- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
EPIDEMIOLOGY PART -2
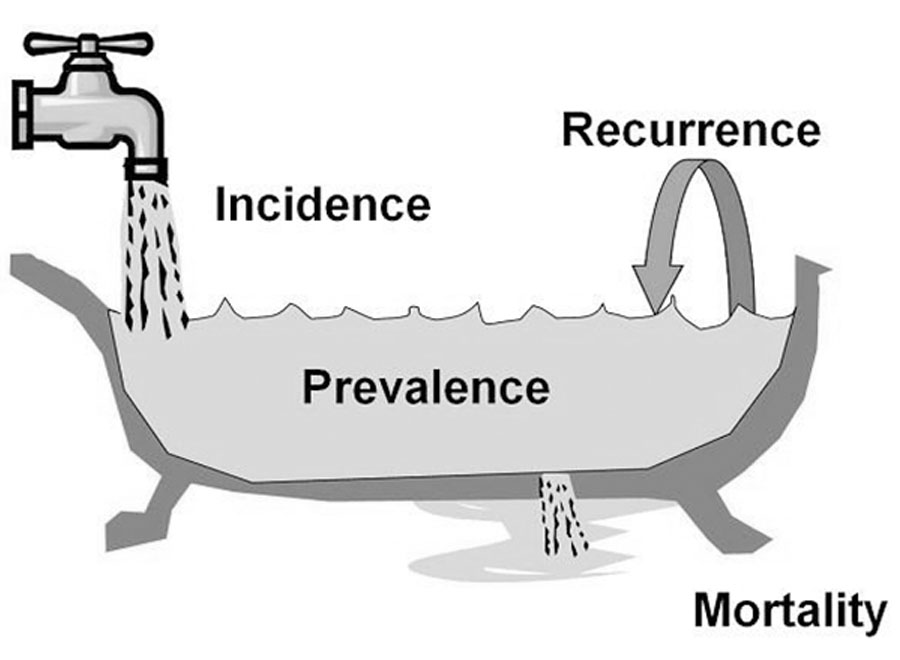
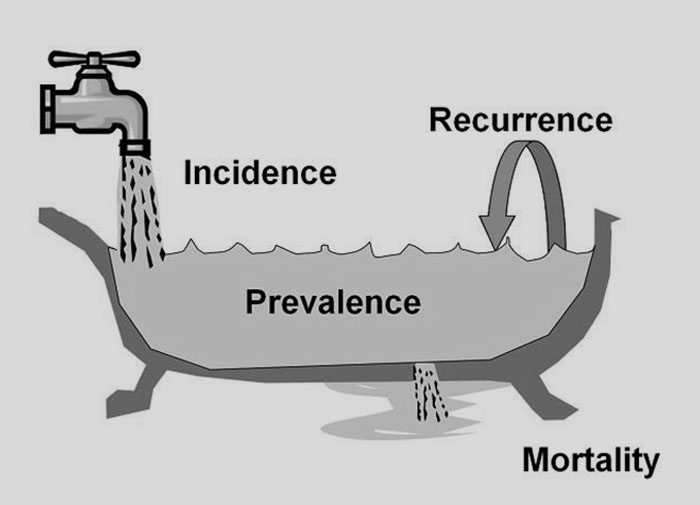
 Prevalence is the proportion of the total number of cases to the total population
(Measure of the burden of the disease on society with no regard to time at risk or when subjects may have been exposed to a possible risk factor.)
Prevalence is the proportion of the total number of cases to the total population
(Measure of the burden of the disease on society with no regard to time at risk or when subjects may have been exposed to a possible risk factor.)
 Incidence is usually more useful than prevalence in understanding the disease etiology: for example, if the incidence rate of a disease in a population increases, then there is a risk factor that promotes the incidence.
Incidence is usually more useful than prevalence in understanding the disease etiology: for example, if the incidence rate of a disease in a population increases, then there is a risk factor that promotes the incidence.
Exposure
Primary case (person who acquires diseases from exposure) Secondary case (person who acquires the disease from an exposure to the primary case) Index case (person that comes to the attention of public health authorities)Common bias
Selection bias

Selection bias
Bias in correct representative of case & controls in general population.
Berksonian’s Bias
Type of selection bias occurs due to different rates of admission to hospital for people with different disease.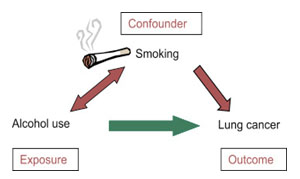
Confounding bias
Multiple risk factors can cause confounding bias.
Hawthorne bias
It’s a measurement bias.( people act differently if they know that they are being watched)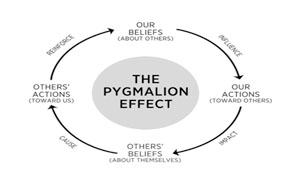
Pygmalion bias
Experimental expectancy or researcher’s belief
Recall / Memory Bias
Case- control groups- cases might not recall about the situation / disease than control.
Interviewer’s bias
It occurs when the interviewers know the hypothesis and about the cases .they will focus more on cases than controlsMCQS
1. The term prevalence refer to
a) No of new casesb) Rate of disease
c) Cumulative effect of a disease
d) Proportion of population affected by a disease.
Ans: d
Prevalence -The number of cases of a disease that are present in a particular population at a given time.2. The purpose of double blinding in clinical trials
a) Achieve comparability between study and controls groupb) Avoid subject bias
c) Avoid observe bias
d) Avoid both subject and observer bias
Answer d.