- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
Caused by Candida albician
CLASSIFICATION

PREDISPOSING FACTOR
• Change in oral microbial flora
– Administration of antibiotics specially broad spectrum
– Xerostomia secondary to anticholinergic agents
– Salivary gland disease
• Local Irritation
– Denture, orthodontic appliance
– Heavy smoking
• Drug therapy
– Corticosteroid or cyto-toxic drug or immunosuppressive drug
– Radiation therapy
• Other systemic disease
– Leukemia
– Lymphoma
– Diabetes
– Tuberculosis
– Epithelial dysplesia
• Malnutrition status
– Low serum vit A
– Pyridoxine
– Iron level
• Age
– Infancy
– Pregnancy
– Old age
• Endocrine deficiency
– Hypoparathyroidism
– Hypothyroidism
– Addison’s disease
• Others
– Tight fitting garments
– Indwelling catheter
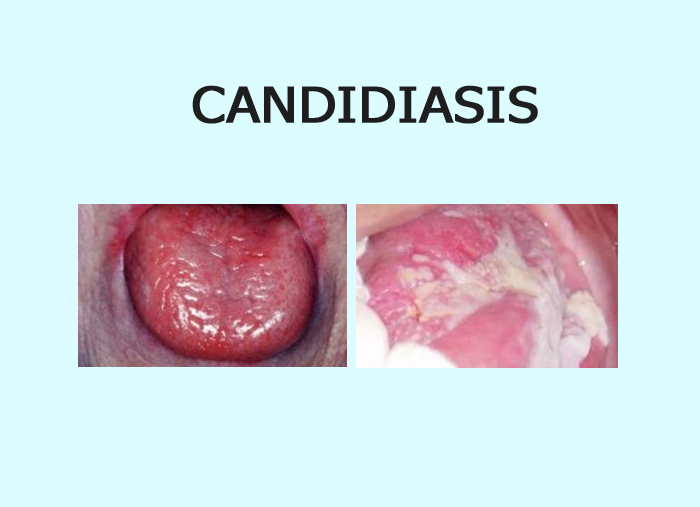
PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS CANDIDIASIS
- Thrush
- Superficial infection of upper layer of oral mucous membrane
- Fungal growth – desquamation of epithelial cell and accumaltion of bacteria, keratin and necrotic tissue forming pseudomembrane
Clinical features:
Infants
- 6th and 10th day after birth
- Infection from maternal vaginal canal
- Soft white/bluish whit, adherent patches on oral mucos
- Painless
- Removed with little difficulty
Adult
– Site : roof of mouth, retromolar area, Mucobuccal fold
– Sex: female
– Prodromal symptom : rapid onset of bad taste and discomfort from spicy food
– Burnig sensation
– White plaque
• pearly white or bluish white – resemble cottage cheese or curdled milk
• Composed of tangled mass of hyphae, yeast, desquamated epithelial cell and debris
• Easily wiped out – erythematous/atrophic area which is painful
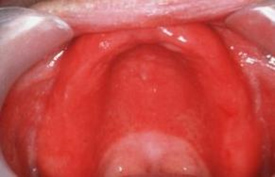
ACUTE ATROPHIC CANDIDIASIS

- Antibiotics sore mouth
- Any site but mainly involves tongue or area facing prosthesis
- Red or erythematous
- Vague pain or burning sensation
- Careful examination – white thickened foci that can be rubbed off
CHRONIC HYPERPLASTIC CANDIDIASIS

- Candidal leukoplakia
- Persist without any pain for years
- Doesn’t rubs off with lateral pressure
- Slightly white to dense white with cracks and fissures occasionally
- Vague border – epithelial dysplasia
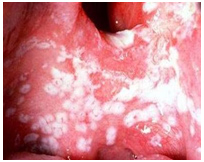
CHRONIC ATROPHIC CANDIDIASIS
- Also known as Denture stomatitis
- Bright red palatal tissue – edematous and granular
- Sharply outline of redness
- Multiple pinpoint foci of hyperemia usually involving the maxilla
ID REACTION
- Secondary response characterized by localized or generalized sterile vesicopapular rash that is believed to be allergic response – candida antigen (monoloids)
TREATMENT OF ORAL CANDIDIASIS
- Topically or systematic
- 7 days treatment
- Oral symptoms disappears in 2-5 days
- Relapse common – underlying immunodeficiency
- Removal of causative factors – Ill fitting denture – Withdrawal or change of antibiotics – Proper cleaning of denture and use of antifungal agent
Topical treatment:Clotrimazole,1% genitian violet, Nystatin, Amphotericin, Mycostatin cream , Idoquinol
Systemic Treatment:Nystatin,Ketaconazole ,Itraconazole,Fluconazole
MCQs
- Candidiasis associated with Dentures is_______?
- Acute Pseudo Membranous
- Acute Atrophic
- Chronic Hyperplastic
- Chonic atrophic
Answer: D




