- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

a) HIV
b) hepatitis C
c) Hepatitis B
d) Hepatitis E
2.The small known articulate protein leading to enhanced replication of HBV as well as HIV is
a) hbcAg
b) HBsAg
c) Hbe Ag
d) Hbx Ag
3.True about immune response of hepatitis B is
a) Antibody of HBs Ag is associated with resistance to infection
b) Antibody to HBC is not protective
c) Highest titres of anti HBC are found in persistent carriers of HBs Ag
d) CMI disappears soon after recover
4.Enterically transmitted NANB hepatitis B.
a) Hepatitis C
b) Hepatitis D
c) Hepatitis E
d) Hepatitis F
5.Which of the following represents the serologic evidence of recent Hepatitis B virus infection during “window” period?
a) HBs Ag
b) IgM 1anti – HBc
c) Anti HBs
d) None of the above
6. Hepatitis C virus belongs to which one of th following virus groups?
a) Picorna viruses
b) Herpes viruses
c) Hepadna viruses
d) Flavi viruses
7. Which of the following correctly indicates the infectivity of hepatitis virus in human?
a) HBCAg
b) HBeAg
c) Anti-HBC
d) Anti – HBS
8. Patients with organ transplants are most frequently infected with:
a) Hepatitis A
b) Hepatitis B
c) CMV
d) EBV
9.Hepatitis A virus is best diagnosed by:
a) IgM antibodies in serum
b) Isolation from stool
c) Culture from blood
d) Isolation from bile
10. young pregnant woman presents with fulminant Hepatic failure. The most likely aetiological agent is
a) Hepatitis B virus
b) Hepatitis C virus
c) Hepatitis F virus
d) Hepatitis A virus
Answer with explanation
1.A
2.D
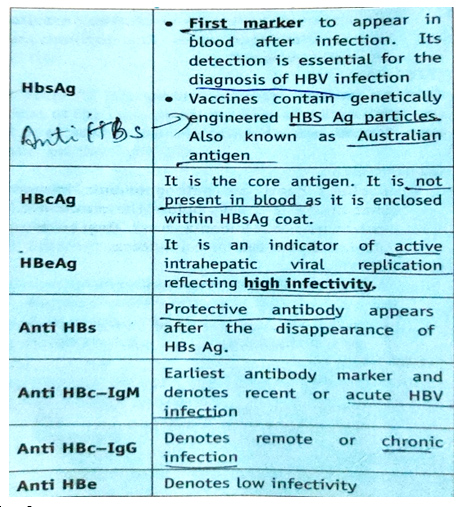
The genome of hepatitis B virus has a compact structure with four overlapping genes i.e., S, C, P and X. The S gene codes for the Surface antigen. The C gene codes for Core antigen. The P gene is the largest and coded for DNA Polymerase enzyme. The ‘X’ gene codes for a small non particulate protein (HBxAg) , which has transactivating effects on both viral and some cellular genes. This leads to enhanced replication of HBV, as well as of some other viruses, such as HIV virus. HBxAg and its antibody are present in patients with severe chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
3.A
4.C
5.B
Anti-HBC is the earliest antibody marker to be seen in blood. As anti-HBC remains lifelong, it serves as a useful indicator of prior infection with HBV, even after all the other viral markers, becomes undetectable. Initially, anti-HBC is predominantly IgM (indicates recent infection), but after 6 months, it is mainly IgG (indicates remote infection).
6. D.
7.B
8.C
Cytomegalovirus infection can occur in transplant recipients, cancer patients on chemotherapy and HIV infected patients.
9.A
10. C
Type E hepatitis or non-A non-B hepatitis is responsible for the majority of epidemic and sporadic hepatitis in adults. A unique feature is the clinical severity and high case fatality rate of 20 – 40 % in pregnant women, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy.




