- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

a) peri implant gingivitis
b) peri implantitis
c) peri- implant mucositis
d) Peri-implantosis
2.Periodontal disease in diabetic patient follows
a) Consistent pattern
b) Distant pattern
c) Circadian pattern
d) No consistent pattern
3. The distance between implant and adjustment tooth should be at least
a) 7 millimetre
b) 1.5 millimetre
c) 3.5 millimetre
d) 3.75 millimetre
4.Not an indication for tooth grinding
a) Wear facets
b) Tmj pain
c) Crepitus
d) Cemental wear
5. A non invasive way of evaluating implant stability by impact resistance
a) periotest
b) trans gingival probing
c) bone sounding
d) probing
6.hydroxyapatite coating of dental implants was introduced by
a) Deroot
b) Hahn and polich
c) Kay
d) Clemow
7.Most plausible factor for dental implant fracture
a) peri implantitis
b) Bending over loads
c) Non passive fit prosthesis
d) Manufacturing imperfections
8.First implant system developed by
a) Noble biocare branemark
b) Noble biocare steri oss
c) ITI – strauman
d) Astra
9.The minimum mesiodistal space required for the placement of two standard diameter implants between teeth is
a) 8mm
b) 20mm
c) 10 mm
d) 14 mm
10.Total arch length reduced due to Mesial migration of teeth
a) one centimetre
b) 3 centimetre
c) 0.5 centimetre
d) 0.15 centimetre
Answers with explanation
1. C.
inflammatory changes confined to the soft tissue surrounding an implant are diagnosed as peri-implant mucositis. Peri implant gingivitis is plaque- induced gingivitis that acquires in the gingival tissues surrounding a dental implant. Peri- implantitis is the destructive inflammatory process affecting the soft and heart issues surrounding dental implants resulting in loss of supporting bone.
2. D
Periodontal disease in diabetic patients follows no consistent or distinct pattern. severe gingival inflammation, deep pockets, rapid bone loss, frequent periodontal lapses often awkward in poorly controlled diabetic patients with poor oral hygiene.
3. B
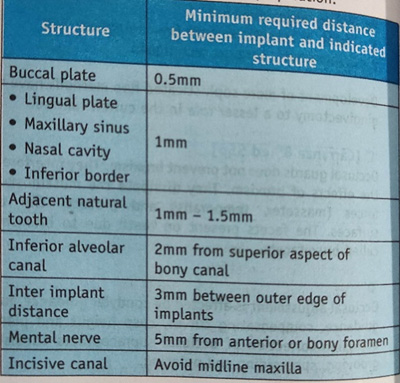
4. A
because occlusal adjustment is an irreversible intervention it should rarely be considered as a primary treatment.
5. A
Two techniques that have been used as non invasive ways of evaluating Implant stability are impact resistance( perio test and resonance frequency analysis). originally designed to evaluate tooth mobility quantitatively, the perio test is a non invasive, electronic device that provides an objective measurement of the reaction of the periodontium to a defined impact load applied to the crown.
6. A
hydroxyapatite coating by plasma spraying of dental implants was introduced by Degroot.
7. B
the most common implant related complications are biomechanical problems that occur after the implant is loaded. Causes of implant fracture – overload induced fracture( para functional habits & bending moment caused by occlusal loads),manufacturing defects,frame work induced fracture.
8. A
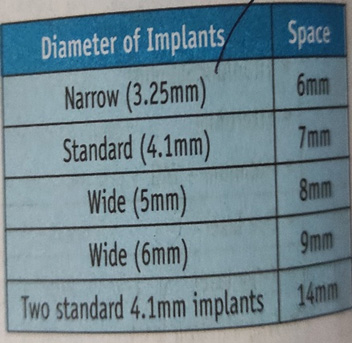
9. D
10.C
tooth movement does not end when active eruption is completed and the tooth is in functional occlusion. With time and wear, The proximal contact areas of the teeth are flattened And the tooth tends to move mesially.This is referred to as physiologic Mesial migration. by age 40 it results in a reduction of about 0.5 centimetre in length off the dental arch from the midline to the third molar.


