- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

Cephalometry is the study and the measurement of the head.
Cephalometric analysis can be used to analyze the facial skeleton, generally in a two-dimensional (2D) fashion and based on specialized lateral and anteroposterior (AP) skull radiographs (cephalograms).
The technique was originally introduced by Broadbent, and since that time, many more complex analytical techniques have been introduced. Cephalometric analysis has many applications, including the following
- Diagnosis (e.g., assessment of the origin of a malocclusion—dental or skeletal)
- Description of patterns of facial symmetry and form—dolichofacial (vertical) and brachyfacial (horizontal), as well as the mesofacial (ideal) form
- Orthodontic and orthognathic treatment planning
- Monitoring of changes due to growth or treatment
- Prediction of orthodontic and orthognathic treatment outcomes
Conventional cephalometric analysis is performed by tracing radiographic landmarks on acetate overlays and measuring linear and angular values
Definitions of cephalometric
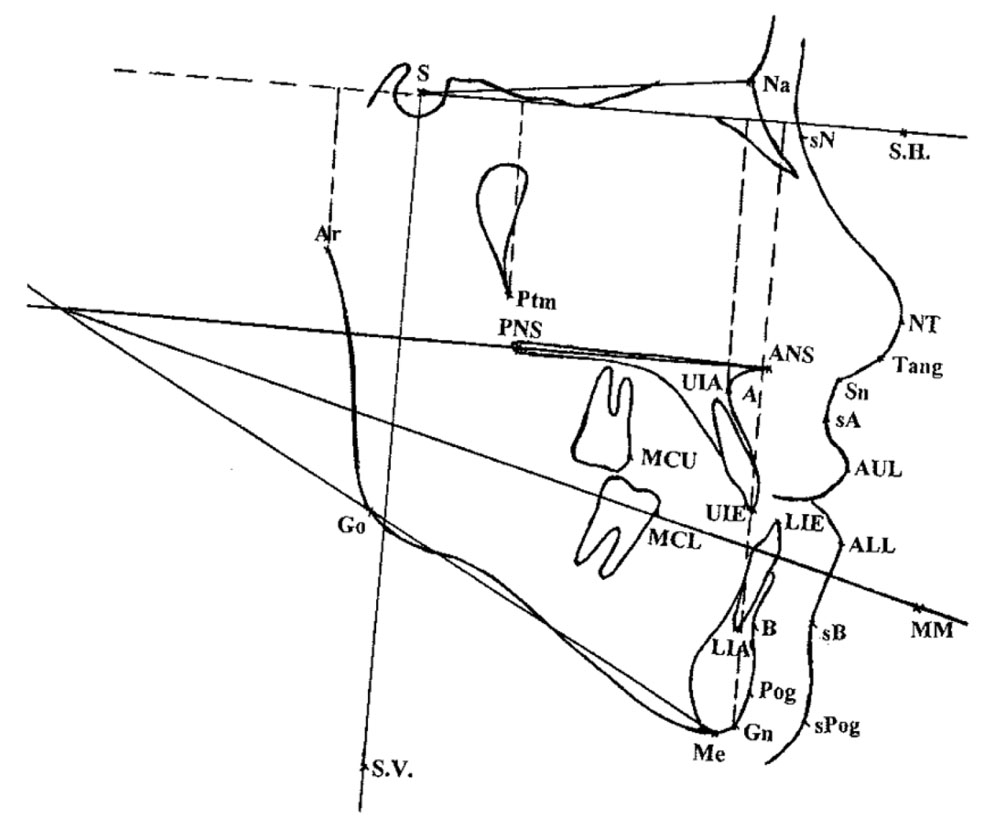
Orbitale (O). The most inferior point on the external border of the orbit.
Condylion (Cd). The most superior point on the articular head of the condyle.
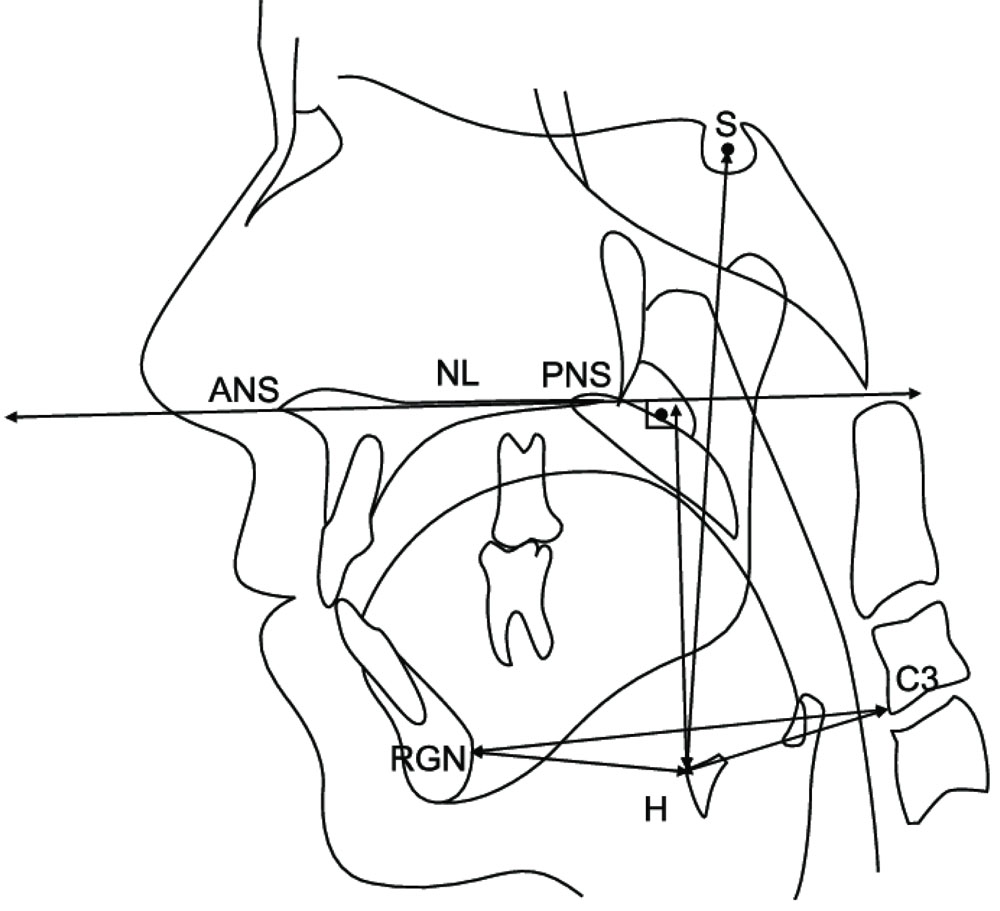
ANS (Anterior nasal spine)—tip of the median sharp bony process of the palatine bone in the hard palate.
A Point—deepest midline point on the maxillary alveolus between ANS and the maxillary alveolar crest.
B Point—deepest midline point between the mandibular alveolar crest and the gnathion.
Ba (Basion)—most inferior point on the anterior margin of the foramen magnum in the median plane.
Go (Gonion)—most lateral external point at the junction of the horizontal and ascending rami of the mandible.
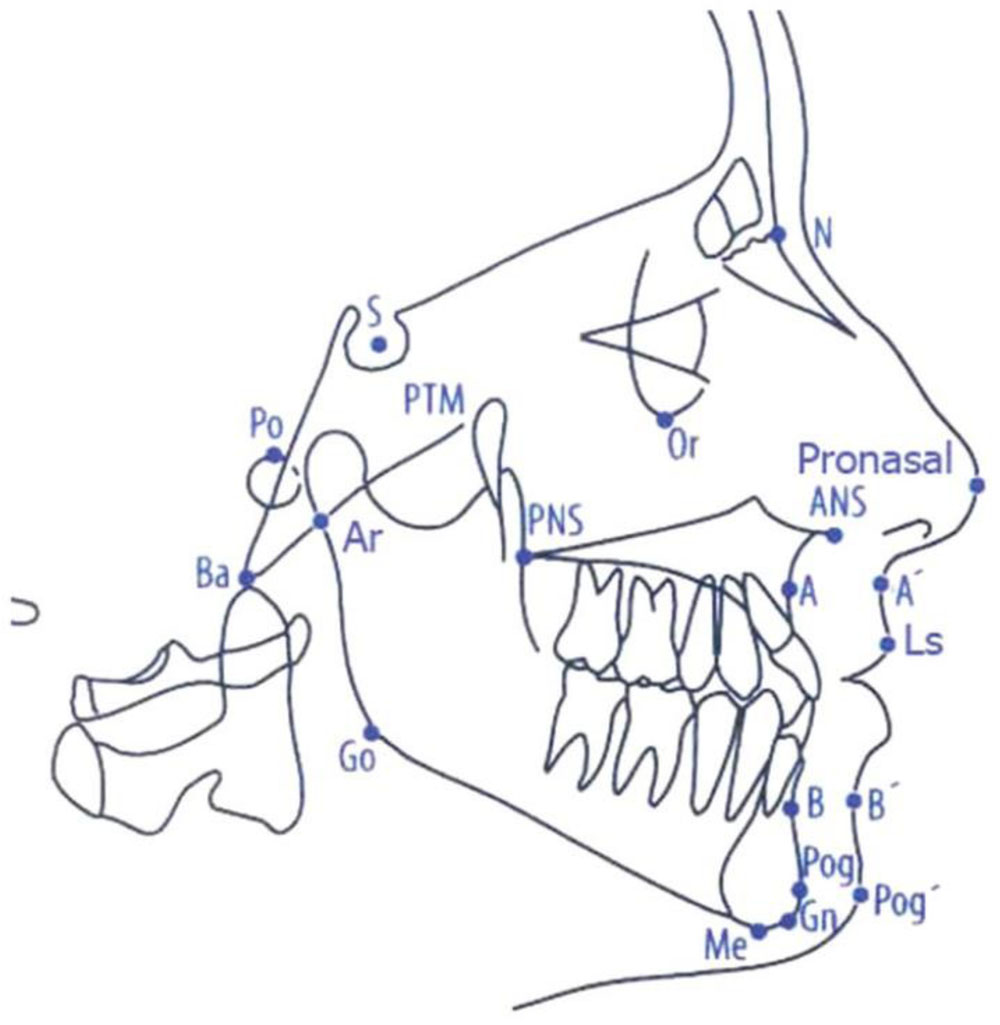
Gn (Gnathion)—most antero-inferior point on the bony mandibular symphysis.
H (Hyoidale)—most antero-superior point on the body of the hyoid bone.
Me (Menton)—lowest point on the bony outline of the mandibular symphysis.
Pogonion (Pg). The most anterior point on the midsagittal mandibular symphysis
Pterygomaxillary fissure (Ptm). A teardrop-shaped fissure, the posterior wall of which is created by the anterior borders of the pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone; the anterior wall represents the posterior border of the maxilla (maxillary tuberosity)
MP (Mandibular plane)—line joining Me and Go.
N (Nasion)—most anterior point of the fronto-nasal suture.
PNS (Posterior nasal spine)—tip of the posterior spine of the palatine bone of the hard palate.
Spt (soft palate tangent)—tangent point on a line parallel to the long axis of the soft palate at the maximum width.
Phw (Posterior pharyngeal wall)—point on the posterior pharyngeal wall at the same horizontal level as spt.
S (Sella)—the center of the sella turcica.
SN—anterior cranial base length.
LAFH —lower anterior face height (ANS-Me).
AFH—anterior face height (N-Me).
PFH—posterior face height (S-Go).
Go-Me—mandibular length.
ANS-PNS—maxillary length.
Co-A—midface length.
MP-H—perpendicular distance from the MP to H.
RPAS—width of nasopharynx (Phw-spt).
PAS—distance between the posterior pharyngeal wall and the dorsal surface of the base of the tongue, measured on the line that intersects Go and B point.
PNS-P—posterior nasal spine to the tip of the soft palate.
Angular Measurements:
| BaSN—cranial base angulation in the mid-sagittal plane. |
| SNA— angle from S to N to A Point. |
| SNB—angle from S to N to B Point. |
| ANB—angle from A Point to N to B Point |
| Y-Axis—facial axis (GnSN). |
| Gonial Angle—angle formed by the posterior border of the mandible and the mandibular plane. |
| CVT-SN—angulation of the cervical spine (C2-C4) with the cranial base (SN). |
| SN-PP—angulation of the cranial base (SN) with the palatal plane. |
| SN-OP—angulation of the cranial base (SN) with the occlusal plane. |
| SN-MP—angulation of the cranial base (SN) with the mandibular plane. |
| PP-MP—angulation of the palatal plane with the mandibular plane. |