- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES (MdS)
Myelodysplastic syndromes refer to a clonal stem cell disorder resulting in ineffective hematopoiesis and increased risk of development into acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
Myelodysplastic syndromes get their name from myelo, meaning bone marrow, and dysplasia, meaning abnormal growth.
- The bone marrow is replaced with multipotent stem cells which can differentiate but in an unorganized and ineffective manner only.
- It has been linked to the exposure to radiation, benzene, alkylating agents and some chromosomal abnormalities. MDS can be classified into:
|
- The bone marrow is usually hypercellular in this condition but the myelodysplastic precursor cells undergo apoptosis at a fast rate resulting in ineffective hematopoiesis.
- MDS is frequently associated with chromosomal abnormalities including monosomy 5 and 7, deletion of 5q and 7q, trisomy 8 and deletion of 20 q
Bone marrow findings
| Erythroid cells | Ringed sideroblasts (Iron laden mitochondria in erythroblasts) with increased iron stores Megaloblasts, nuclear budding, intranuclear bridging, irregular nuclei |
| Megakaryocytes | Pawn ball megakaryocytes (Megakaryocytes with multiple separate nuclei) |
| Neutrophils | Dohle bodies (toxic granulations) are seen, Pseudo-Pelger-Huet cells (Neutrophils with two nuclear lobes) are also seen |
Symptoms
- Some people with a myelodysplastic syndrome do not have any symptoms at all.
- The symptoms are caused by a drop in the number of blood cells and could include tiredness and sometimes breathlessness because of a low red blood cell count (anaemia)
- Frequent infections
- Bleeding (such as nosebleeds) or bruising easily because of a low platelet count
Types
Different types of MDS
- MDS with single lineage dysplasia (MDS-SLD)
- MDS with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS)
There are two subtypes of MDS-RS:
- MDS-RS-SLD – This means MDS with single lineage dysplasia and ring sideroblasts. Single lineage dysplasia means the MDS affects a single type of blood cell.
- MDS-RS-MLD – This means MDS with multiple lineage dysplasia and ring sideroblasts. Multiple lineage dysplasia means the MDS affects more than one type of blood cell.
- MDS with multilineage dysplasia (MDS-MLD)
- MDS with excess blasts (MDS-EB)
- MDS-EB is split into MDS-EB-1 and MDS-EB-2. In MDS-EB-2, there are more blast cells in the blood and bone marrow than in MDS-EB-1.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome unclassified (MDS-U)
Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R)
The system for grouping MDS according to likely outcome is called the Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R). There are 5 risk groups:
- very low risk
- low risk
- intermediate risk
- high risk
- very high risk
The risk group depends on:
- The number of immature cells (blasts) in your bone marrow and blood
- Whether there are chromosome changes in the affected blood cells
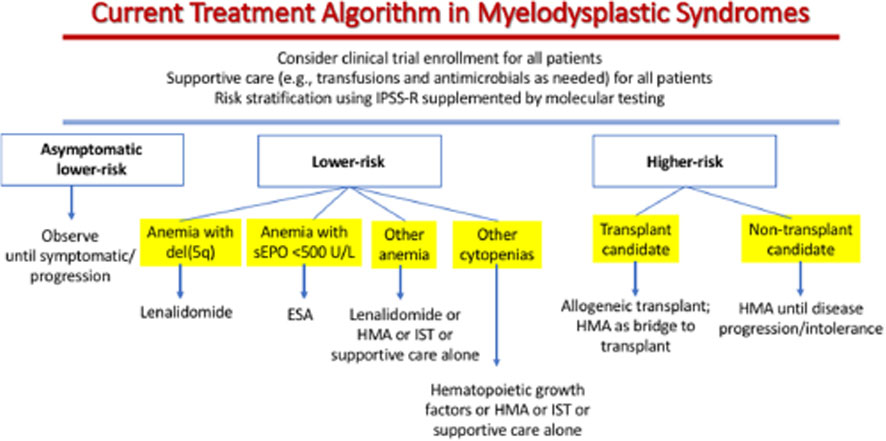
Treatment plan
Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




