- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
A. 10cm
B. 12cm
C. 15cm
D. 18cm
Ans. D
In lateral cephalometrics the distance at which film is placed from mid sagittal plane is 7 inches or 18cm
2. Which of the following landmarks are not located in mandible
A. Pogonion
B. Gnathion
C. Menton
D. Porion
Ans. D
| Cranial land marks | Maxillary land marks | Mandible |
| Nasion, Basion, Bolton, sella | Point A, ANS, PNS, PTM, Keyridge | Point B, Gonion, Menton, Pogonion, Gnathion, Articulare, Condylion |
3. The interincisal angle in Bimaxillar protrusion is
A. Increased
B. Decreased
C. Normal
D. Variable
Ans. B
4. In bimaxillary prognathism malocclusion
A. SNA is increased
B. SNB is increased
C. Both SNA and SNB are increased
D. Both SNA and SNB are decreased
Ans. C
5. Cranial base length is measured from
A. Nasion to bolton
B. Nasion to sella
C. Sella to bolton
D. None of the above
Ans. A
Boltons plane: This is the plane that connects the boltons point and nasion. It gives total cranial base length
6. Nasion is situated at
A. Frontonasal suture
B. Zygomatic process
C. Orbital floor
D. None of the above
Ans. A
Nasion is the anterior most point of the frontonasal suture in the median plane
7. Which cephalometric point represents centre of ramus of mandible
A. Pm point
B. Xi point
C. PTM point
D. N point
Ans. B
Xi point is a constructed geometrical centre point of the ramus, approximate for inferior alveolar foramen(Ricketts)
8. Mandibular plane angle is formed by
A. FH line and NH pogline
B. FH line and mandibular plane
C. FH line and SNA
D. FH line and SNB
Ans. B
| ANALYSIS | REFERENCE POINT |
| Down’s | Gonion- menton line |
| Steiner’s | Gonion- gnathion line |
| Tweed | Tangent to lower border of mandible |
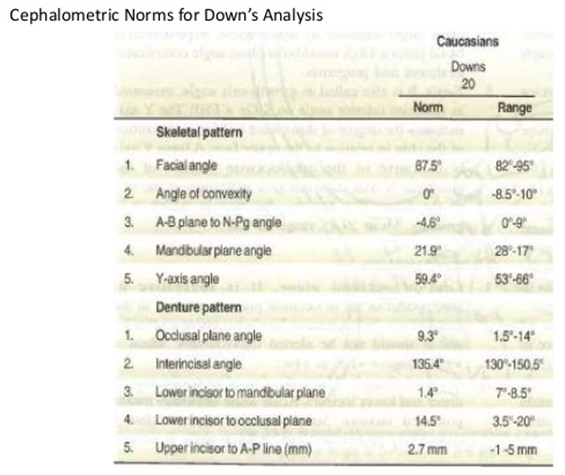
9. Average angle of convexity
A. 85
B. 90
C. 59
D. 0
Ans. D
10. Decreased interincisal angle indicates
A. Retrusion of teeth
B. Protrusion of teeth
C. Vertical overlap
D. Horizontal overlap
Ans. B




