- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

In addition to the pharynx, the larynx and hyoid bone are also one of the important factors during swallowing to ensure that food boluses are smoothly carried to the oesophagus without aspiration.
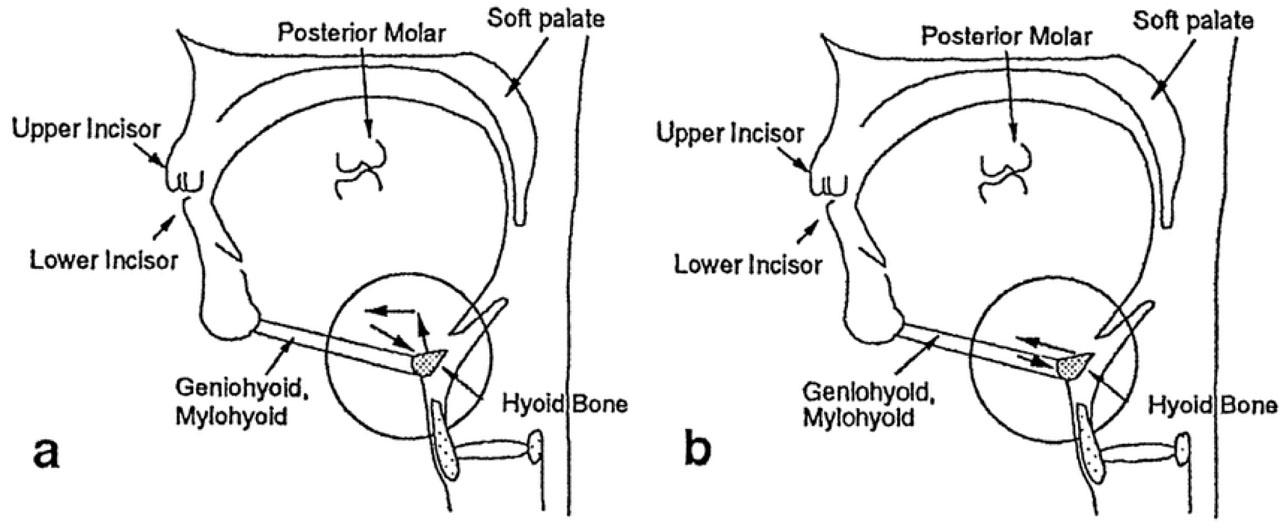
Movement of hyoid bone, especially during elevation during deglutition, is a common cause of aspiration in the elderly.
Probability of dysphagia increases with age as the hyoid bone lowers in position.
Upper oesophageal sphincter opening results due to anterior displacement of the hyoid bone whereas laryngeal closure results in superior displacement.
Anterior displacement of the hyoid bone is primarily due to the movement of the geniohyoid, and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle works as auxiliary.
Superior displacement of the hyoid bone involves mylohyoid as the primary muscle and the posterior belly of the digastric muscle works as the auxiliary muscle.




