- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
| Three phases of hepatitis | |
| Pre-Icteric: (also called prodromal) | Maximal infectivity period. Circulating immune complexes may cause fatigue, anorexia, depression, headache, weight loss, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, changes in taste and smell, and fever. Right upper quadrant tenderness may be noted |
| Icteric: (clinical stage) | Characterized by jaundice. There is a defective uptake, conjugation and/or distribution of bile. Bilirubin is diffusing into the tissues. Urine is darker. Stools are clay colored.
|
| Post-Icteric: (recovery stage) |
|
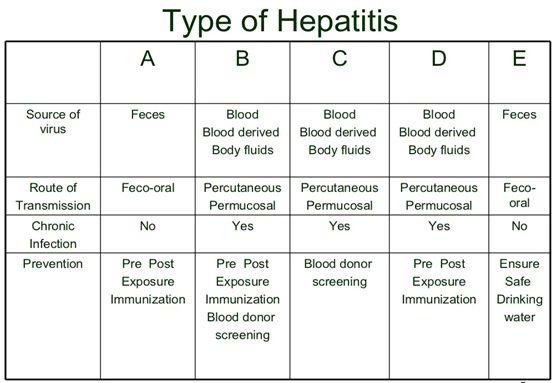
Types of hepatitis virus group consist of A, B, C, D, E, F & G.
| Type – A | Infective or Infectious hepatitis |
| Type – B | Serum hepatitis / Transfusion Hepatitis |
| Non-A & Non-B hepatitis | Causes by uncharacterized viruses other than type A or Type B Eg: C,D,E,F,G viruses |
| Type-C | Transfusion associated hepatitis |
| Type-D or Delta virus | Depends on type B virus |
| Type-E | Transmitted by feco-oral route, and prevalent in developing nations only. |
| Type-F | Variant of hepatitis B virus and is believed to cause transfusion associated hepatitis. |
Hepatitis A
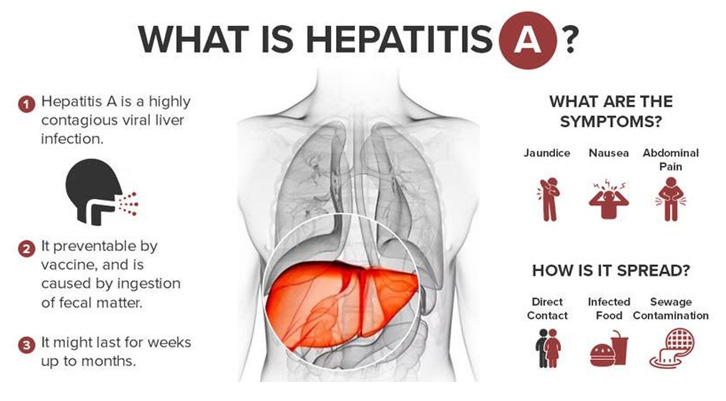
Transmission: fecal/ oral route (infected human waste)
- Contaminated food& water (especially shellfish)
- May be transmitted sexually
- May be transmitted by someone with a sub clinical infection
- Can be destroyed by bleach and hot temps > 195 F.
Incubation period: (time from infection to the time when symptoms appear)
- Short 2-6 weeks (15-50 days)
Vaccine: yes “Havrix” and Vaqta- inactivtaes Hep A virus
MANAGEMENT
- There are no drug therapies for the treatment of acute hepatitis A.
- Rest according to patient’s level of fatigue.
- Hospital ization.
- Small, frequent feedings of a high calorie, low fat diet, proteins are restricted.
- Vit K injection if PT is prolonged.
- I.V. fluid and electrolyte replacement.
- Antiemetic drugs.
Hepatitis B

- Transmission: Infected blood, and body secretions
- sweat, tears, semen, vaginal secretions
- Persons at high risk include IV drug users, and fetus of infected mothers.
- Health care workers are at high risk! Has a very high titer, which means it’s highly infectious!
- Incubation period: 25-180 days
- Vaccine: yes “Heptavax” Given in 3 doses over 6 months
(The second follows the first after one month, the third is given 6 months after the initial dose.)
Given to babies at birth. This greatly reduces the risk of babies become carriers of the disease.
Immune Serum Globulin: Hepatitis B immune globulin
- Provides passive immunity for those who were exposed to the HBV
- The cost is high. Given only when there was known exposure.
Seriousness: Up to 10% develop carrier state, or chronic hepatitis. –hepatocellular CA in US.
Most cases do clear the virus and then have immunity.
Dx: anti HBc Igm or HBsA
MANAGEMENT
- Treatment of acute hepatitis B is indicated only in patients with severe hepatitis and fiver failure. Rest, vitamin supplements. Avoid alcohol.
- Treatment ot aiitis B :
- Nucleoside and Nucleotide analog such as Tenofovir, adenoiovir, lamivudine.
- Interferon: Standard interferon( Intron A), Pegylated interferon ( Peglntron,)
- Liver transplant.
Hepatitis C
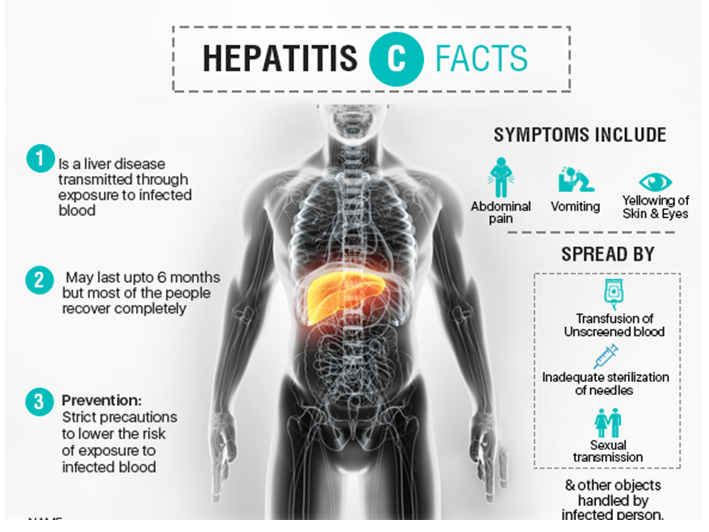
Transmission: blood, body fluids
- Present in 1% of blood donor population.
- Due to screening of blood, risk due to transfusion is now less than 1%.
- Incubation period: average 7 weeks…
- Vaccine: none
- Immune serum globulin: not used
- Seriousness: Increases the incidence of primary liver CA
- Most do not clear the virus and a chronic condition develops.
- DX: ELISA – initial screening
- recombinant immunoblot assay= RIBA (more confirmatory) or anti-HCV
MANAGEMENT
In a patient with acute hepatitis C , treatment with Pegylated interferon within the 12-24 weeks of infection reduce the development of chronic hepatitis C.
Chronic HCV; Pegylated interferon, Ribavirin Rebetol, Protease inhibitors such as incivek and Boceprevir.
Hepatitis D
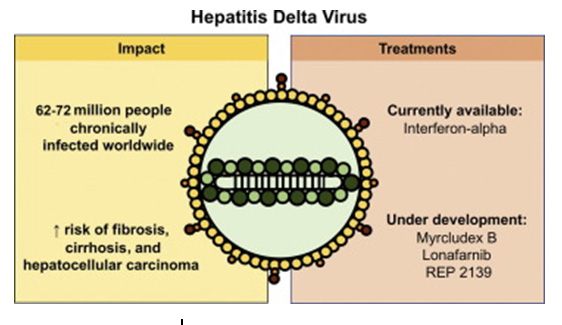
- Transmission: Parenteral route
- Same as Hepatitis B. Must be positive for the HbsA in order to contract Hepatitis D. The HDV is an incomplete strand of RNA that can only affect you if you are a carrier of HBV or have the surface antigen.
- Incubation period: 14-56 days, but only if HBV present.
- Vaccine: yes, same as Hepatitis B
- Immune Serum Globulin: Hepatitis B immune globulin
- Seriousness: Higher incidence of chronicity and cirrhosis than with Hepatitis B alone
- Treatment : Interferon
Hepatitis E
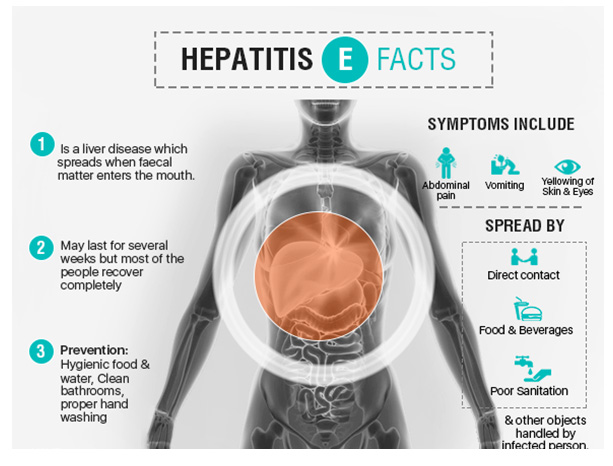
Transmission: fecal/ oral route
- Only found in US when individuals have visited underdeveloped countries. (Asia, Africa, India, Central America)
- Incubation period: 15-64 days
- Vaccine: none
- Immune serum globulin: not effective
- Seriousness: No evidence of chronic or carrier state… Self-limiting in its course.
TREATMENT
• There is no specific treatment capable of altering the course of acute hepatitis E.
• As the disease is usually self-limiting, hospitalization is generally not required. Hospitalization is required for people with Fulminant hepatitis.


