- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. Arch wire used as material of choice for initial alignment in fixed appliance therapy
A. Stainless steel
B. Nitinol
C. Elgiloy
D. Cu Niti
Answer- B
2. What percentage of cleft lip patients have cleft palate as a concurrent abnormality ?
A. 60%
B. 70%
C. 80%
D. 90%
Answer- A
3. Chances of true skeletal changes in maxilla using face mask is best before the age of
A. 8 years
B. 10 years
C. 12 years
D. 14 years
Answer- A
Due to the natural growth direction of the nasomaxillary complex, treatment with a facemask should be expected to yield the most pronounced skeletal effects up to 8 years of age.
4. Opening of bite with anterior biteplane in the correction of deep bite occurs due to
A. Intrusion of lower anterior teeth
B. Proclination of upper anterior teeth
C. Eruption of posterior teeth
D. All of the above
Answer- C
Even though the mode of action of ABP has a mild relative intrusion of lower anteriors, it shows a mild proclination tendency of lower anteriors too.
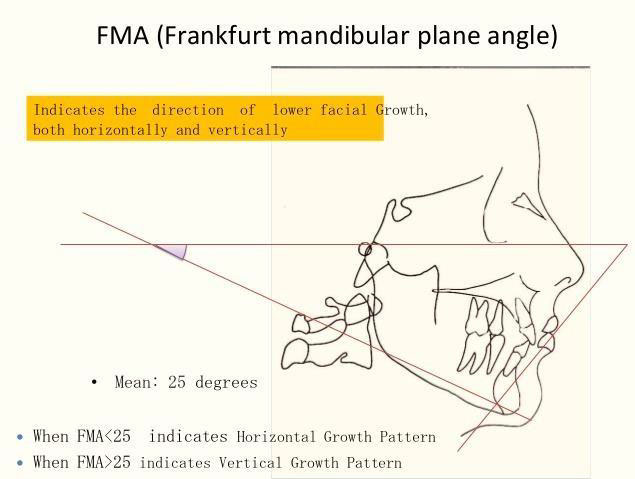
5. Which of the following cephalometric values express the variations in the vertical height of the face ?
A. FMA
B. IMPA
C. FMIA
D. ANB
Answer- A
This angle demonstrate the growth pattern in a normal/horizontal /vertical direction when the mandibular plane is compared to the FH plane
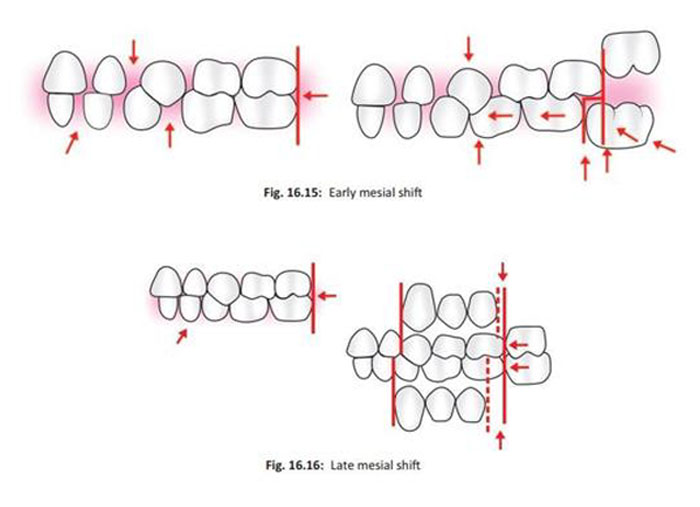
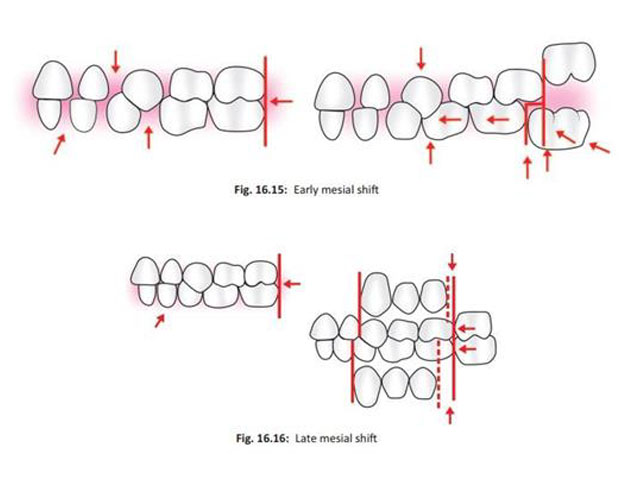
6. Early mesial shift of the first permanent molar
A. Compensates for incisal liability
B. Corrects the developing midline diastema
C. Utilizes the anthropoid space
D. Depends on the leeway space
Answer- C
Primary molar guidance
• Dsired Class I relationship is established by the mesial shift.
Early mesial shift
• If the deciduous dentition is spaced
• the eruptive force of permanent molars causes a closing of any existing spaces between the primary molars or primate spaces
Late mesial shift
• When no spaces exist,
• primary molar exfoliates the permanent molar migrates mesially to use up the leeway space(E space)
• Difference between the mesio distal width of primary C,M1,M2 and their permanent successors.
• It is 1.8 mm (0.9 mm on each side) in maxillary arch and 3.4 mm (1.7 mm on each side) in mandibular arch.
7. Choking off effect of enamel is seen
A. After hand over mouth exercise
B. After sodium fluoride application
C. After a traumatic dental injury
D. In a young permanent tooth with a deep dentinal carious lesion
Answer- B
Sodium Fluoride (2%) Sodium fluoride was developed by Knutson et al in 1947.
Application: Knutson technique: First thorough oral prophylaxis is done. The teeth are isolated with cotton rolls. Sodium fluoride is applied using cotton applicators. It is applied only once due to formation of CaF2, which prevents further diffusion of F- ions. This is called choking off phenomenon. The patient should refrain from eating and drinking for next 30 minutes
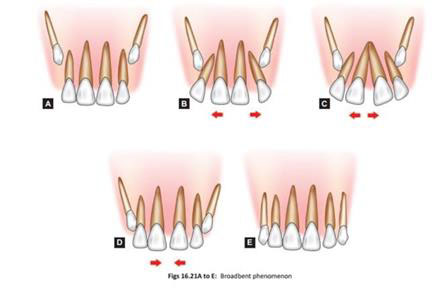
8. Broadbent phenomenon is a
A. Normal feature in the pre-dentate stage
B. Carious lesion in an unerupted tooth
C. Presence of multiple supernumerary teeth
D. Transient malocclusion
Answer- D
As the permanent maxillary canines erupt they displace the roots of maxillary lateral incisors mesially. This force is transmitted to the central incisors and their roots are also displaced mesially. Thus, the resultant force causes the distal divergence of the crown in an opposite direction, leading to midline spacing This is called Ugly Duckling Stage or Broadbent phenomenon. The term ugly duckling stage indicates the unesthetic appearance of child during this stage.
This condition corrects itself after the canines have erupted. The canines after eruption apply pressure on the crowns of incisors thereby causing them to shift back to original positions. No orthodontic treatment should be attempted at this stage as there is a danger of deflecting the canine from its normal path of eruption
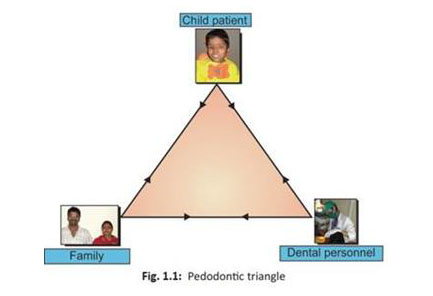
9. The apex of the pedodontic triangle is occupied by the
A. Pedodontist
B. Parent/caretaker
C. Child
D. Society
Answer- C
- Pedodontic triangle was first explained and conceptualized by GZ Wright in 1975.
- Patient-doctor relation in adults is linear but in Pedodontics the relation is triangular.
- child is at the apex of triangle as he is the focus of attention
10. Which of the following conditions is not associated with self-injury behavior in children ?
A. Lynch syndrome
B. Autism spectrum disorders
C. Cornelia de Lange syndrome
D. Cerebral palsy
Answer- A
Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), is the most common cause of hereditary colorectal (colon) cancer. People with Lynch syndrome are more likely to get colorectal cancer and other cancers, and at a younger age (before 50), including Uterine (endometrial), Stomach, Liver, Kidney, Brain, and Certain types of skin cancers