- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
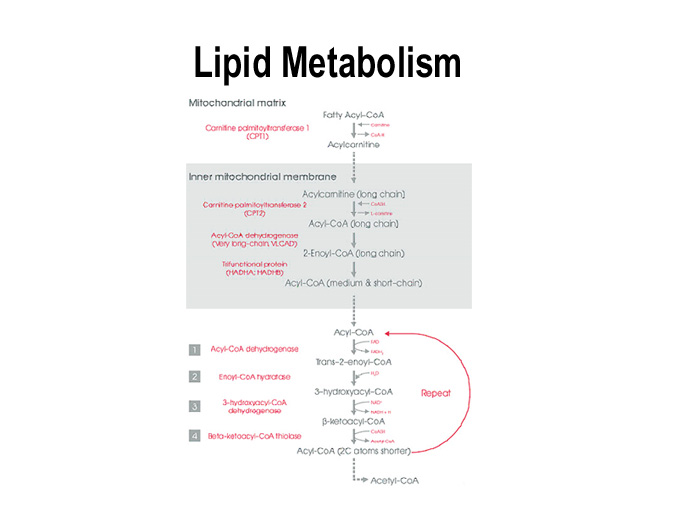
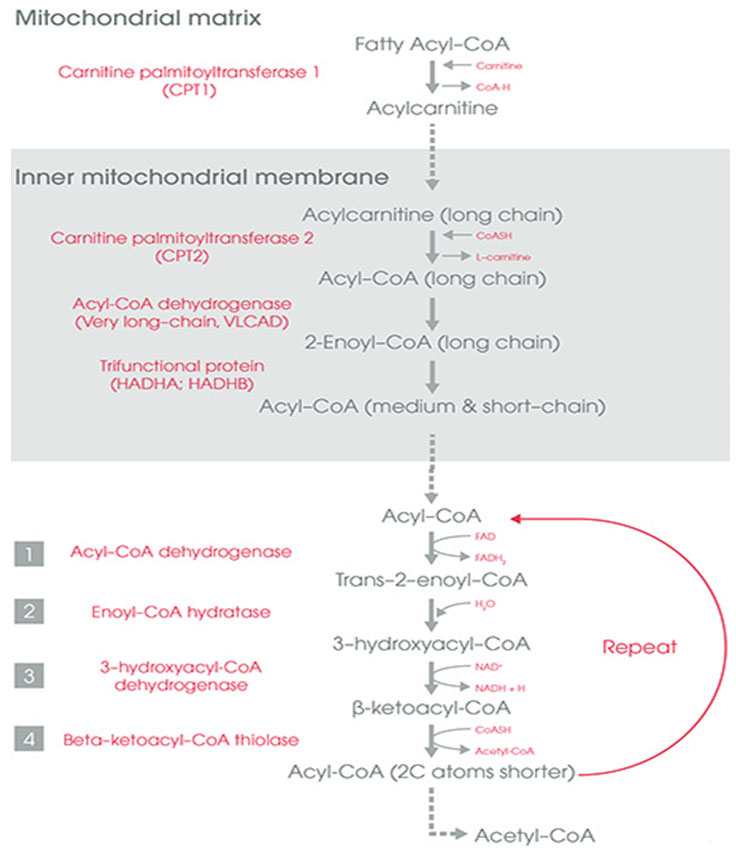
1. BETA OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS
This process is known as beta oxidation, because the oxidation and splitting of two carbon units occur at the beta carbon atom. The oxidation of the hydrocarbon chain occurs by a sequential cleavage of 2 carbon atom.
Preparative step 1: Activation of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are activated to their coenzymes A (CoA) derivative. ATP is hydrolyzed to AMP and PPi and the energy from hydrolysis of PPi drives the reaction forward. Thus 2 high energy bonds are utilized in this reaction
Preparative step 2: Role of Carnitine
Fatty acids are activated in the cytoplasm, but the beta oxidation is in mitochondria. So transport of fatty acids through the mitichondrial membrane is essential. The long chain fatty acyl CoA cannot pass through the inner mitichondrial membrane.
Preparative step 3: Carnitine Acyl Transferase
The enzyme carnitine acyl transferase I (CAT-I) will transfer the fatty acyl group to carnitine to form acyl carnitine. The reaction occurs om the cytosolic side of inner mitochondrial membrane.
Beta oxidation steps:
Step 1: The fatty acyl CoA is dehydrogenated with the FAD accepting the hydrogen atoms. FADH2 when oxidised in electron transport chain will produce 2 ATP molecules
Step 2: This step forms a beta hydroxy fatty acyl CoA
Step 3: Another dehydrogenation takes place with the help of NADH which when oxidised in electron transport chain will generate 2.5 ATPs
Step 4 : One molecule of acetyl CoA is liberated, leaving behind a fatty acid with 2 carbon atoms less.
The newly formed fatty acyl CoA will sequentially undergo further cycles of step 1, 2, 3 and 4 of beta oxidation untill the fatty acid is completely converted to acetyl CoA.
2. OXIDATION OF ODD CHAIN FATTY ACIDS
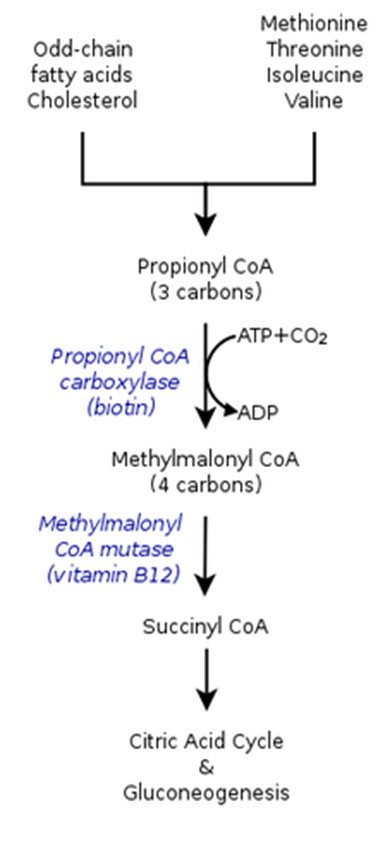
The odd chain fatty acids are oxidized exactly in the same manner as even fatty acids. However, after successive removal of 2 carbon units, at the end one 3 carbon unit, propionyl CoA is produced. Fate of propionyl CoA: with the help ofcarboxylase, racemase and mutase, propionate is converted into succinyl CoA . Carboxylase is biotin dependent while mutase is vitamin B12 dependent. The succinyl CoA then enters TCA cycle , finally converted into oxaloacetate , and is used for gluconeogenesis.
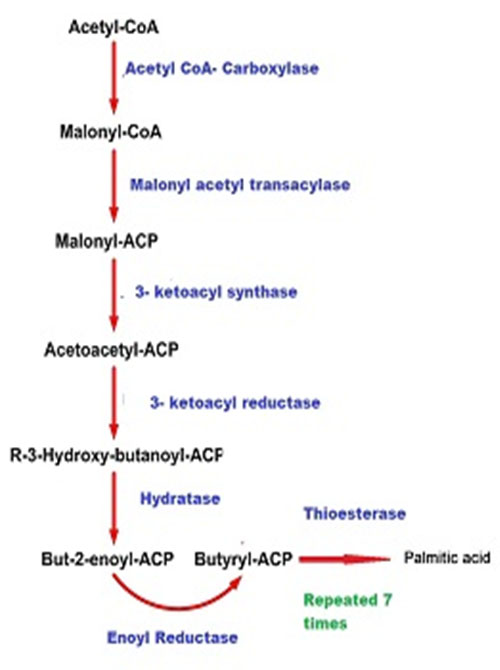
3. DENOVO SYNTHESIS OF FATTY
Fatty acids are synthesised mainly by a de novo synthetic pathway operating in the cytoplasm. So it is referred to as extramitochondrial or cytoplasmic fatty acid synthase system. The major fatty acid synthesised de novo is palmitic acid, the 16C saturated fatty acid. The processs occurs in liver, adipose tissue, kidney, brain, and mammary glands.
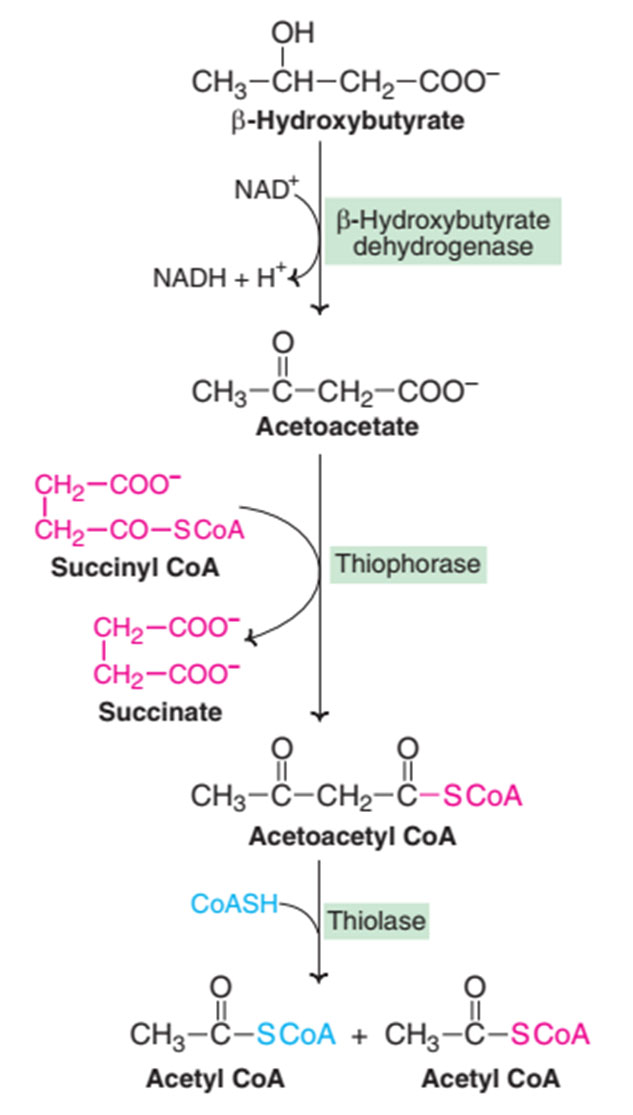
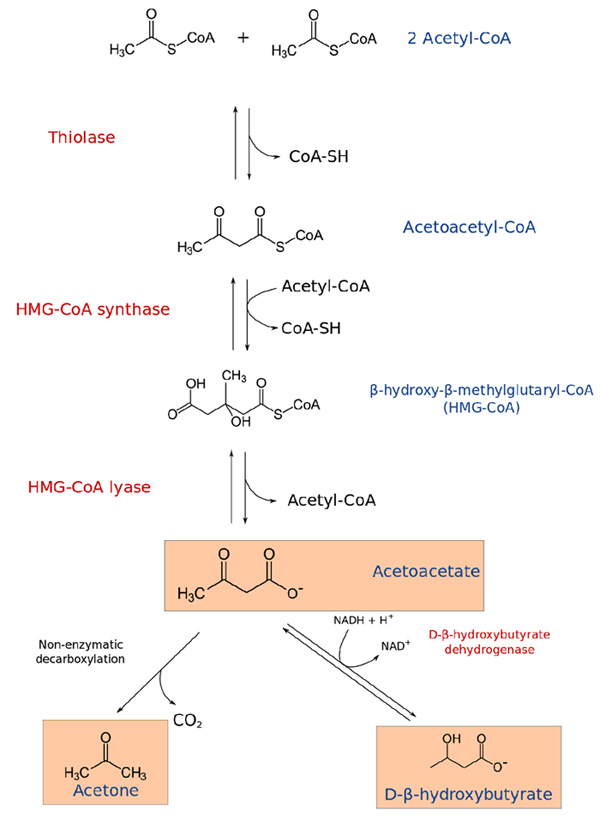
4. METABOLISM OF KETONE BODIES
Carbohydrates are essential for the the metabolism of fat or fat is burned under the fire of carbohydrates. The acetyl CoA formed from fatty acids can enter and get oxidized in TCA cycle only when carbohydrates are available.
A) KETOGENESIS
B) KETOLYSIS