- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1.Trapezoidal outline of incisor teeth is which characteristic of dentition:
a) Class
b) Arch
c) Type
d) Quadrant
ANSWER a
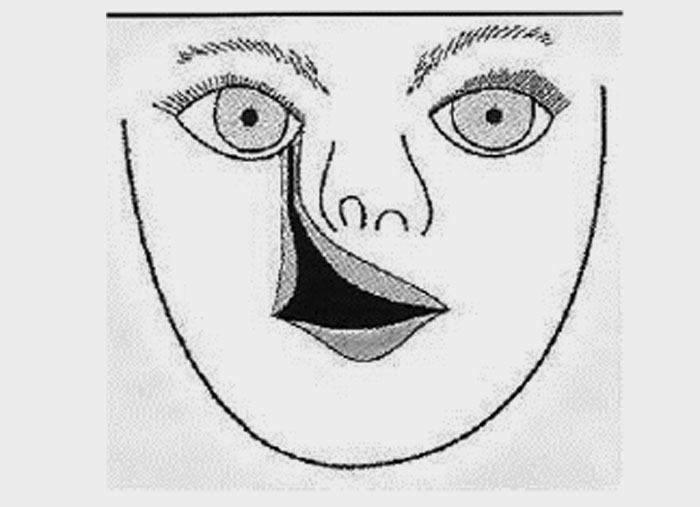
2.Type of cleft that develops when the maxillary process does not fuse with
lateral nasal process is:
a) Oblique facial cleft
b) Cleft lip
c) Cleft palate
d) Submucous cleft
ANSWER a
Oblique facial cleft is a rare defect that results when the nasolateral process fails
to fuse with the maxillary process, usually resulting from hypoplasia of one of
the tissue masses
3.Drug used in treatment of hemophilia:
a) Desmopressin
b) Glucocorticoids
c) ACE inhibitors
d) Calcium Channel Blockers
ANSWER a
Desmopressin (DDAVP®) is used to help stop bleeding in patients with von Willebrand’s disease or mild hemophilia A. DDAVP causes the release of von Willebrand’s antigen from the platelets and the cells that line the blood vessels where it is stored. Von Willebrand’s antigen is the protein that carries factor VIII.
4. A dentist while extraction of the upper first molar accidentally creates a small perforation into the maxillary sinus. What is the test to check presence of the Oro antral communication?
a) Valsalva maneuver
b) Irrigation
c) Aspiration
d) Manual exploration of site
ANSWER a
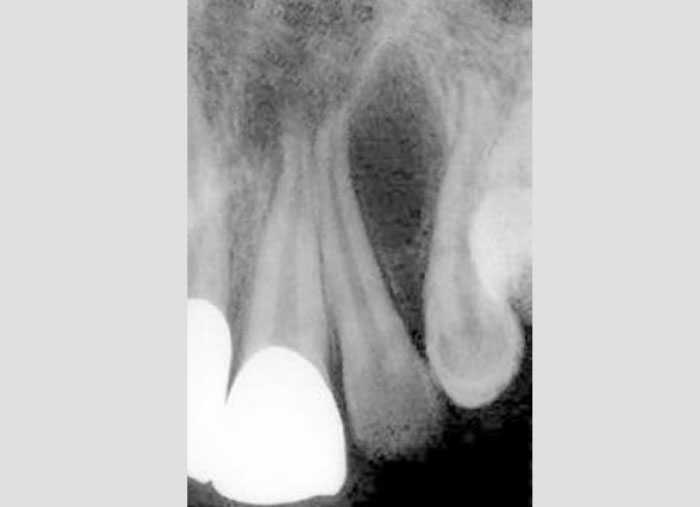
OROANTRAL COMMUNICATION- This is a common complication, which may occur during an attempt to extract the maxillary posterior teeth or roots. It is identified easily by the dentist, because the periapical curette enters to a greater depth than normal during debridement of the alveolus, which is explained by its entering the sinus.
VALSALVA TEST: To confirm if OAC has occurred
The Valsalva manoeuvre is performed by moderately forceful attempted exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one’s mouth, pinching one’s nose shut while pressing out as if blowing up a balloon. Oroantral communication can also be confirmed by observing the passage of air or bubbling of blood from the post-extraction alveolus when the patient tries to exhale gently through their nose while their nostrils are pinched. If the patient exhales through their nose with great pressure, there is a risk of causing oroantral communication, even though communication may not have occurred initially, such as when only the mucosa of the maxillary sinus is present between the alveolus and the antrum.
5.Mjor Site of exchange of ions from saliva in the salivary gland:
a) Acini
b) Striated duct
c) Serous demilunes
d) Intercalated duct