- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Cherubism
ALSO KNOWN AS
- Familial benign giant-cell tumor of the jaw
- Familial fibrous dysplasia of jaw
- Familial multilocular cystic disease of the jaws
INTRODUCTION
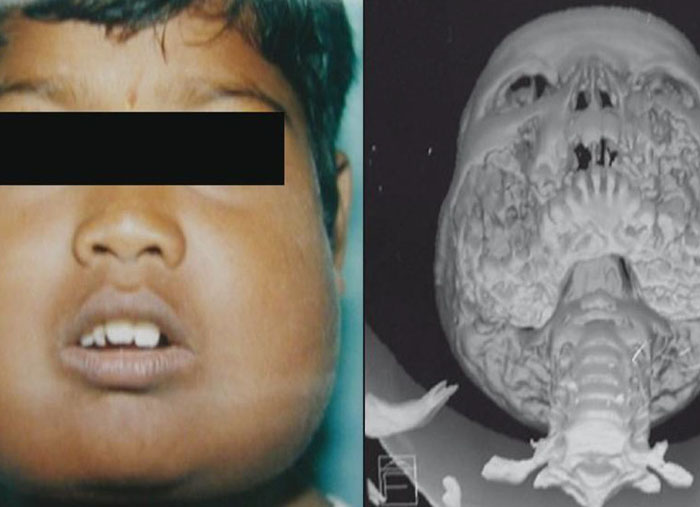
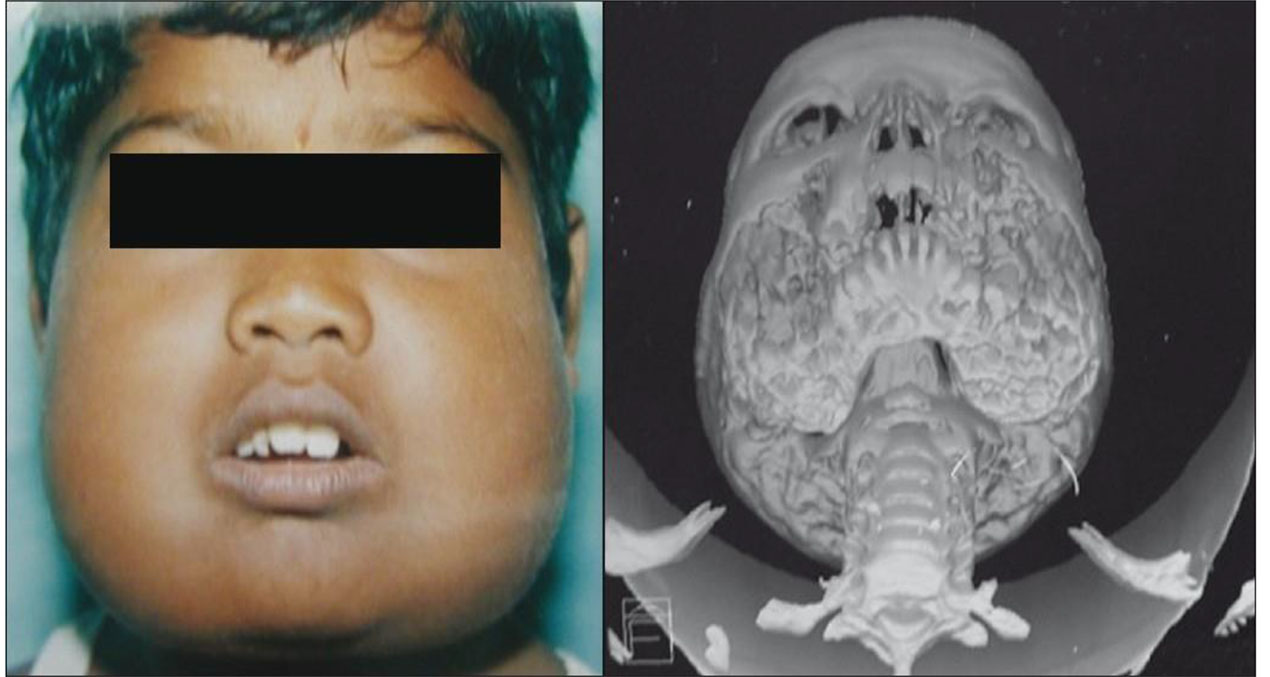
Cherubism is a congenital childhood disease of autosomal dominant inheritance. This disease is characterized by painless bilateral enlargement of the jaws, in which bone is replaced with fibrous tissue
ETIOLOGY
- Mutations in the SH3BP2 gene lead to production of an abnormal protein
- And possible degradation of the Msx-1 gene which is involved in the regulation of mesenchymal interaction during craniofacial morphogenesis
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- Abnormal protein produced that does not get broken down when it is no longer needed.
- Too much SH3BP2 protein likely increases signaling in certain cells, causing an immune reaction (inflammation) in the jaw bones and also triggering the production of osteoclasts,
- An excess of these bone-destroying cells contributes to the destruction of bone in the upper and lower jaws.
- A combination of bone loss and inflammation likely underlies the cystlike growths characteristic of cherubism.
- Usually diagnosed in children aged 2 to 7 years, with the observation of exacerbation of its manifestations within the first 2 years after diagnosis and of stabilization or even regression after puberty,
- Boys are more affected than girls at the proportion of 2 : 1
CLINICAL FEATURES
- Painless, frequently symmetrical, enlargement of the jaws as a result of the replacement of bone with fibrous tissue
- Rounded face
- Swollen cheeks accompanied by upward-looking eyes.
- The concomitant presence of cervical and/or submandibular lymphadenopathy
- The first signs of manifestation of the disease are generally observed at about 2 years of age, followed by accelerated growth from 8 to 9 years and spontaneous interruption after puberty
- Early exfoliation of deciduous teeth, impaction and/or displacement of teeth
- Ectopic tooth eruption
- Agenesis of permanent teeth, mainly of the second and third molars
- Malocclusion as well as in problems of phonation and swallowing,
BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS
- Serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations and TSH, FSH, LH, T4 and T3 hormone levels are usually within normal limits,
- But alkaline phosphatase levels might be elevated
RADIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
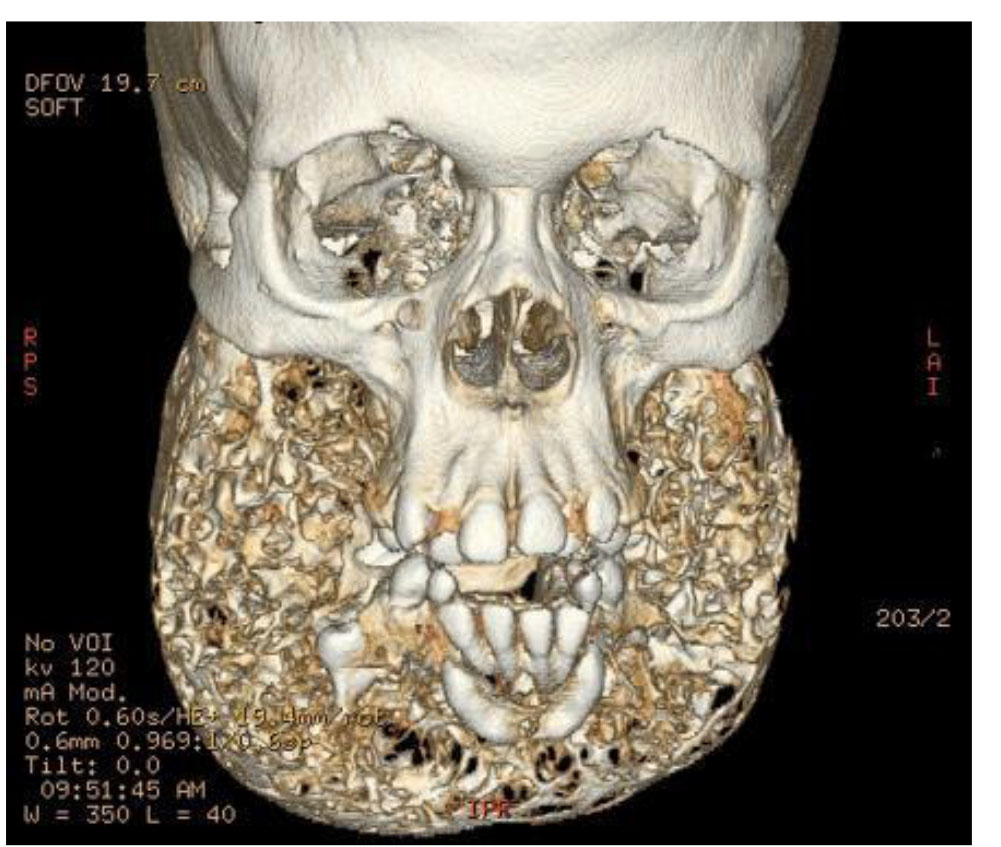
- Exfoliation of deciduous teeth, impaction and/or displacement of teeth radiographically seem to float in radiolucent areas, conferring the socalled "floating tooth appearance
- Characterized by expansive radiolucent, generally multiloculated lesions clearly delimited by cortical bone and distributed bilaterally in the posterior quadrants of the mandible and/or maxilla
- Involvement of the condyle is rare
- In more severe cases, infiltration of the orbital cavities may cause exacerbated exophthalmia and limiting ocular movements
- The teeth are found to be displaced and impacted and root resorption is observed
- Mandibular canal is often displaced
- The facial sinuses frequently appear to be obliterated
- Grade I, bilateral involvement of the ascending ramus of mandible
- Grade II, bilateral involvement of the ascending ramus of mandible and maxillary tuberosity
- Grade III, complete involvement of the maxilla and mandible compromising the coronoid processes and condyles
TREATMENT
- Because cherubism changes and improves over time,
- Treatment should be individually determined.
- Generally, moderate cases are watched until they subside or progress into the more severe range.
- Severe cases may require surgery to eliminate bulk cysts and fibrous growth of the maxilla and mandible.
- Surgical bone grafting of the cranial facial bones may be successful on some patients. Surgery is preferred for patients aged 5 to 15.
- Orthodontic treatment is generally required to avoid permanent dental problems arising from malocclusive bite and misplaced permanent teeth that have not erupted.
Related posts
April 10, 2025


