- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

1. Secondary amyloidosis is associated with (AI 2012)
- Ab
- AL
- AA
- APrP
ANSWER c
2. A 60 year old female is suffering from renal failure and is on hemodialysis since last 8 years. She developed carpal tunnel syndrome. Which of the following finding will be associated? (AIIMS Nov 2011)
- AL
- AA
- ATTR
- β2 microglobulin
ANSWER d
Hemodialysis associated amyloidosis is caused by the deposition of the b2 microglobulin which is a component of MHC class I molecule and cannot be filtered through the cuprophane dialysis membrane. It gets deposited in the synovium, joints and the tendon sheaths. Deposition of the amyloid in long term hemodialysis takes place in joints and in the carpal ligament of the wrist, the latter leading to development of ‘carpal tunnel syndrome’
3. The best investigation for the diagnosis of amyloidosis is (AIIMS May 2010)
- Colonoscopy
- Rectal biopsy
- Upper GI endoscopy
- CT scan
ANSWER b
The histological examination of the biopsy material is the commonest and confirmatory method for the diagnosis in a suspected case of amyloidosis. The sites for the biopsy can be the renal tissue, rectum, abdominal fat aspiration and gingiva. The rectum is the best site for taking the biopsy in the options provided.
4. Which type of amyloidosis is caused by mutations in transthyretin gene? (AI 2005)
- Familial Mediterranean fever
- Familial amyloidosis polyneuropathy
- Dialysis associated amyloidosis
- Prion protein associated amyloidosis
ANSWER b
Transthyretin is a normal serum protein that binds and transports thyroxine and retinol (transthyretin). A mutant form of transthyretin is deposited in a group of genetically determined disorders referred to as familial amyloid polyneuropathies’.
- Inherited amyloidosis due to ATTR is autosomal dominant.
- Even normal transthyretin (pre-albumin) can form fibrils and lead to senile systemic amyloidosis.
5. In Hemodialysis associated amyloidosis, which of the following is seen: (AI 2008)
- Transthyretin
- b2 Microglobulin
- SAA
- a2 Microglobulin
ANSWER b
6. Bone marrow in AL amyloidosis shows: (AI 2007)
- Bone marrow plasmacytosis
- Granulomatous reaction
- Fibrosis
- Giant cell formation
ANSWER a
AL (Amyloid Light chain) protein is produced by immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and their deposition is associated with some form of monoclonal B cell proliferation. These patients have a modest increase in the number of plasma cells in the bone marrow (plasmacytosis) which presumably secrete the precursors of AL protein.
7. A diabetic patient is undergoing dialysis. Aspiration done around the knee joint would show: (AI 2007)
- A beta 2 microglobulin
- AA
- AL
- Lactoferin
ANSWER a
8. What is the best method for confirming amyloidosis? (AI 2007)
- Colonoscopy
- Sigmoidoscopy
- Rectal biopsy
- Tongue biopsy
ANSWER c
9. Neointimal hyperplasia causes vascular graft failure as a result of hypertrophy of: (AI 2006)
- Endothelial cells
- Collagen fibers
- Smooth muscle cells
- Elastic fibers
ANSWER c
The proliferation of smooth muscle cells is a critical event in the neointimal hyperplastic response. Several studies have clearly demonstrated that blockade of smooth muscle cell proliferation resulted in preservation of normal vessel phenotype and function, causing the reduction of neointimal hyperplasia and graft failure.
10. Which one of the following stains is specific for Amyloid? (AI 2005)
- Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
- Alizarin red
- Congo red
- Von-Kossa
ANSWER c
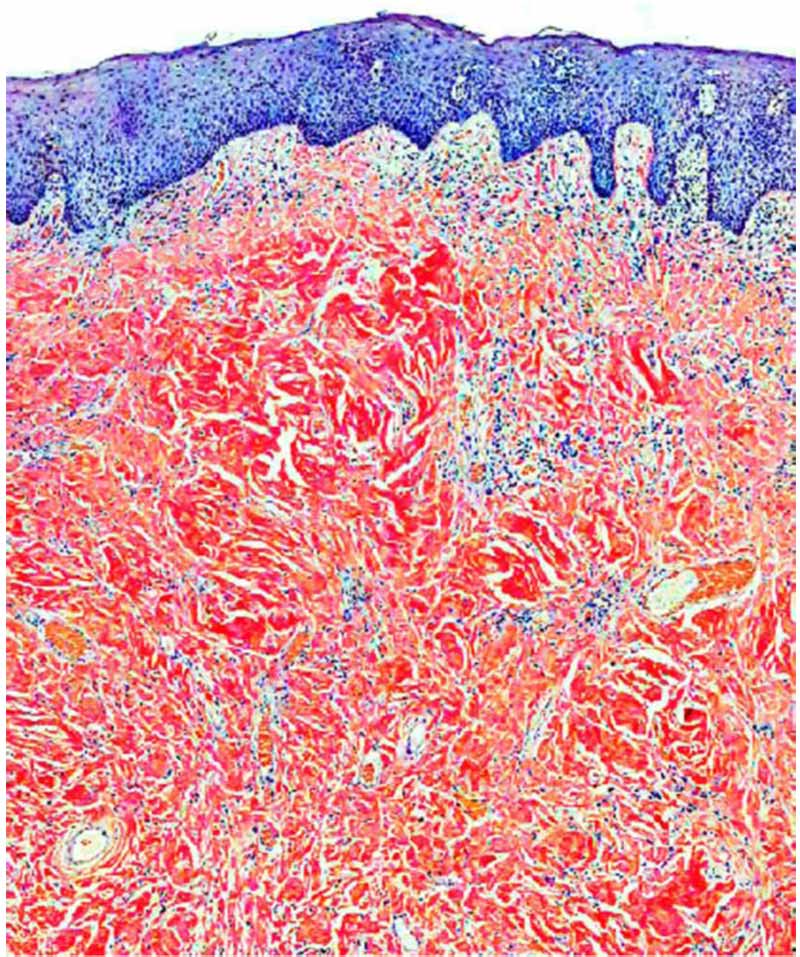
congo red stain




