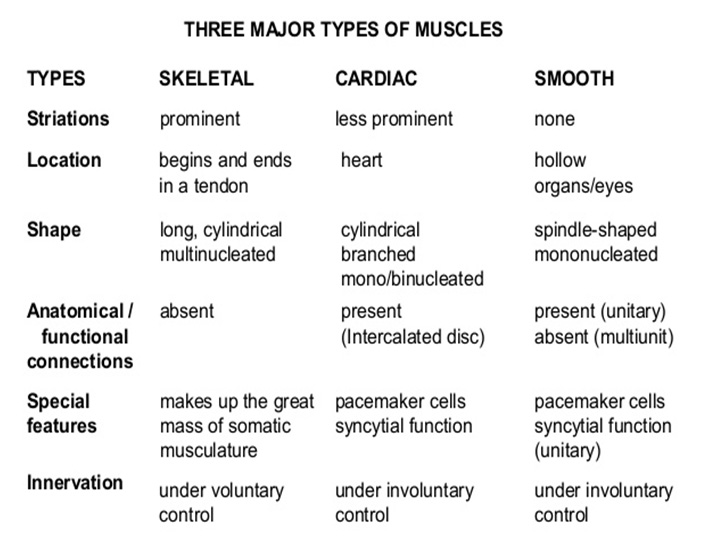
♦ troponin is replaced by calmodulin in the smooth muscles..CONTRACTILE MECHANISMS
SLIDING FILAMENT MECHANISM- Increase in Ca2+ starts filament sliding
- Decrease in Ca2+ turns off sliding process
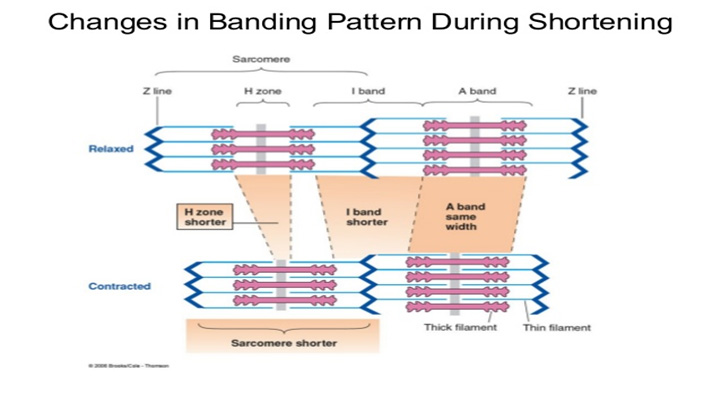
- Thin filaments on each side of sarcomere slide inward over stationary thick filaments toward center of A band during contraction
- As thin filaments slide inward, they pull Z lines closer together
- Sarcomere shortens
- Activated cross bridge bends toward center of thick filament, “rowing” in thin filament to which it is attached
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca2+ into sarcoplasm
- Myosin heads bind to actin
- Myosin heads swivel toward center of sarcomere (power stroke)
- ATP binds to myosin head and detaches it from actin
- Hydrolysis of ATP transfers energy to myosin head and reorients it
- Contraction continues if ATP is available and Ca2+ level in sarcoplasm is high
- All sarcomeres throughout muscle fiber’s length shorten simultaneously
- Contraction is accomplished by thin filaments from opposite sides of each sarcomere sliding closer together between thick filaments
Relaxation
- Depends on reuptake of Ca2+ into sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
- Acetylcholinesterase breaks down ACh at neuromuscular junction
- Muscle fiber action potential stops
- When local action potential is no longer present, Ca2+ moves back into sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Rigidity caused by loss of all the ATP which is required to cause the separation of the cross- bridges from the actin filament during the relaxation process.
- Thus, several hours after death the muscles of the body go into a state of contracture, called “ Rigor Mortis”, i.e. the muscle contracts and becomes rigid even without action potential.
- The muscle remains in rigor until the muscle proteins are destroyed by autolysis
MCQs.
1. Which is most likely to extend entire length of a muscle fibre?
a) Sarcomere
b) Myofibril
c) Myosin filament
d) M-line
Answer: B
Myofibrils extend the length of a muscle fibre, whereas many sarcomeres in series make up the length of a myofibril. Myosin filaments are contained within each sarcomere. The M-line is part of the cytoskeleton that stabilizes each sarcomere.2. Which of the following is true about muscle structure?
a) Myofibrils make up about 15% of the contents of a muscle fibre.
b) Even the largest (thickest) muscle fibres would contain only about 100 myofibrils.
c) Actin filaments are arranged so that 6 actin filaments surround each myosin filament.
d) Myosin filaments are about twice as thick as actin filaments.
Answer: C
Six actin filaments surround each myosin filament, producing a hexagonal array. Muscle fibres can contain up to a few thousand myofibrils, which make up about 85% of the content of a muscle fibre. Myosin filaments are close to 3 times as thick as actin filaments.



