- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

DEFINITION
Hypoxia is a state in which oxygen is not available in sufficient amounts at the tissue level to maintain adequate homeostasis; this can result from inadequate oxygen delivery to the tissues either due to low blood supply or low oxygen content in the blood (hypoxemia).
- Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no oxygen in the blood.
- Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia.
ETIOLOGY
There are two major causes of hypoxia at the tissue level, low blood flow to the tissue, or low oxygen content in the blood (hypoxemia)
Reduced arterial PO2 it can be due to
| Reduced Oxygen Tension | Hypoventilation | VentilationPerfusion Mismatch (V/Q Mismatch | Right to Left Shunt | Impaired Diffusion of Oxygen |
1. Reduced Oxygen Tension
- As in cases of high altitude.
2. Hypoventilation
- Airway obstruction can be proximal as in laryngeal edema or foreign body inhalation, or distal as in bronchial asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Impaired respiratory drive as in cases of deep sedation or coma.
- Restricted movement of the chest wall as in obesity hypoventilation syndrome, circumferential burns, massive ascites, or ankylosing spondylitis.
- Neuromuscular diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or phrenic nerve injuries.
3. Ventilation-Perfusion Mismatch (V/Q Mismatch)
- Decreased V/Q Ratio (impaired ventilation or high perfusion) such as chronic bronchitis, obstructive airway disease, mucus plugs, pulmonary edema impair the ventilation and therefore decrease the ratio of ventilation to perfusion.
- Increased V/Q Ratio (impaired perfusion): such as in cases of pulmonary embolism or increased ventilation as in emphysema (large bullae in the lungs) the surface area available for gas exchange is decreased, which causes higher ventilation in comparison to perfusion leading to a high V/Q ratio.
4. Right to Left Shunt
- The blood crosses from the right to the left side of the heart without being oxygenated. Causes include:
- Anatomic Shunts: Blood bypasses the alveoli, e.g., intracardiac shunts (ASD, VSD, PDA), pulmonary arteriovenous malformations, fistulas, and hepato-pulmonary syndrome.
- Physiologic Shunting: Blood passes through non-ventilated alveoli, for example, pneumonia, atelectasis, and ARDS.
5. Impaired Diffusion of Oxygen
- Oxygen diffusion is impaired between the alveolus and the pulmonary capillaries. Causes are usually interstitial edema, interstitial inflammation, or fibrosis. Clinical examples include pulmonary edema and interstitial lung disease
TYPES OF HYPOXIA
- Hypoxic hypoxia
- Anaemic hypoxia
- Stagnant(ischaemic) hypoxia
- Histotoxic hypoxia
HYPOXIC HYPOXIA OR GENERALIZED HYPOXIA
This refers to hypoxia resulting from an inadequate saturation of blood oxygen due to a reduced supply of oxygen in the air, decreased lung ventilation or respiratory disease.
Some of the causes of hypoxic hypoxia include:
- A high altitude, where the concentration of atmospheric oxygen is decreased.
- Deep sea diving if there is an inadequate supply of oxygen in the breathing gas or if a rusting cylinder has extracted oxygen, for example.
- The inhalation of nitrous oxide or laughing gas on a repeated basis for recreational purposes can decrease oxygen availability while increasing carbon dioxide levels.
- Sleep apnea or obstructive sleep apnea can interrupt airflow to the lungs.
- Certain diseases such as bronchial asthma, respiratory arrest, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease causing inadequate ventilation of the lungs.
Characteristics of hypoxic hypoxia
- Low arterial Po2
- Low % saturation of Hb
- Low content of o2
- Low Arterio-venous Po2 difference
HISTOTOXIC HYPOXIA
- This refers to when oxygen is delivered to the tissues but they fail to utilize it effectively because the cells are damaged and cannot extract and absorb oxygen from circulating blood.
- This may occur with the overuse of alcohol or drugs and is also seen in cyanide poisoning.
- Cyanide disrupts cytochrome oxidase, an important enzyme in cell respiration.
ANEMIC HYPOXIA
In anemic hypoxia arterial pO2 is normal but the amount of haemoglobin available to carry oxygen is reduced.
Causes :
- Anemia
- Haemorrhage
- Conversion of haemoglobin to some abnormal form
Characterized by:
- Normal arterial po2
- Arterial O2 content moderately reduced
- A-V pO2 difference is normal
STAGNANT (ISCHEMIC) HYPOXIA
Blood flow to the tissue is so low that adequate oxygen is not delivered to them despite normal arterial pO2 and haemoglobin concentration
Causes :
- Circulatory failure
- Hemorrhage via baroreceptors leading to reflex vasoconstriction
Characterized by:
- Normal arterial po2
- Normal arterial O2 content
- Normal arterial % O2 saturation of hemoglobin
- A-V difference more than normal
SYMPTOMS
- Hyperventilation is seen in all types of hypoxia except anemic hypoxia
- In all types of hypoxia the first symptoms are like that of alcohol overdose(drowsiness, depression/excitement, emotional outburst)
- If oxygen saturation of haemoglobin falls below 60% there unconsciousness within 20 seconds, causing death in 4-5 minutes.
- Severe hypoxia( except anaemic) causes increase in heart rate and systemic blood pressure.
Although they can vary from person to person, the most common hypoxia symptoms are:
- Changes in the color of your skin, ranging from blue to cherry red
- Confusion
- Cough
- Fast heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Slow heart rate
- Sweating
- Wheezing
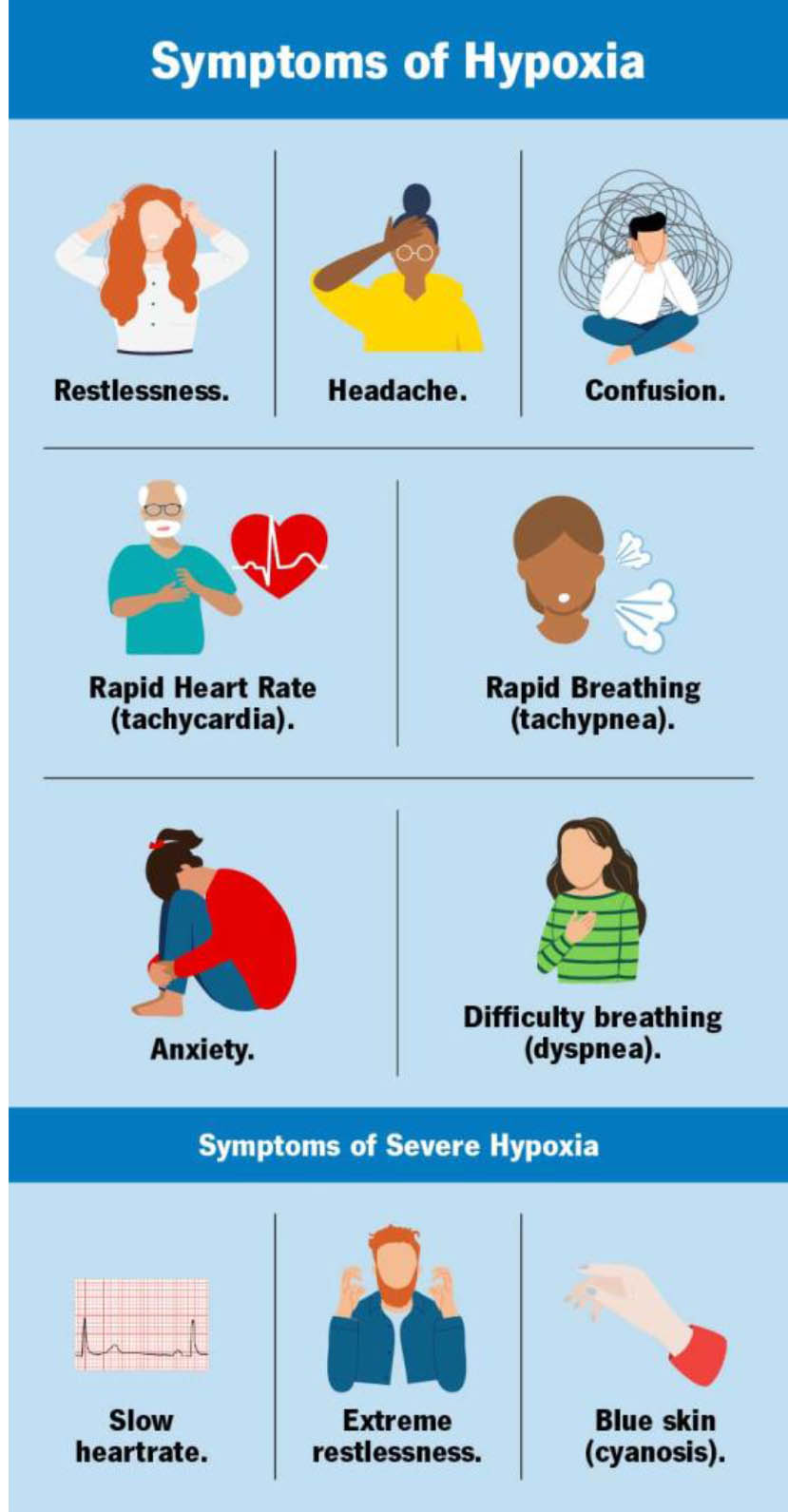
EFFECT OF HYPOXIA
Hypoxia is low levels of oxygen in your body tissues.
It causes symptoms like confusion, restlessness, difficulty breathing, rapid heart rate, and bluish skin. Many chronic heart and lung conditions can put you at risk for hypoxia. Hypoxia can be life-threatening
TREATMENT
Treatment of the underlying cause- depending upon the type of hypoxia
- Oxygen therapy
- Inhalation of 100% pure oxygen
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
COMPLICATIONS
- Local tissue death and gangrene is a relatively common complication of ischaemic hypoxia. (diabetes, etc.)
- Brain damage – cortical blindness is a known but uncommon complication of acute hypoxic damage to the cerebral cortex.
- Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is a risk factor for cerebrovascular disease and cognitive dysfunction.




