- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

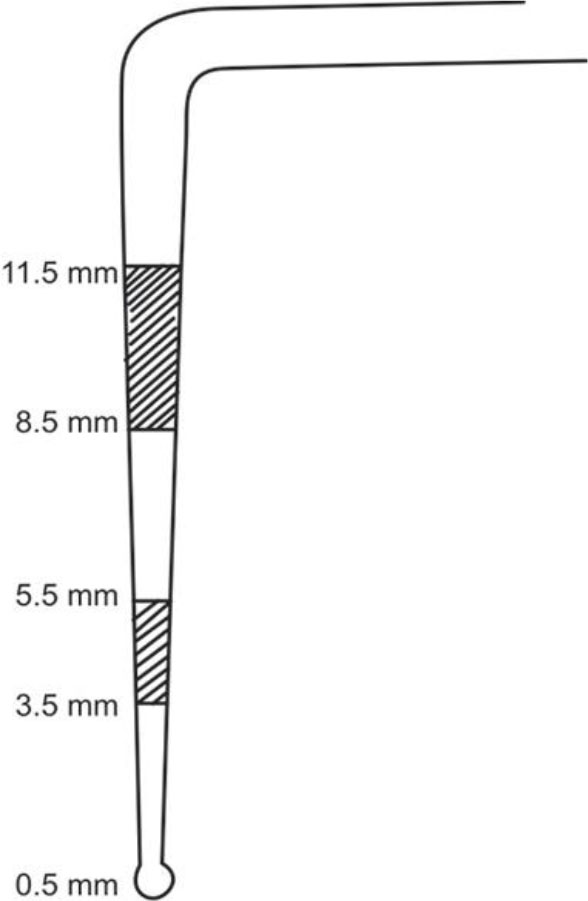
1. The following figure shows

a) WHO probe, dark band from 3.5 -5.5 and 8-11.5
b) CPITN probe, dark band from 3-5.5 and 8-11.5
c) Williams probe , dark band from 3.5-5.5 and 8.5-11.5
d) CPITN probe, dark band from 3.5-5.5 and 8.5-11.5
ANSWER d
CPITN assesses the presence or absence of gingival bleeding on probing, supra or subgingival calculus and periodontal pockets by using a 0.5 mm ball tip WHO probe.
2. Health education involves all, except?
a) Makes people think for themselves
b) Develops reflexive behavior
c) Appeals to reasoning
d) Trains primitive desires
ANSWER c
3. Which is true for Type B Autoclave?
a) Has vaccum cycle for drying
b) Has gravity displacement for drying
c) Has Unsaturated chemical vapour for sterilization
d) Use dry heat as a sterilization source
ANSWER a
- A Class B Sterilizer is a steam sterilizer that uses a vacuum pump to remove air/steam mixtures from the chamber prior to sterilization cycle beginning .
- This process can remove 99% of the air inside of the chamber before the temperature and pressure increases to it’s necessary parameters.
- This dynamic air removal provides the necessary conditions to sterilize any load type, including porous or hollow materials, products in pouches, textiles and hollow items like wands, turbines, handpieces and tips
- According to the Public Health of Ontario Dynamic Air Removal Sterilizers (Class B) are the preferred method of sterilization.
HOW DOES Class B Sterilizer Works?
Step 1- Air Removal: Vacuum pump removes air from the chamber with short pulses. This conditioning process of the chamber for sterilization will remove 99% of the air inside the chamber.
Step 2 – Heating: Once all the air is removed, the steam generator will inject small burst of steam into the chamber until the pressure and temperature reaches the appropriate parameters to start the sterilization time (holding time).
Step 3 – Sterilization: Once the temperature and pressure is reached the system will maintain this temperature and pressure throughout the sterilization time. This is the stage where the sterilization takes place.
Step 4 – Exhaust : The exhaust valve/solenoid valve will open to release the pressure/steam inside the chamber until the pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure.
Step 5 – Drying: After all the air is exhausted after the sterilization cycle. The vacuum pump will again pump out all the moisture and steam from the load until the load is completely dry. The heating elements around the chamber will stay on to allow the water to evaporate into gas and be pumped out by the vacuum.
Step 6- Completion: After the drying is done, the cycle is complete and you can open the door.

4. Localised juvenile periodontitis primary pathogen is?
a) Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans
b) Prevotella intermedia
c) Mycoplasma
d) All of the above
ANSWER a
The following reasons have been proposed regarding the limited localization of lesions in LAP
- A Actinomycetemcomitans affects the host response in many ways after colonization in first molars and incisors
- A actinomycetemcomitans secretes a factor that inhibits Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) chemotaxis.
- A actinomycetemcomitans secretes some factors such as endotoxin, collagenase and leukotoxin to facilitate the colonization of bacteria in the periodontal pocket and cause destruction of periodontal tissues.
- Antagonistic bacteria against to A. actinomycetemcomitans. Colonize the periodontal tissues and prevent the colonization of A. actinomycetemcomitans in other areas of the mouth. This situation leads the localization of infection and tissue destruction.
- For unknown reasons, A. actinomycetemcomitans may lose its ability to produce leukotoxin. In this case, the disease progression slows down and colonization of new areas is prevented
5. Multifactorial causation theory was given by?
a) McMohan Pugh
b) Pettenkofer of Munich
c) Winslow
d) Robert Koch
ANSWER b
Multifactorial causation: Pettenkofer proposed that disease is a result of many factors as opposed to germ theory where the idea of a single cause was used. Improvements in public health and medicine brought about a decline in communicable diseases. But other noncommunicable ailments were on a rise which could not be explained based on the germ theory of disease. Hence single cause was deemed to be oversimplifying etiology of a disease where factors such as social, cultural, genetics, and economic factors were overlooked. Also having multiple causes for a disease meant numerous method of preventing that disease. But it was essential to prioritize the sequence of modification of the causal factors to tackle the disease causation




