- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. Which of the following lymph nodes are usually not palpable
a. Axilla
b. Neck
c. Groin
d. Abdomen
ANSWER d
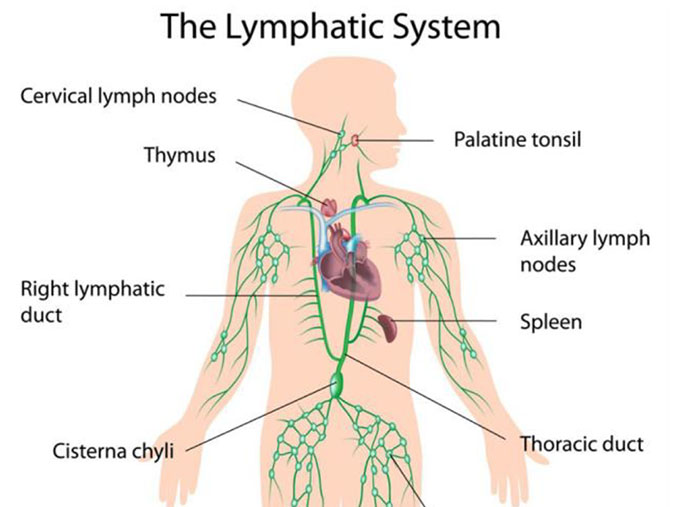
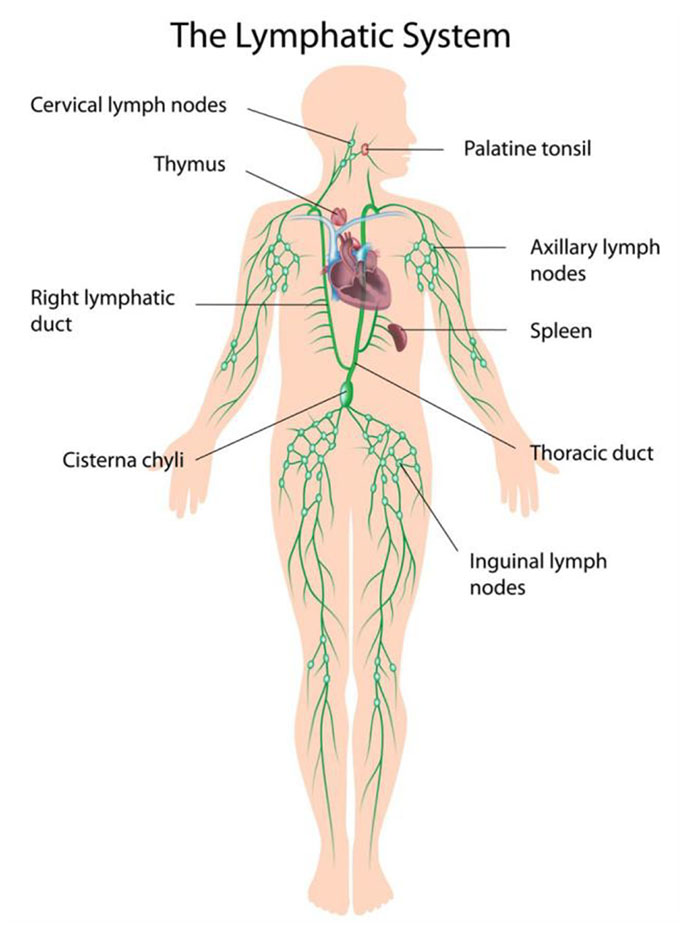
Lymph nodes exist throughout your body. They normally reside where two or more major blood vessels come together (converge) on your body including:
- Neck.
- Armpit (axillary).
- Chest.
- Abdomen.
- Groin.
- Behind your ear
Lymph Node Exam Technique
- Always evaluate for symmetry: clinically significant nodes classically asymmetric.
- Identify salivary glands by location as non-lymph nodes.
- Identify carotid artery/bulb by pulsation as non-lymph nodes.
- Supraclavicular fossa most significant area: often indicates a process deep in body.
- Left supraclavicular node (Virchow’s node) classical sign of abdominal process.
- Right superclavicular node classic sign of intrathoracic process.
- Trim fingernails!
- Infraclavicular fossa nodes: classically breast cancer or malignant lymphoma.
- Epitrochlear lymph nodes: best felt when moving fingers up and down.
- Most lymph nodes lie too deep to be accessible via physical examination.
- The superficial nodes are most efficiently assessed during regional examinations of the head and neck, breasts and axillae, upper extremities, lower extremities, and/or external genitalia
In the above give option Abdomen lymph nodes are not palpable
2. Destruction of the vertebral bone along with the intervertebral disc is a characteristic of
a. Metastasis
b. Tuberculosis
c. Multiple myeloma
d. Lymphoma
ANSWER b
The characteristic clinical features of spinal tuberculosis
- Include local pain,
- Local tenderness,
- Stiffness and spasm of the muscles,
- A cold abscess, gibbus, and a prominent spinal deformity.
- The cold abscess slowly develops when tuberculous infection extends to adjacent ligaments and soft tissues.
- Spinal deformity is a hallmark feature of spinal tuberculosis.
- Type of spinal deformity depends on the location of the tuberculous vertebral lesion.
- Kyphosis, the most common spinal deformity, occurs with lesions involving thoracic vertebrae. The severity of the kyphosis depends on the number of vertebrae involved
3. A 70year old patient refused administration of influenza vaccine 1 week later she pneumonia she died due to pneumonia , organisms of pneumonia in such cases is
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Cytomegalo virus
c. Leigonella
d. Measles virus
ANSWER a
4. In a pregnant Women which of the following vaccines is not indicated
a. MMR
b. Hepatitis B
c. DPT
d. Rabies
ANSWER a
Theoretically the live attenuated virus in a vaccine could cross the placenta and result in viral infection of the fetus. Owing to this concern, most live attenuated vaccines, including the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) and varicella vaccines, are contraindicated during pregnancy.
5. Which of the following liver function test is useful in diagnosis of dubin johnsons syndrome
a. Serum transaminase
b. Gamma glutaryl transferase
c. Bromosulphalein (BSP)
d. Hippurate test
ANSWER a
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome is a rare genetic condition that affects your liver.
- A genetic mutation causes a buildup of bilirubin in your body.
- Bilirubin is a yellow substance produced when red blood cells reach the end of their lifespan.
- Bilirubin should release into your bile, a substance to help move waste out of your liver and digestive system. Instead, bilirubin collects in your liver and bloodstream and causes symptoms of jaundice, where your skin and the whites of your eyes appear yellow.
- A mutation of the ABCC2 gene causes Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- The ABCC2 gene is responsible for making a protein that removes waste from cells, specifically, it removes bilirubin (a yellow substance made up of the remains of red blood cells at the end of a cell’s lifecycle) from cells in your liver and moves it as bile (digestive fluid).




