- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
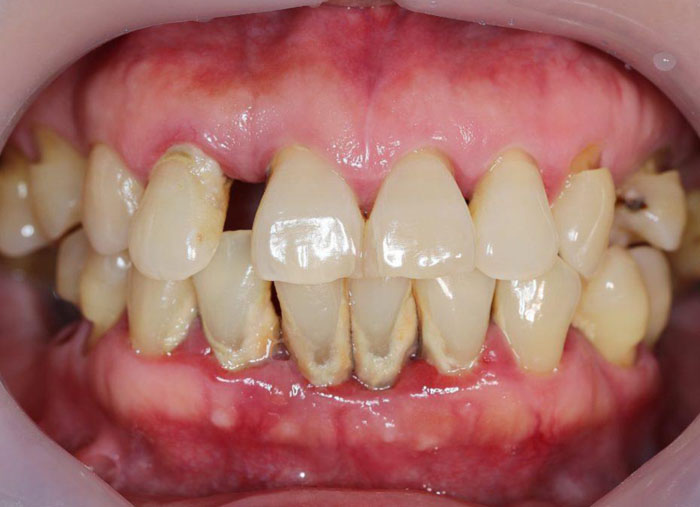
Has been defined as “an infectious disease resulting in inflammation with in supporting tissues of the teeth, progressive attachment loss and bone loss”.
Etiologic characteristics
- Microbial plaque formation
- Periodontal inflammation,
- Loss of attachment and alveolar bone.
Prevalence
- Affects male and female
- Increases with age.
- Age associated disease not age related and occurs depending on disease duration.
Clinical features
- Most prevalent in adults but can occur in children
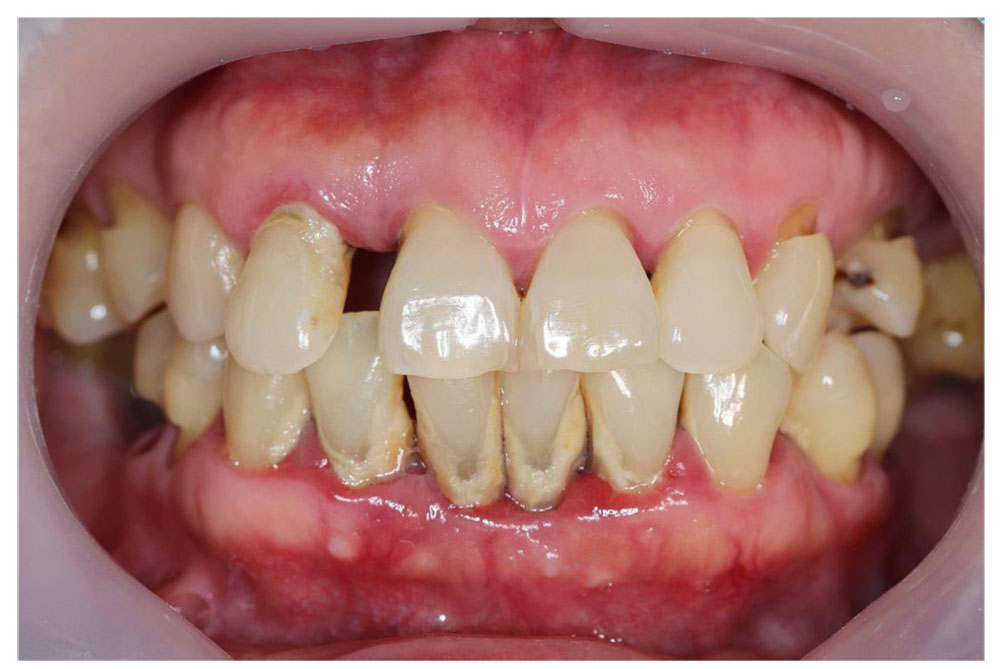
- Supragingival and subgingival plaque accumulation
- Gingival inflammation
- Loss of periodontal attachment
- Occasional suppuration
- Poor oral hygiene – gingiva is typically may be slightly to moderately swollen
- Colour magenta
- Consistency – soft or firm
- Surface topography – loss of stippling
- Blunted or rolled gingival margin
- Flattened or cratered papillae.
- Tooth mobility.
- Furcation involvement
- Spontaneous gingival bleeding.
- Pocket depths are variable and both suprabony and intrabony pockets can be found.
Symptoms
- Bleeding gums
- Loose teeth Usually painless, but sometimes localized dull pain radiating deep into the jaw
- Sensitivity to heat, cold, or both due to exposed roots
- Food impaction
- Halitosis
- Gingival tenderness or itching
- It is considered to be as “site specific disease”
Chronic periodontitis may be described as:
Localized: Periodontitis is considered localized when <30% of the sites assessed in oral cavity demonstrate attachment loss and bone loss.
Generalized: Periodontitis is considered generalized when >30% of the sites assessed demonstrate attachment loss and bone loss.
The pattern of bone loss in chronic periodontitis can be vertical or horizontal.
Localized ≤ 30% of the sites are affected
Generalized > 30% of the sites are affected
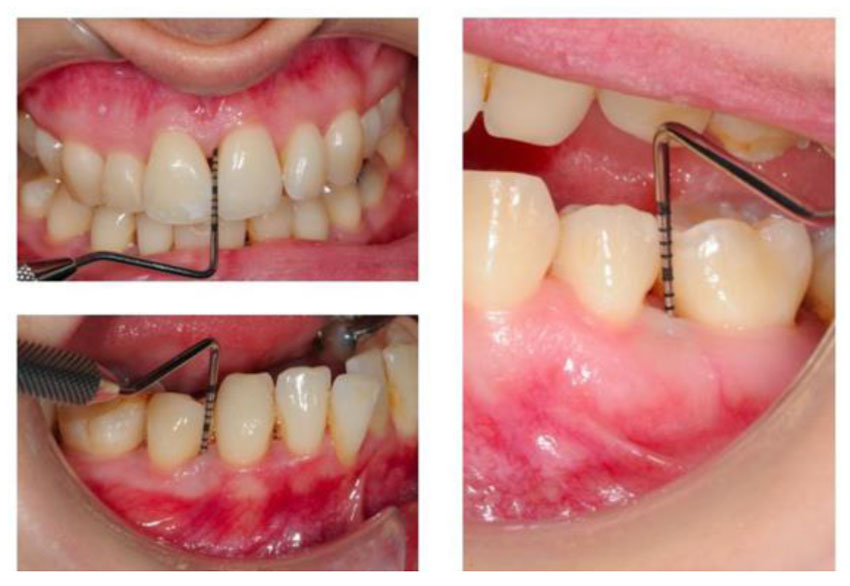
Severity can be categorized on the basis of the amount of Clinical attachment loss (CAL) as follows:
MILD PERIODONTITIS 1 to 2 mm CAL
MODERATE PERIODONTITIS 3 to 4 mm CAL
SEVERE PERIODONTITIS ≥ 5 mm CAL
Clinical Diagnosis
- Inflammation of the marginal gingiva extent to the attached gingiva.
- Clinical attachment loss.
- Radiographs(in case of bone loss).
Radiographic features
- Pattern of bone loss may be :
Vertical bone loss is usually associated with intra bony pocket formation.
Horizontal bone loss is usually associated with supra bony pockets.
Risk factors for disease
- Prior History of Periodontitis
- Local Factors
- Systemic Factors
- Environmental and Behavioral Factors
- Genetic Factors
| LOCAL FACTORS | SYSTEMIC FACTORS |
|---|---|
|
|
Causative organisms of chronic periodontitis are:
- Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis)
- Prevotella intermedia (P. intermedia)
- Treponema denticola
- Capnocytophaga
- A.actinomycetemcomitans (A.a)
- Eikenella corrodens (E. corrodens)
- Campylobacter rectus (C. rectus)
Treatment
| NON SURGICAL THERAPY | SURGICAL THERAPY |
|---|---|
|
|




