- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. Most common odontogenic cyst is
A. Radicular cyst
B. Dentigerous cyst
C. Odontogenic keratocyst
D. Gingival cyst
Answer- Option A
The radicular cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. The usual etiology is an infected tooth leading to necrosis of the pulp.
2. “Floating tooth syndrome” appearance is seen in
A. Fibrous dysplasia
B. Cherubism
C. Vanishing bone
D. Paget’s disease
Answer- Option B
Cherubism presents as well defined corticated radiolucency with fine granular bone and wispy trabeculae forming a prominent multilocular pattern. Severe displacement of teeth resulting in a floating teeth appearance is noted.
Vanishing bone disease or Gorham’s disease is a rare entity of unknown etiology characterized by destruction of osseous matrix and proliferation of vascular structures, resulting in destruction and absorption of bone. Majority of the cases involve the maxillofacial region. (Rahman NA, Harun MH, Mohammad NSA. J Taibah Uni Med Sci.2020 Apr; 15(2): 160-165. [pubmed])
3. Gustatory sweating is
A. Auriculotemporal syndrome
B. Fothergill’s disease
C. Crocodile tears
D. Sphenopalatine neuralgia
Answer- option A
Auriculotemporal syndrome or Frey syndrome or Gustatory sweating arises as a result of damage to auriculotemporal nerve and subsequent innervation of sweat glands by parasympathetic salivary fibres. Patient exhibit flushing and sweating of the involved side of the face especially temporal area during eating.
4. Widespread Carious destruction of deciduous teeth most commonly four maxillary incisors followed by first molars with absence of caries in the mandibular incisiors
A. Chronic caries
B. Acute caries
C. Nursing caries
D. Rampant caries
Answer- C
The disease of early childhood caries is the presence of 1 or more decayed (non-cavitated or cavitated lesions), missing (due to caries), or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth in a child 71 months of age or younger
Terminologies for ECC
- Nursing caries: Winter (1966)
- Tooth clearing neglect: Moss (1996)
- Infant and early childhood dental decay: Horowitz (1998)
- ECC: Davies (1998)
- MDSMD: Maternally derived Streptococcus mutans disease
Rampant caries – as suddenly appearing widespread, rapidly spreading, burrowing type of caries, resulting in early involvement of pulp and affecting those teeth, which are usually regarded as immune to decay
5. Thistle tube shaped pulp chamber is seen in
A. Dentinogenesis imperfect-2
B. Type 2 dentin dysplasia
C. Type 1 dentin dysplasia
D. Odontodysplasia
Answer- B
This is the appearance seen in permanent teeth characterized by an abnormally large pulp chamber in the coronal portion of the tooth. Type -1 dentin dysplasia exhibits the appearance of “lava flowing around boulders”.
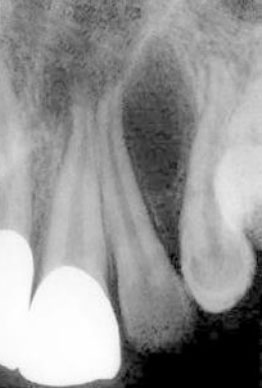
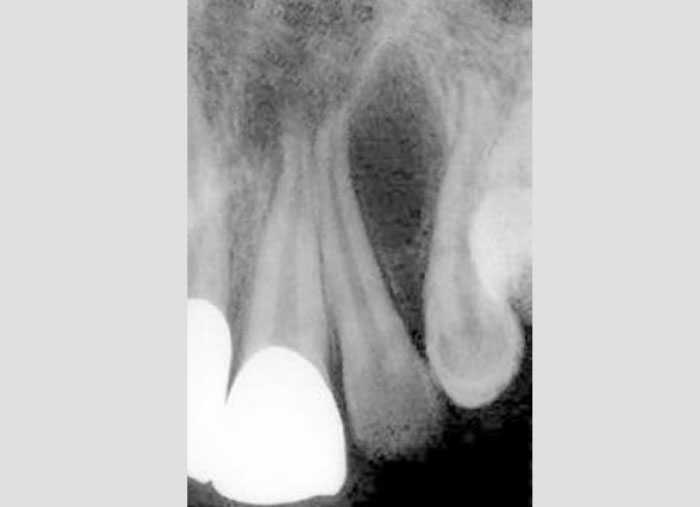
6. Which of the following cyst manifests typically between roots of maxillary lateral incisor and canine?
A. Nasoalveolar cyst
B. Nasopalatine duct cyst
C. Globulomaxillary cyst
D. Median palatal cyst
Answer- C
Globulomaxillary cyst is seen as an inverted pear shaped radiolucency between maxillary lateral incisor and canine.
7. Which of the following bacteria is more important for producing cellulitis?
A. Streptococci
B. Pneumococci
C. Staphylococci
D. Helicobacter pylori
Answer- A
Streptococcus pyogenes is the major organism causing cellulitis. The widespread infection is caused due to the action of hyaluronidase enzyme produced by the bacteria.
8. Discharging sinuses with sulphur granules are a feature of
A. Tuberculosis
B. Actinomycosis
C. Ludwig’s angina
D. Pindborg tumor
Answer- B
Actinomyces israelii causes actinomycosis, characterized by cervicofacial woody indurated lesion with suppuration characterized with discharging sinuses containing sulphur granules (represent colonies of the bacteria).
9. Which of the following lesions does not manifests as multilocular radiolucency?
A. Ameloblastoma
B. Odontogenic keratocyst
C. Periapical cyst
D. Adenoameloblastoma
Answer- C
- Ameloblastoma- The most common manifestation is a soap bubble or honey comb appearance (multilocular radiolucency).
- Odontogenic keratocyst- May present with curved internal septae giving a mutilocular appearance.
- Adenoameloblastoma or adenomatoid odontogenic tumor- Eventhough unilocular radiolucency is the most common presentation, multilocular appearance have also been reported.
- Periapical cyst is very rare to present as a multilocular radiolucency
10. Which of the following lesions manifest with intraoral vesicles and prodromal fever and
malaise?
A. Bullous pemphigoid
B. Lichen planus
C. Psoriasis
D. Herpes simplex
Answer -D
Since prodromal symptoms are present, it points to a viral infection, ie intraoral Herpes simplex virus infection.


