- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
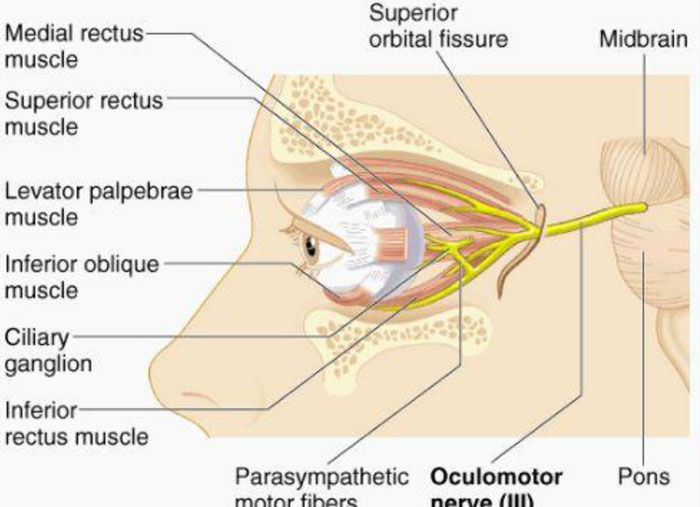
The oculomotor nerve is the third cranial nerve. It is motor in function and supplies the muscles of the eye.
It is primarily a motor nerve. It produces eye movement, opening of eyelid, constriction of pupil, and focusing.

Functional Components
The oculomotor nerve comprises three types of fibres:
- General somatic efferent fibres: These supply the extraocular muscles except the superior oblique and lateral rectus; the levator palpebrae superioris help in movement of the eyeball.
- General visceral efferent/parasympathetic fibres: These fibres innervate the intraocular muscles, sphincter pupillae and ciliaris muscle to perform functions such as contraction of pupil and accommodation.
- General somatic afferent fibres: These fibres carry proprioceptive impulses of eye muscles to be relayed to the brain. These neurons originating from the eye are relayed at the mesencephalic nucleus.
Origin
The nuclei from which the fibres of the oculomotor nerve arise are as follows
- Oculomotor nucleus : It is an aggregation of a number of smaller nuclei present in the mid-brain at the level of the superior colliculus and gives rise to general SE fibres.
- Edinger–Westphal nucleus : This nucleus is located in the midbrain. It contributes para-sympathetic fibres for the constriction of pupil. Fibres from the nucleus are preganglionic and synapse in the ciliary ganglion.
Postganglionic fibres supply the ciliary and sphincter pupillae muscles of the eyeball.
Anatomical Course
The nuclei from which the fibres of the oculomotor nerve arise are as follows
- The oculomotor nerve originates from the oculomotor nucleus – located within the midbrain of the brainstem, ventral to the cerebral aqueduct. It emerges from the anterior aspect of the midbrain, passing inferiorly to the posterior cerebral artery and superiorly to the superior cerebellar artery.
- The nerve then pierces the dura mater and enters the lateral aspect of the cavernous sinus. Within the cavernous sinus, it receives sympathetic branches from the internal carotid plexus. These fibres do not combine with the oculomotor nerve – they merely travel within its sheath.
- The nerve leaves the cranial cavity via the superior orbital fissure. At this point, it divides into superior and inferior branches.
- Superior branch – provides motor innervation to the superior rectus and levator palpabrae superioris.
- Sympathetic fibres run with the superior branch to innervate the superior tarsal muscle.
- Inferior branch – provides motor innervation to the inferior rectus, medial rectus and inferior oblique.
- Also supplies pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres to the ciliary ganglion, which ultimately innervates the sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscle.
Motor Functions
The oculomotor nerve innervates many of the extraocular muscles. These muscles move the eyeball and upper eyelid.
Superior Branch
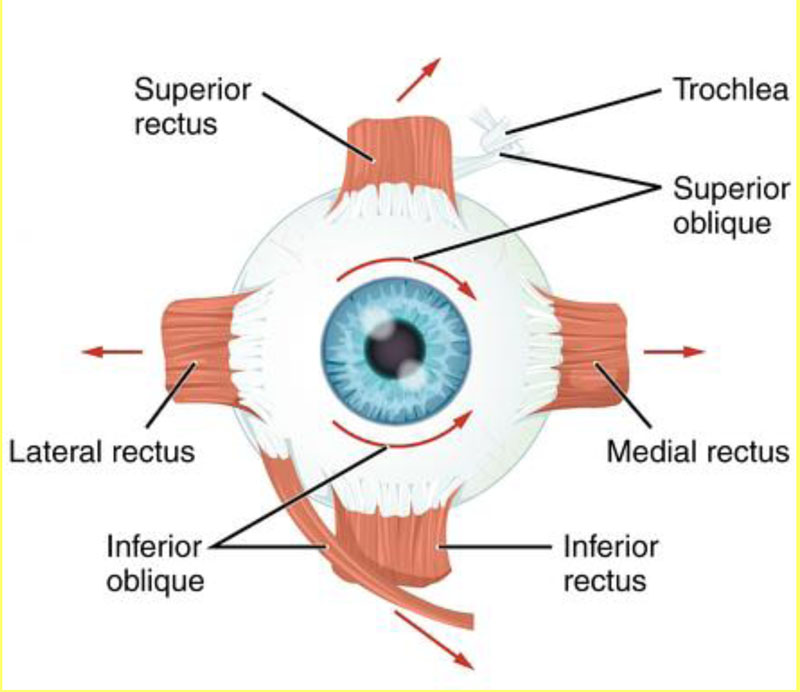
Superior rectus – elevates the eyeball
Levator palpabrae superioris – raises the upper eyelid.
Additionally, there are sympathetic fibres that travel with the superior branch of the oculomotor nerve. They innervate the superior tarsal muscle, which acts to keep the eyelid elevated after the levator palpabrae superioris has raised it.
Inferior Branch:
Inferior rectus – depresses the eyeball
Medial rectus – adducts the eyeball
Inferior oblique – elevates, abducts and laterally rotates the eyeball
Parasympathetic
- There are two primary functions of the autonomic parasympathetic (involuntary) oculomotor nerve.
- It constricts the pupil (miosis) by innervating the smooth muscle (sphincter pupillae) near the pupil. It also innervates the ciliary muscles.
- The sphincter pupillae causes narrowing of the pupil in order to prevent diverging light rays from the corneal periphery creating a blurred image.
- The ciliary muscle changes the shape of the lens during accommodation.
Sympathetic
- The oculomotor nerve has no direct function, but sympathetic fibres run with the oculomotor nerve to innervate the superior tarsal muscle (helps to raise the eyelid).
Applied Anatomy
Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) Injury
This causes paralysis of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle, and the upper eyelid droops. This condition is called ptosis. Also, paralysis of one or more extraocular muscles can lead to double vision called diplopia.




