- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

1. Enzymes found in CSF: (AIIMS Nov 2012)
- GGT+ALP
- ALP+CK-MB
- CK+LDH
- Deaminase and Peroxidase
ANSWER c
The following enzymes are present in the CSF:
Aspartate transaminase (AST) : 5- 12 units/ml. Its value increases in abscess, cerebral hemorrhage and infarction and in primary or metastatic malignant disease. It may increase in some patients with multiple sclerosis. |
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): normal value is 5- 40IU/l. Its value increases in abscess, cerebral hemorrhage and infarction and in metastatic malignant disease. Increase in LDH4 isoenzyme of CSF is seen in tuberculous meningitis. |
Creatine kinase (CK): CK-BB is present in the brain. Its value increases in associated with meningitis, cerebral hemorrhage and infarction. >30 units/ml is suggestive of tubercular meningitis and <30 units/ml is suggestive of pyogenic meningitis. |
In MI, lDH1 increases but in heart failure, LDH 5 increases because right sided heart failure causing hepatic congestion and release of LDH5 from them.
2. A 17 year old female presents with a history of fever and headache and now develops altered sensorium. CT scan shows basal exudates with meningeal enhancement. The CSF is most likely to show (AIIMS Nov 2011)
- Lymphocytic pleocytosis, low sugar, low protein
- Polymorphonuclear pleocytosis, normal sugar, high protein
- Lymphocytic pleocytosis, low sugar, high protein
- Lymphocytic pleocytosis, normal sugar, high protein
ANSWER c
CT scan shows basal exudates with meningeal enhancement is highly suggestive of tuberculous meningitis.
Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is caused by the seeding of the meninges with the bacilli of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) and is characterized by inflammation of the membranes (meninges) around the brain or spinal cord.
“The combination of unrelenting headache, stiff neck, fatigue, night sweats, and fever with a CSF lymphocytic pleocytosis and a mildly decreased glucose concentration is highly suggestive of tuberculous meningitis.”
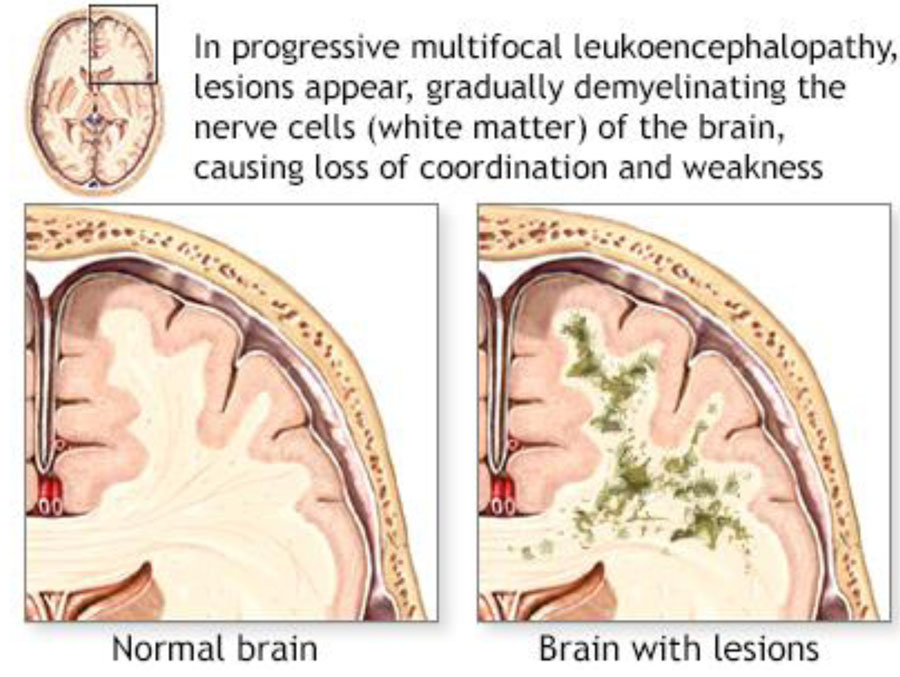
3. Inclusion body in oligodendroglia is a feature of which of the following? (AIIMS Nov 2010)
- Progressive Multifocal Leucoencephalopathy
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Polio
- CJD
ANSWER a
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that results from infection of oligodendrocytes by the JC polyomavirus.
- It occurs almost exclusively in immunocompromised individuals as in HIV due to reactivation of the virus.
- Microscopic examination shows lesions in the white matter which is an area of demyelination, in the center of which are scattered lipid-laden macrophages and a reduced number of axons.
- At the edge of the lesion are greatly enlarged oligodendrocyte nuclei whose chromatin is replaced by glassy amphophilic viral inclusion.
- In PML, the virus also infects astrocytes, leading to bizarre giant forms with irregular, hyperchromatic, sometimes multiple nuclei that can be mistaken for tumor.
4. Which of the following is not a Prion disease?
- Creutzfeldt- Jakob disease
- Fatal familial insomnia
- Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome
- Parkinson’s disease
ANSWER d
Prion diseases occur when normal prion protein, found on the surface of many cells, becomes abnormal and clump in the brain, causing brain damage. This abnormal accumulation of protein in the brain can cause memory impairment, personality changes, and difficulties with movement.
Prion’s disease of humans include:
- Iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Fatal Familial Insomnia
- Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome
- Sporadic Fatal Insomnia
- Kuru
Parkinson's disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. As the disease progresses, people may have difficulty walking and talk.
How Parkinson's disease is caused?
Parkinson's disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in the part of the brain called the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in this part of the brain are responsible for producing a chemical called dopamine.
5. All of the following diseases show abnormal folding of proteins except: (AIIMS Nov 2008)
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Prion disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Amyloidosis
ANSWER c
Disorders caused by misfolding of proteins are :
- Amyloidosis
- Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases
- Transmissible prion diseases like CJD
- Some genetic diseases caused by mutations that lead to misfolding of protein and loss of function, such as certain of the cystic fibrosis mutations.
Prions are infectious proteins that cause degeneration of the central nervous system (CNS).
Prion diseases are disorders of protein conformation, the most common of which in humans is called Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
CJD typically presents with dementia and myoclonus, is relentlessly progressive, and generally causes death within a year of onset.




