- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

A. Causes increase in stippling of attached gingiva
B. Results from inflammatory oedema
C. Associated with gingival recession
D. Results from tetracycline therapy
Ans. B
2. Hyperplastic gingiva is found in all of the following conditions except
A. Chronic inflammation
B. Nifedipine therapy
C. Hereditary fibromatosis
D. Faulty tooth brushing
Ans. D
3. The conditioned gingival enlargement
A. Requires presence of local irritants
B. Exacerbates existing inflammation
C. Pregnancy and puberty are the examples
D. All of the above
Ans. D

4. Conditional gingival enlargement is usually not associated with
A. Hormonal
B. Leukaemic
C. Granuloma pyogenicum
D. Drug induced
Ans. D
● Hormonal, Leukaemic and pregnancy induced all are systemic changes which might produce the gingival growth.
● But drug induced is a different category according to the classification
5. Gingival manifestation is seen maximum with
A. AML
B. CLL
C. CML
D. ALL
Ans. A
Gum hypertrophy due to leukemic infiltration of the gingiva is a frequent finding in
M4: Acute myelomonocytic leukaemia(Naegeli type)
M5: Acute monocytic leukaemia(Schilling type)
6. The gingival enlargements in leukaemia mainly result from
A. An inflammatory reaction to plaque
B. Leukaemic cellular infiltration of gingiva
C. Hormonal disturbances

D. Developmental in origin
Ans. B
Leukaemic enlargement is generally bluish red and has a shiny surface
7. Gingivitis in leukaemic patient resemble
A. Pyogenic granuloma
B. Herpetic gingivostomatitis
C. Hairy cell leukoplakia
D. ANUG
Ans. D
ANUG in Leukaemia is not produced by leukemia per se but may be the result of a reduction in host defense mechanism seen in leukaemia. However, ANUG may be superimposed on gingival tissue alterations caused by leukaemia. The granulocytopenia resulting from the replacement of bone marrow by leukaemic cells reduces the tissue resistance to oportunistic micro oraganisms and leads to ulcerations and infections.
Discrete, punched out ulcers penetrating deeply into the submucosa and covered by a firmly adherend white slough can be found in the oral mucosa.
8. Drug associated with gingival changes are
A. Phenytoin, Cyclosporine and Nifedipine
B. Nifedipine, ibuprofen and lignocaine
C. Cyclosporine, chlorine and iodine
D. Phentoin, hydrogen, hydrogen peroxide and paracetamol
Ans. A
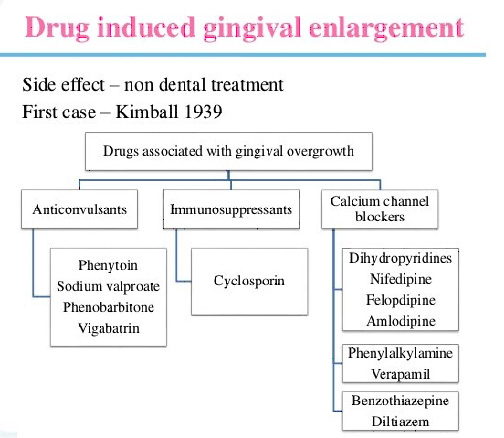
9. Drug induced hyperplasia of gingiva is mainly seen in
A. Marginal gingiva
B. Attached gingiva
C. Palatal gingiva
D. Interdental papilla
Ans. D
10. Cyclosporine enlargement of gingiva can be classified as
A. Non inflammatory
B. Inflammatory
C. Developmental
D. Malignant
Ans. A




