- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

a) 5
b) 4
c) 2
d) 3
Answer: D
Explanation: The blood corpuscles are of 3 types. They are colored corpuscles- erythrocytes, Colorless corpuscles – Leucocytes and blood platelets.
2. Which leucocytes release heparin and histamine in blood?
a) Neutrophil
b) Basophil
c) Eosinophil
d) Monocytes
Answer: B
Explanation: Basophil contains heparin which is an anticoagulant. It is a type of white blood cell.
3. Vitamin essential for blood clotting is _____
a) Vitamin K
b) Vitamin A
c) Vitamin B
d) Vitamin C
Answer: A
Explanation: Vitamin K is used by the body to help blood clot. Warfarin is used to slow blood clotting. By helping the blood clot vitamin k might decrease the effectiveness of warfarin.
4. Absence of which clotting factor leads to Hemophilia-A?
a) Factor VII
b) Factor VIII
c) Factor IX
d) Factor X
Answer: B
Explanation: Hemophilia-A is also called factor VIII deficiency or classic hemophilia. It is a genetic disorder caused by missing or defective factor VIII a clotting protein.
5. Red cell count is carried out by ___
a) Electrogram
b) Sphygmomanometer
c) Haemoglobinometer
d) Haemocytometer
Answer: D
Explanation: Haemocytometer is a device designed and used for counting blood cells. It was invented by Louis Charles Malassez.
6. Which anemia is classified as not being able to use iron properly to synthesize hemoglobin because of a inherited cause.
A. Iron deficiency anemia
B. hypochromic anemia
C. aplastic anemia
D.sickle cell anemia
Answer: B
7. Which one of the following statements is true?
(a) Normal adult blood contains two haemoglobins
(b) Erythropoietin production is 50% renal and 50% hepatic
(c) A reticulocyte contains RNA as well as DNA
(d) The red cell membrane has a bipolar lipid layer
Answer: D
Normal blood contains three haemoglobins, normal adult Hb A (>95%), fetal haemoglobin, Hb F and Hb A2. Erythropoietin is >90% produced by the kidneys. A reticulocyte contains RNA but not DNA. Red cells survive for about 120 days in the circulation.
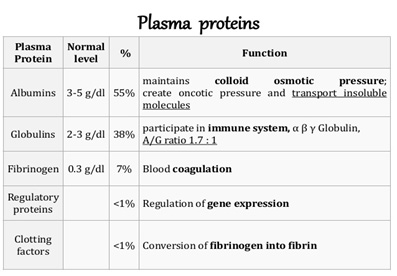
8. Which of the following is a function of plasma protein;
A. Oxygen transport
B. Blood buffers
C. Exerts osmotic pressure
D. All of the above
Answer D
9. In which stage of erythroblast, haemoglobin appears first;
A. Late erythroblast or early normoblast
B. Late normoblast
C. Early erythroblast
D. Early normoblast
Answer: A
The blood cells begin their lives in the bone marrow from a single type of cell called the pleuri potential haematopoetic stem cell. These cells are differentiated in to a committed stem cell and produce colonies of specific types of blood cells.
Stages of development of RBC;
BFU. E -> proerythroblast (E1) -> Early normoblast -> intermediate normoblast -> late normoblast -> reticulocyte-> matured erythrocyte
10. Which of the following is not present in normal blood;
A. Fibrinogen
B. Thrombin
C. Prothrombin
D. Albumin
Answer: B




