- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

ETIOLOGY:
The causes of inflammation are many and varied:
- Exogenous causes
- Physical agents
- Mechanic agents: fractures, foreign corps, sand, etc.
- Thermal agents: burns, freezing
- Chemical agents: toxic gases, acids, bases
- Biological agents: bacteria, viruses, parasites
- Circulation disorders: thrombosis, infarction, hemorrhage
- Enzymes activation – e.g. acute pancreatitis
- Metabolic products – uric acid, urea
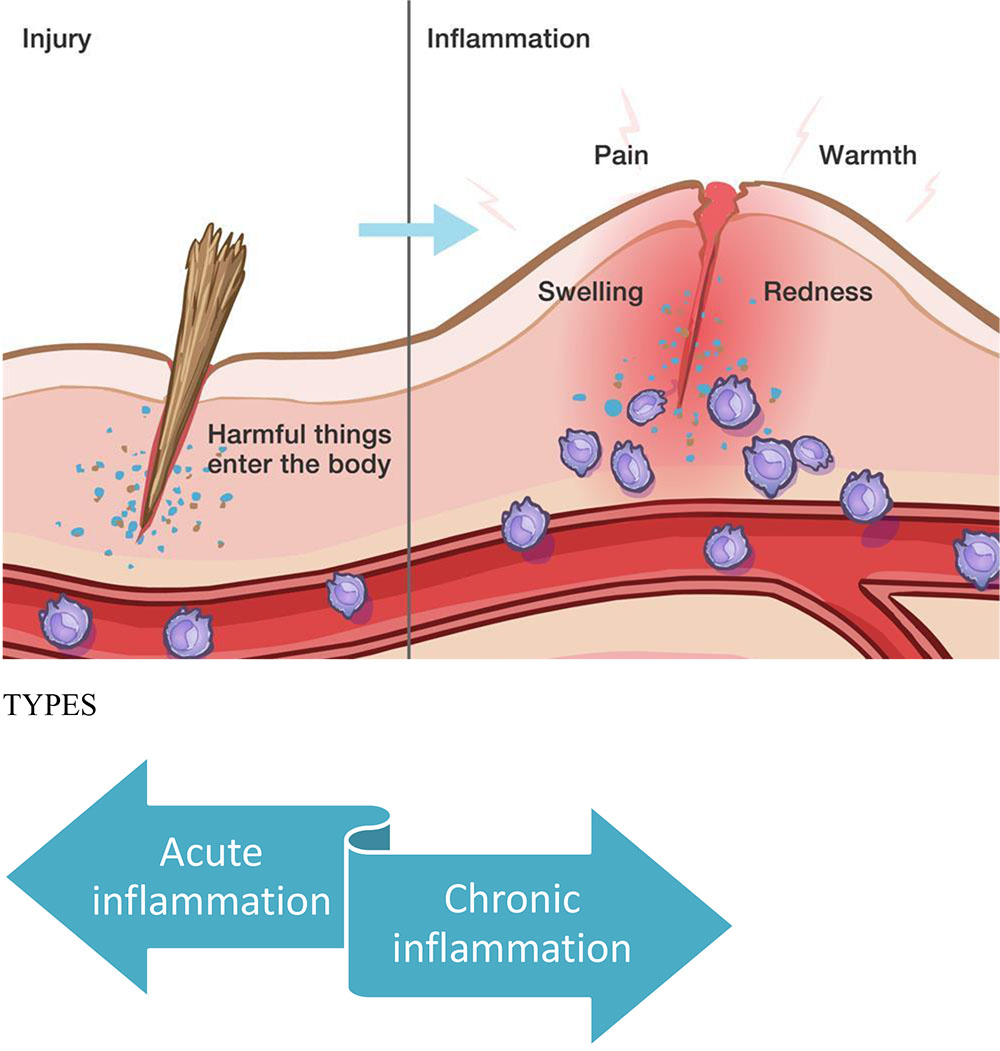
SIGNS OF INFLAMMATION
The Roman writer “Celsus” in 1st century AD named the famous four cardinal signs of inflammation as:-
|
MEDIATORS AND BIOMARKERS OF INFLAMMATION
The discovery of cellular and molecular inflammatory mediators and the development of sensitive biomarkers have rapidly advanced our understanding of inflammation and its role in pathology. These biomarkers include:
- Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen oxide species (ROS and RNOS)
- Formation of DNA adducts
- Cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and TNF-alpha) and chemokines
- Acute-phase proteins (e.g., C-reactive protein or CRP) Acute inflammation Chronic inflammation
- Prostaglandins
- Cyclooxygenase (COX)-related metabolites
- Inflammation-related growth factors and transcription factors (e.g., NFkappaB)
- Major immune cell types
The specific immune cells and mediators at play are variable and dependent upon the injury, the onset/duration of the injury, and multiple genetic loci
| CRP is a widely used clinical inflammatory biomarker present in two forms with distinct functions. One form is a homopentamer termed native-CRP (nCRP), and the other is a monomer (mCRP). There are two clinical assays for CRP, a standard assay and a high-sensitivity assay (hs-CRP). |
Immune cells that contribute to inflammation include:
Neutrophils: These are the most common type of white blood cells and are often the first cells to arrive at the site of injury or infection. They are responsible for engulfing and destroying invading pathogens. Neutrophils are often seen in areas of acute inflammation.
Macrophages: These are large white blood cells that play a key role in the immune system‟s response to infection and inflammation. They are involved in phagocytosis, the process of engulfing and destroying invading pathogens. Macrophages inside tissue are called histiocytes.
Mast cells: These white blood cells are involved in the body‟s allergic response and are responsible for releasing histamine, a chemical that causes blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable.
T cells: These white blood cells help coordinate the immune response. They can either promote or suppress inflammation depending on the situation. T cells play an important role in the fight against viral infections.
B cells: These white blood cells are responsible for producing antibodies, which can help to neutralize invading pathogens and prevent them from causing further damage.
Eosinophils: These cells are involved in the body‟s response to parasitic infections and allergic reactions.
Basophils: These white blood cells play a role in the body‟s defense against parasitic infections and allergic reactions
ACUTE INFLAMMATION:-
It is of short duration and represents the early body reaction and is usually followed by repair.
It’s main features are:-
- Accumulation of fluid and plasma at the affected site.
- Intravascular activation of platelets.
- Polymorphonuclear neutrophils as inflammatory cells.
PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE INFLAMMATION
Acute inflammatory response by the host to any agent is a continuous process.It can be divided into following two events:-
| Vascular events |
| Cellular event |
VASCULAR EVENTS:-
Alternation in the microvascular (arterioles,capillaries and venules) is the earliest response to tissue injury.These alternations include:-
i) Haemodynamic changes
ii) Changes in vascular permeability
i) HAEMODYNAMIC CHANGES:-
The earliest features of inflammatory response result from changes in the vasular flow and calibre of small blood vessels in the injured tissue.The sequence of these changes is as under:-
- Transient vadoconstriction
- Vasodilation
- Local hydrostatic pressure
- Slowing or stasis
- Leucocytic margination
ii) ALTERED VASCULAR PERMEABILITY:-
In and around the inflamed tissue,there is accumulation of oedema fluid in the interstitial compartment which comes from blood plasma by its escape through the endothelial wall of peripheral vascular bed.
In the initial stage,the escape of fluid is due to Vasodilation and consequent elevation in hydrostatic pressure. This is transudate in nature.
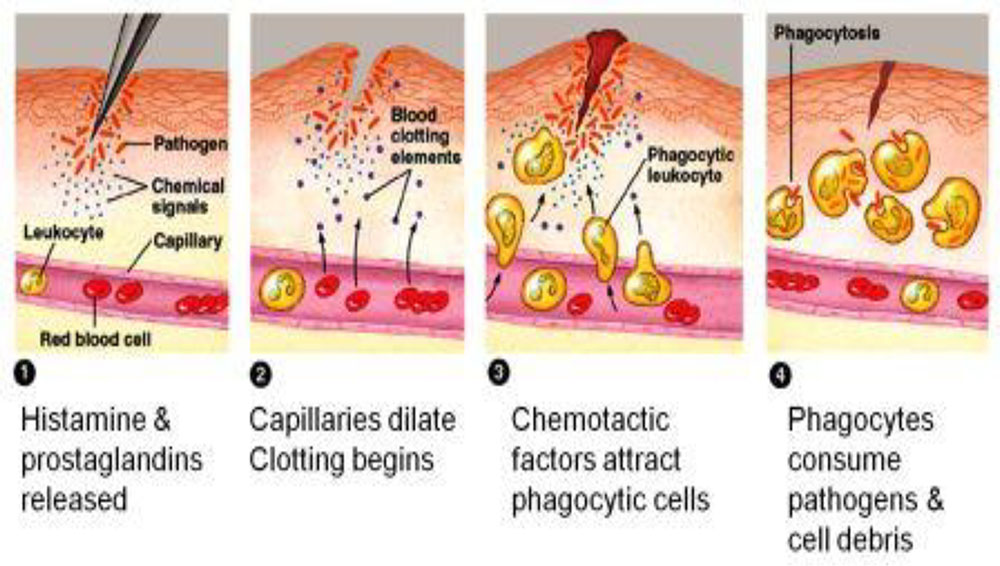
CELLULAR EVENTS:
The cellular phase of inflammation consists of two processes:-
i) Exudation of leucocytes
ii)Phagocytosis
i) EXUDATION OF LEUCOCYTES:-
The sequence of these leucocytic events can be divided into:-
- Margination
- Adhesion
- Emigration
- Chemotaxis
ii) PHAGOCYTOSIS:-
Phagocytosis is defined as the process of engulfment of solid particulate material by the cells (cell-eating).
The cells performing this function are called phagocytes.
There are 2 main types of phagocytic cells:-
- Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) which appear early in acute inflammatory response,sometimes called as “microphages”.
- Circulating monocytes and fixed tissue mononclear phagocytes called as “macrophages”.
Fate of acute inflammation
The acute inflammatory process can culminate in one of the following outcomes:
- Resolution: complete return to normal tissue following acute
inflammation. - Healing: Fibrosis takes place when the tissue destruction in acute inflammation is extensive so that there is no tissue regeneration. But
when tissue loss is superficial, it is restored by regeneration. - Ulcer: Loss of the mucosa and deeper tissues.
- Fistula: Anomalous patent connection between two organs; most commonly organs with a lumen.
- Suppuration: When the pyogenic bacteria causing acute inflammation result in severe tissue necrosis, the process progresses to suppuration. Subsequently, mixture of neutrophils, bacteria, fragments of necrotic tissue, cell debris and fibrin comprise pus which is contained in a cavity to form an abscess.
- Scar formation: Replacement of lost parenchyma with disorganized connective tissue (e.g., collagen).
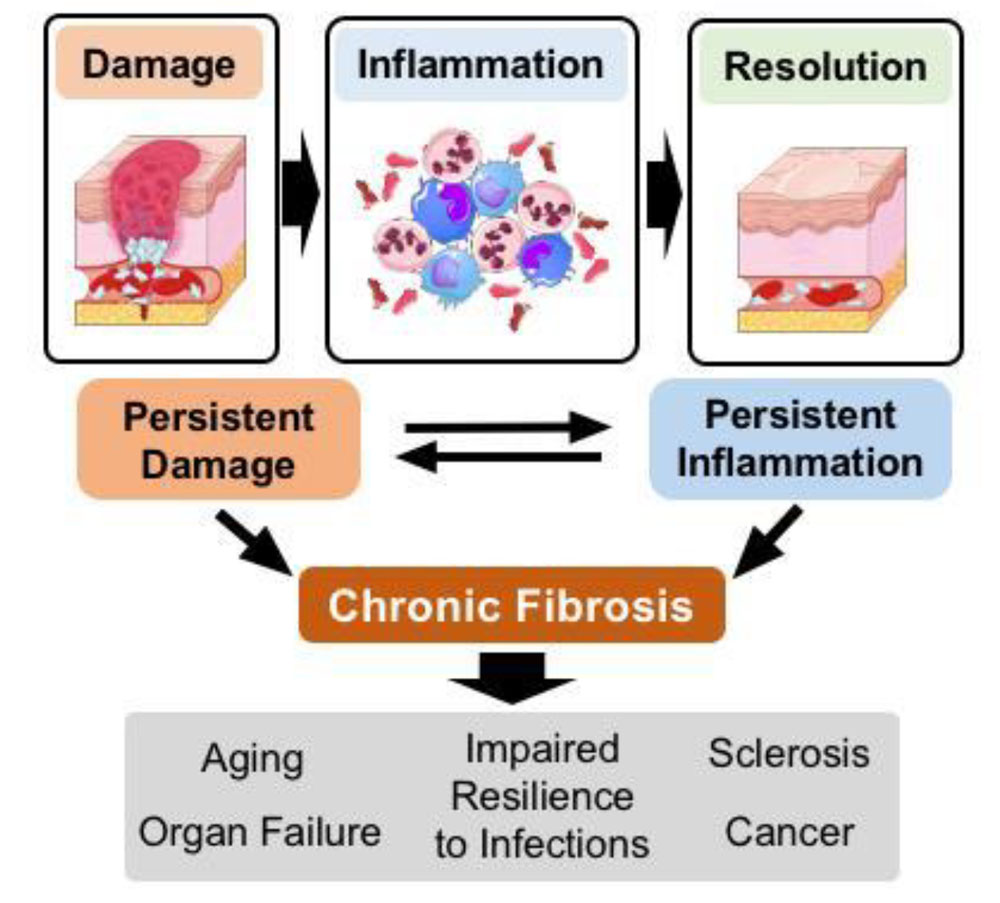
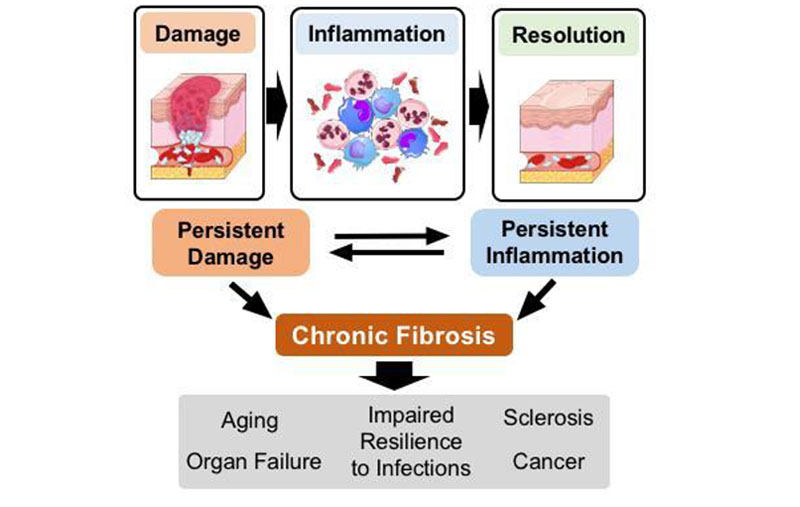
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION:-
It is of longer duration and occurs either after the causative agent of acute inflammation persists for a long time or the stimulus is such that it induces chronic inflammation from the beginning.
The characteristic features of chronic inflammation is presence of chronic inflammatory cells such as lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages.
Types of chronic inflammation
Based on histological features, chronic inflammations are classified as following 2 corresponding types –
- Chronic non-specific inflammation: It is characterised by non-specific inflammatory cell infiltration e.g. chronic osteomyelitis, lung abscess.
- Chronic granulomatous inflammation: It is characterised by formation of granulomas e.g. tuberculosis, leprosy, syphilis, actinomycosis, sarcoidosis etc. Actinomycosis Histology of lung Histology of lung with pulmonary tuberculosis
Cells involved in chronic inflammation is as mentioned above
Systemic effects of chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation is associated with following systemic features:
- Fever
- Anaemia
- Leucocytosis
- ESR (elevated in all cases of chronic inflammation}
- Amyloidosis (long-term, chronic suppurative inflammation may develop secondary systemic (AA) amyloidosis)


