- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
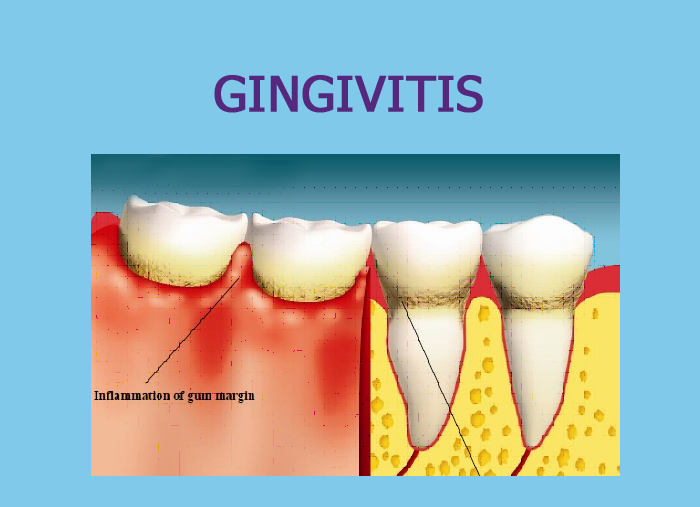
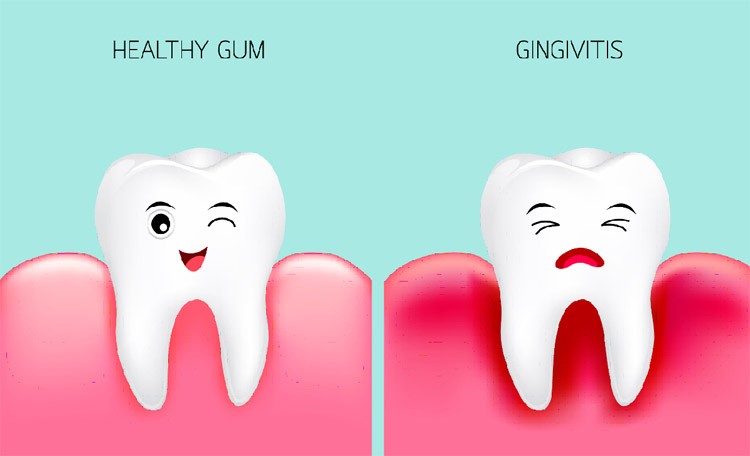
- Gingivitis is the most common form of gingival disease.
- Only some cases of gingivitis progress to periodontitis
- About 90% of population is affected by gingivitis by the time they cross their puberty.
- Local factors are the common aethiological agents of periodontal diseases
- Most common cause of gingivitis is bacteria laden local plaque.
- Systemic factors cause periodontitis in the presence of local factors by exaggerating the tissue response to local factors.
Gingivitis is most frequently caused by plaque.
- Gingivitis is at peak level during puberty (12-15 years)
- Local conditions such as material alba and poor oral hygiene favour the accumulation of plaque
- Calculus formation is less common in children
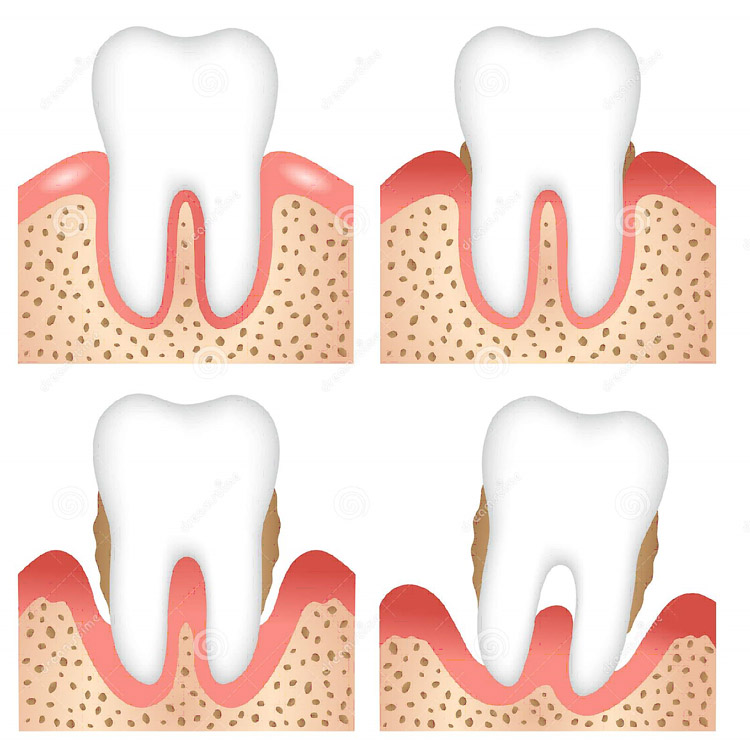
- Gingivitis is inflammation of soft tissues only and it does not involve the supporting tissues, so no radiographic changes are seen in patients with gingivitis.
- Role of immunoglobulins:
The proportion of lymphocytes to plasma cells varies with the level of inflammation present in the tissues. In early stages, T lymphocytes dominate whereas in established cases of gingivitis plasma cells /B cells dominate. The immunoglobulins are produced by B cells/ plasma cells. The initial reaction is cell mediated immunity in early gingivitis followed by humoral immunity following antigenic insult. The first immunoglobulin produced is secretory, that is IgA which later shifts to predominantly humoral immunity with the production of IgG. Activation of humoral immunity leads to an accumulation of plasma cells and the production of immunoglobulins . Each gingival plasma cells make a single class of antibody (ie, IgG, IgA or IgM) specific for a single antigen.
| STAGES OF GINGIVITIS | ||
| STAGE I | 2-4 DAYS |
|
| STAGE II OR EARLY LESION | 4-7 DAYS |
|
| STAGE III OR ESTABLISHED LESION | 14-21 DAYS |
|
| STAGE IV OR ADVANCED LESION |
|
|