- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Dental Caries

Definition (Shafer’s)
- Microbial disease of the calcified tissues of the teeth, characterized by demineralisation of the inorganic portion and destruction of the organic substance of the tooth.
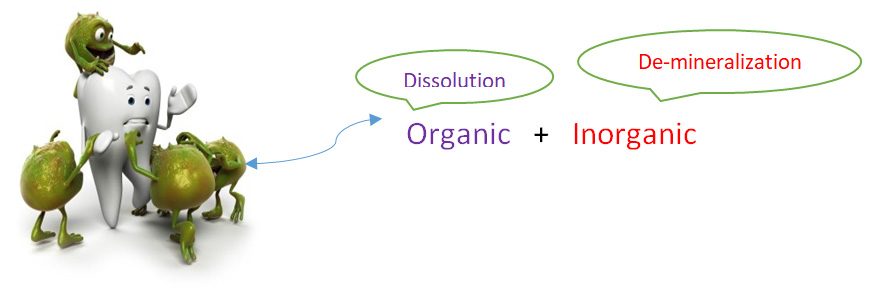
Etiology of caries concept
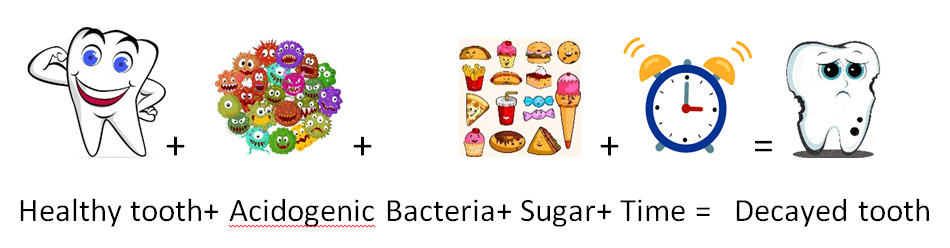
Some important concepts to understand
- Initiation of dental caries - Streptococcus mutans
- Propagation – Lactobacilli
- Root surface Caries – Actinomyces Species
Critical pH of dental caries – 5.5
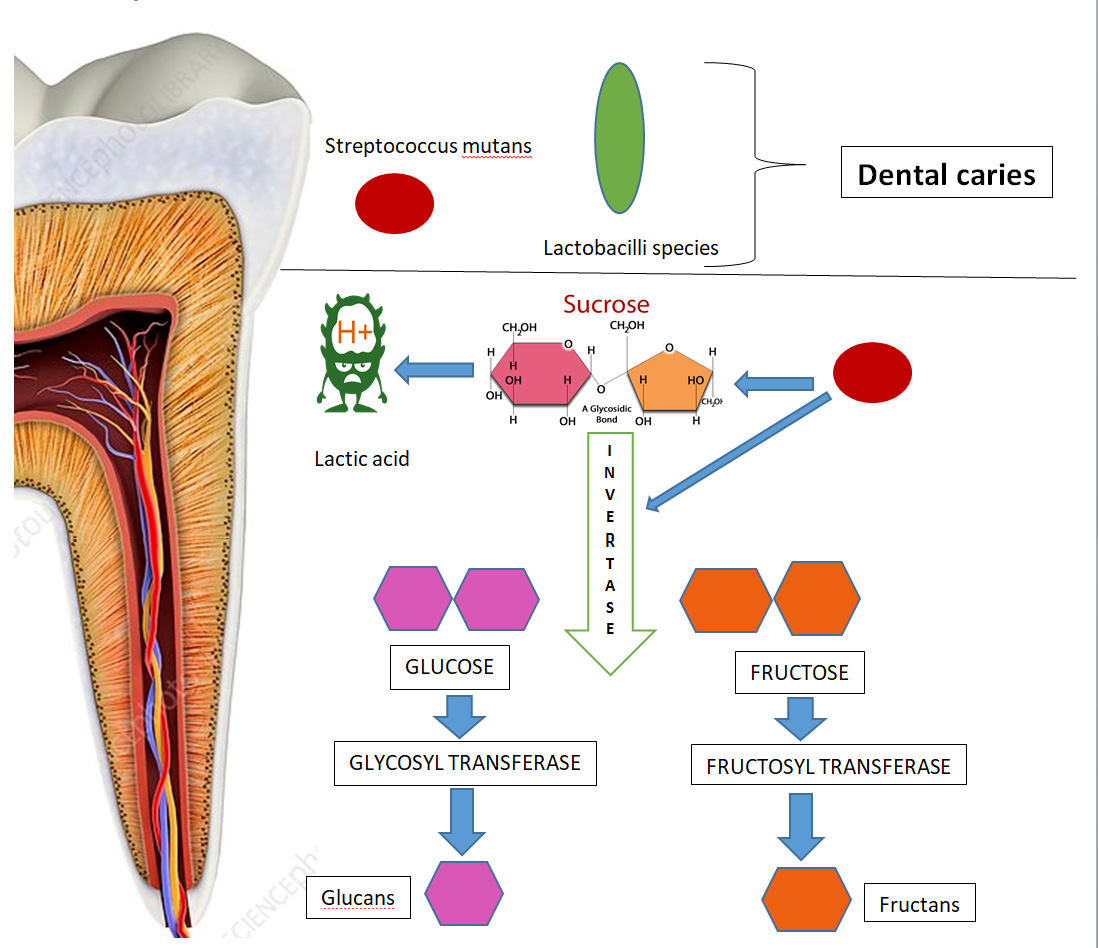
- The most important substrate for the involvement of S.mutans in the caries is the Sucrose.
- The transport of sucrose into the cell interior is accompanied by direct phosphorylation for energy utilization through glycolytic pathway leading to lactic acid production.
- Degradation of sucrose to free glucose and fructose by invertase enzyme produced by S.mutans.
- Glycosyl transferase & fructose transferase à enzyme responsible for the synthesis of extracellular Glucans and fructans.
Early Theories of Caries




Zones of dental caries

MCQs
1. The type of caries describe to the lesions which are not clinically diagnosed but detected only on radiographs?
a) Secondary cariesb) Chronic caries
c) Occult caries
d) Incipient caries

Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




