- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Natal and Neonatal Teeth
Synonyms: Congenital teeth, Prediciduous teeth, dentition praecox, foetal teeth, natal and neonatal teeth.
Etiology
• Superficial position of the tooth germs.• Infection
• Malnutrition
• Eruption accelerated by febrile incidents or hormonal stimulation.
• Hereditary transmission of a dominant autosomal gene.
• Osteoblastic activities inside the tooth germ area related to bone remodeling phenomena.
• Hypovitaminosis
Associated with some genetic syndromes, such as
• Ellis – Van Creveld Syndrome
• Riga-Fede Disease
• Pachyonychia congenital
• Hallemann – Steriff Syndrome
• Sotos Syndrome
• Cleft palate
• Ellis – Van Creveld Syndrome
• Riga-Fede Disease
• Pachyonychia congenital
• Hallemann – Steriff Syndrome
• Sotos Syndrome
• Cleft palate
Incidence
► Nearly 90% of these teeth are normal primary teeth.► In 85% : mandibular primary incisors.
► 5% are maxillary incisors and molars.
► Remaining 10% are supernumerary calcified structures
Clinical features:
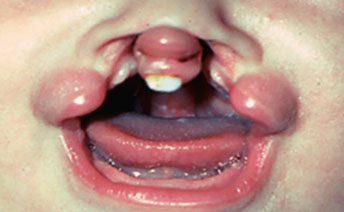
► Morphologically, natal and neonatal teeth may be conical or may be normal in size and shape and opaque yellow – brownish in colour.► These children show other associated symptoms such as dystrophic finger nails, hyperpigmentation etc.
Radiographs
• A radiograph should be made to determine the amount of Root development and the relationship of prematurely erupted teeth to its adjacent teeth.• Most prematurely erupted teeth are hyper mobile because of the limited root development.

Histological characteristics
► Hypoplastic enamel with varying degrees of severity.► Absence of root formation
► Ample vascularised pulp
► Irregular dentin formation
► Lack of cementum formation are characteristic features.
Harmful Effects
1. Laceration of the lingual surface of tongue.2. difficulties for a mother who wishes to breast-feed her infant.
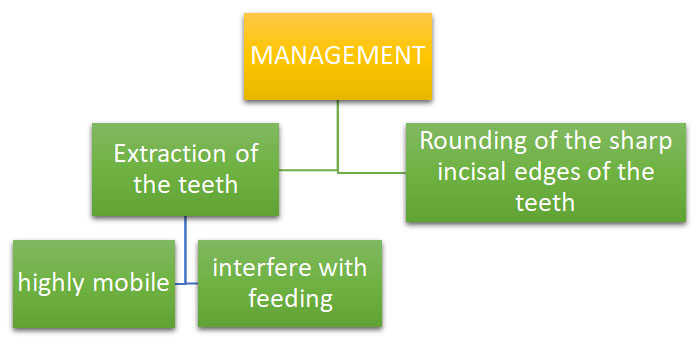
If the treatment option is extraction precautions to be taken are
• Avoiding extractions upt 10th day of life, need to wait for the commensal flora of the intestine to be established to produce vitamin K.
• If extractions are planned and the new born is not medicated with vitamin K immediately after birth, vitamin K supplements can be given before extractions to prevent hemorrhagic disease of the new born (hypoprothrombinemia)
• Avoiding extractions upt 10th day of life, need to wait for the commensal flora of the intestine to be established to produce vitamin K.
• If extractions are planned and the new born is not medicated with vitamin K immediately after birth, vitamin K supplements can be given before extractions to prevent hemorrhagic disease of the new born (hypoprothrombinemia)
MCQs
1.Teeth that erupt within 30 days of birth are called;A. Natal teeth
B. Neonatal teeth
C. Primary teeth
D. Prenatal teeth
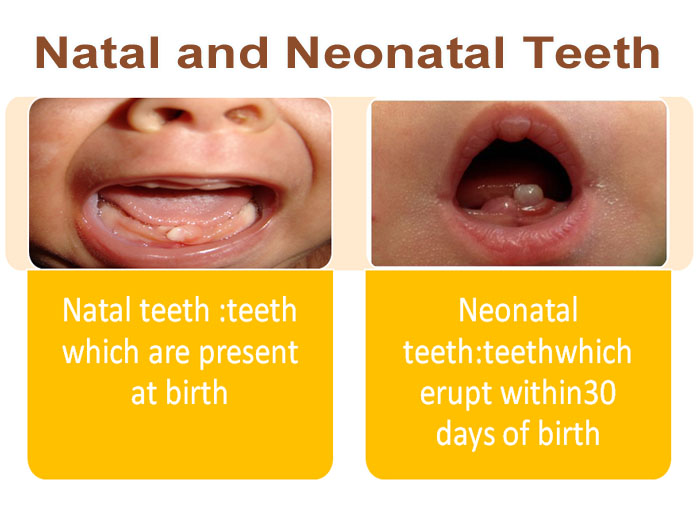
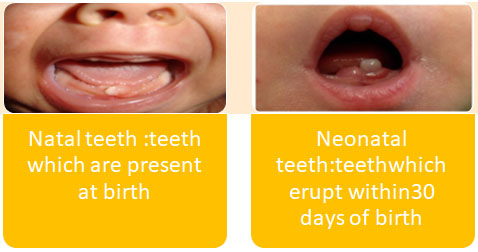
• Natal teeth :teeth which are present at birth
• Neonatal teeth:teethwhich erupt within30 days of birth
2.Ulcers commonly seen in ventral surface of tongue and lingual vestibule in children due to mucosal irritation is known as
A. Crohns disease.
B. Rega feda
C. Darrier disease
D. Ranula
Rega fede disease: Early eruption of teeth ( natal or neonatal) cause ulceration on the ventral surface of the tongue by the sharp edges of the tooth. This may interfere with the infants feeding and suckling which may inturn affect nutrition.
Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




