- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
a)0ccipital myotomes
b)1st pharyngeal arch
c)Lateral lingual swellings
d)Preoptic myotome muscles
Ans: a
The musculature of the tongue is derived from occipital myotomes. This explains its nerve supply by the hypoglossal nerve, which is the nerve of these myotomes.
The occipital myotomes migrate to the floor of the developing oral cavity and form the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
2. Which of the following precancerous lesion has malignant potential
a) OSMF
b) Erythroplakia
c) Oral lichen planus
d) Syphilitic glossitis
Ans: b
Erythroplakia is defined as “A fiery red patch that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other definable disease”. Clinical appearance is characterized by flat or even depressed erythematous change of the mucosa without a patch lesion. Both red and white changes in the same lesion refer to as “erythroleukoplakia”. Erythroplakia has the highest risk of malignant transformation compared to all other oral mucosal premalignant lesions. The malignant transformation rate for erythroplakia varies from 14 to 50%
Mostly, a solitary lesion occurs over the surface of any part of the oral cavity. But the most commonly affected areas were reported as the soft palate, the floor of the mouth, and the buccal mucosa. Owing to the high malignant transformation rate, early effective treatment is mandatory. Surgery, either by cold knife or by laser, is the recommended therapy.
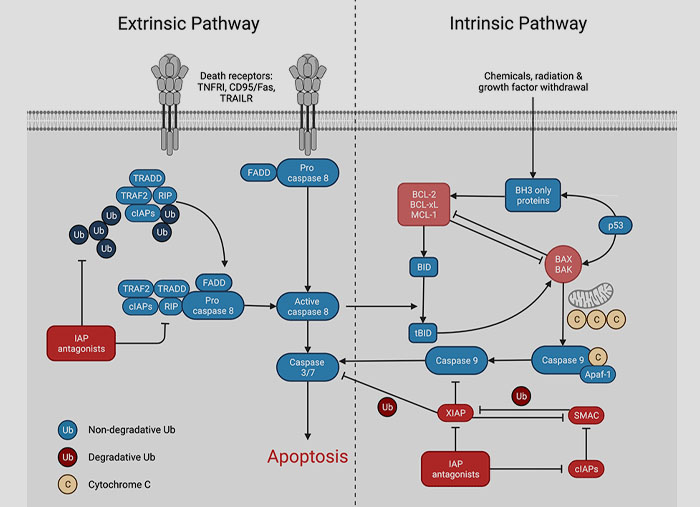
3. Which of the following is an antiapoptotic gene
a) BAX
b) p53
c) BAK
d) BCL-2
Ans: d
Apoptosis: Programmed cell death in which there is death of individual cells without inciting inflammatory processes.
There are two pathways of initiation of apoptosis:
- Extrinsic receptor initiated pathway
- Intrinsic mitochondrial pathway These two pathways are interconnected and converge to activate caspases
Extrinsic pathway: On cross linkage of Fas (Death domain) by its ligand three or more molecules come together and bind to cytoplasmic Fas-associated death domain (FADD) which in turn binds to inactive forms of caspase-8 via death domain. These activated caspases trigger a cascade of caspase activation and mediate execution phase of apoptosis. FLIP protein inhibits apoptosis by binding to procaspase-8. This mechanism is used to protect infected normal cells from Fas mediated apoptosis.
Intrinsic mitochondrial pathway: There are more than 20 antiapoptotic proteins. Of which Bcl-2 and Bcl-x are located on the mitochondrial membrane of cytoplasm. Bcl-2 and Bcl-x are replaced when cells are deprived of survival signals or stress by proapoptotic members like Bak, Bax and Bim. This leads to increased mitochondrial membrane permeability and release of several proteins which activate caspase cascade e.g. cytochrome C from mitochondria which binds to Apaf-1(Apoptosis activating factor-1protein). The complex activates caspase-9. Apoptosis activating factor from mitochondria also neutralizes various apoptotic inhibitors which block caspase activation
4. Dentigerous cyst arises from
a) Unerupted teeth
b) Teeth with root caries
c) Irritated PDL cells
d) Osteomyelitis
Ans: a
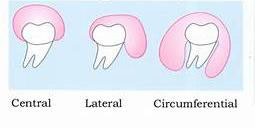
Dentigerous cyst can be defined as an odontogenic cyst that surrounds the crown of an impacted/unerupted tooth; caused by fluid accumulation between the reduced enamelepithelium and the enamel surface.
Radiographic features: exhibit three different presentations namely, the central, lateral, and circumferential types
Syndrome association: Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, Cleidocranial dysplasia, Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome
5. The fibre group that bears maximum of masticatory forces and transfers it as tension to alveolar bone is
a) Horizontal
b) Oblique
c) Alveolar crest
d) Apical
Ans: b
The main principal fiber group is the alveolodental ligament, which consists of five fiber subgroups: alveolar crest, horizontal, oblique, apical, and interradicular on multirooted teeth.
The alveolar crest fibres run in an apically inclined direction, from the cementum of the tooth just beneath the junctional epithelium towards the alveolar crest. They act to prevent extrusion of teeth and resist lateral tooth movements.
Horizontal fibres run perpendicularly to the long axis of the tooth, from cementum to alveolar bone, covering the apical two-thirds of the root.
Oblique fibres are the most abundant fibre group in the PDL, extending from the cementum in a coronal direction obliquely to the alveolar bone. They resist vertical and intrusive forces, thus bear a large part of the vertical masticatory stresses and transfer them into tension on the alveolar bone.
Apical fibres radiate in an irregular manner from the cementum to alveolar bone at the apical region of the socket and form only after the root is completely formed




