- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

Human germ cells (ova and sperms) contain 23 chromosomes (haploid or 1N) while all the nucleated somatic cells of the human body contain 23 pairs of chromosomes (diploid or 2N)—44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, being XX in females (46, XX) and XY in males (46, XY)
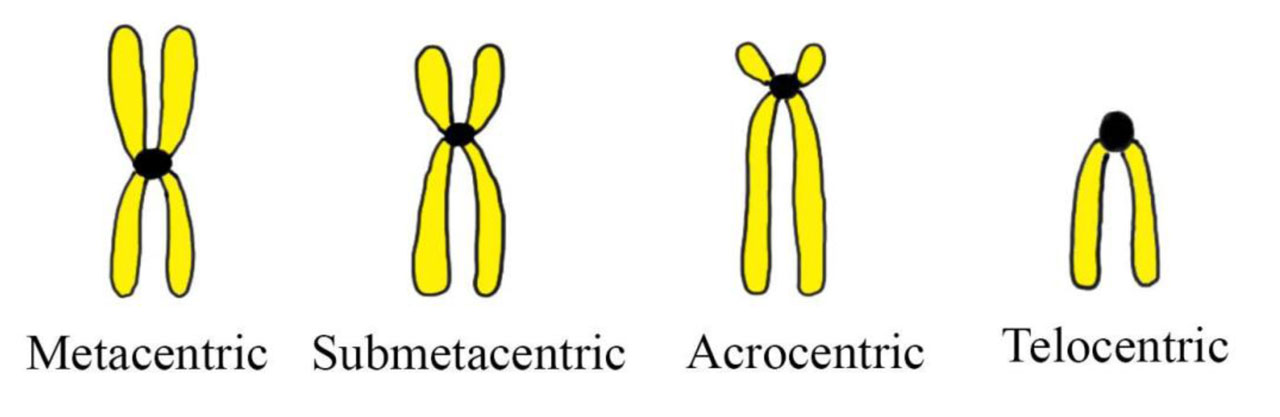
Based on centromeric location, they are classified into 3 groups:
Metacentric chromosomes (numbers 1, 3, 16, 19, 20) are those in which the centromere is exactly in the middle.
Submetacentric chromosomes (numbers 1, 3) in which the centromere divides the chromosomes into short arm (p arm; petit means short in French) and long arm (q arm; for alphabet next to p).
Acrocentric chromosomes(numbers 13, 14, 15, 21, 22, and Y) have very short arm and the centromere is eccentrically located.
Based on length of chromosomes, they are divided into 7 groups—A to G, called Denver classification
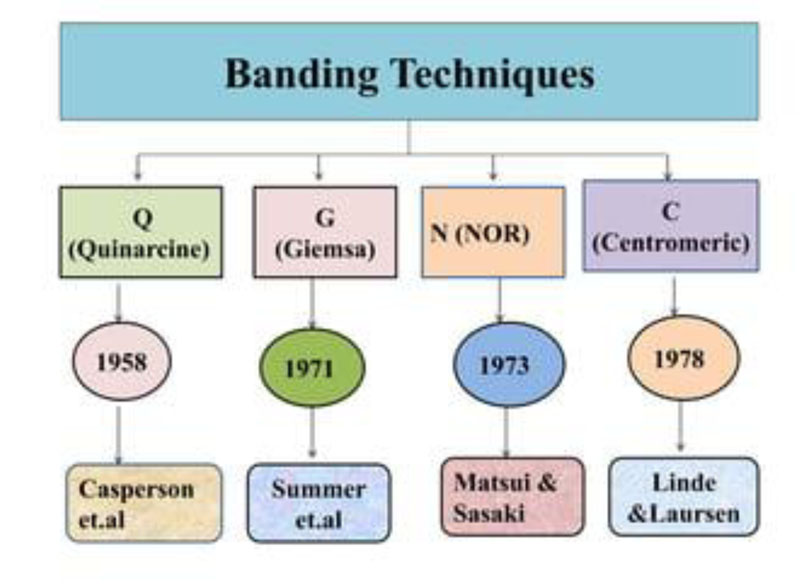
Chromosomal banding techniques
Chromosomal bands are unique alternate dark and light staining patterns. Banding techniques include:
- G-banding (Giemsa stain);
- Q-banding (quinacrine fluorescence stain);
- R-banding (reverse Giemsa staining); and
- C-banding (constitutive heterochromatin demonstration).
Abnormalities of chromosomes which can be divided into 2 types:
- Numerical abnormalities; and
- Structural abnormalities.
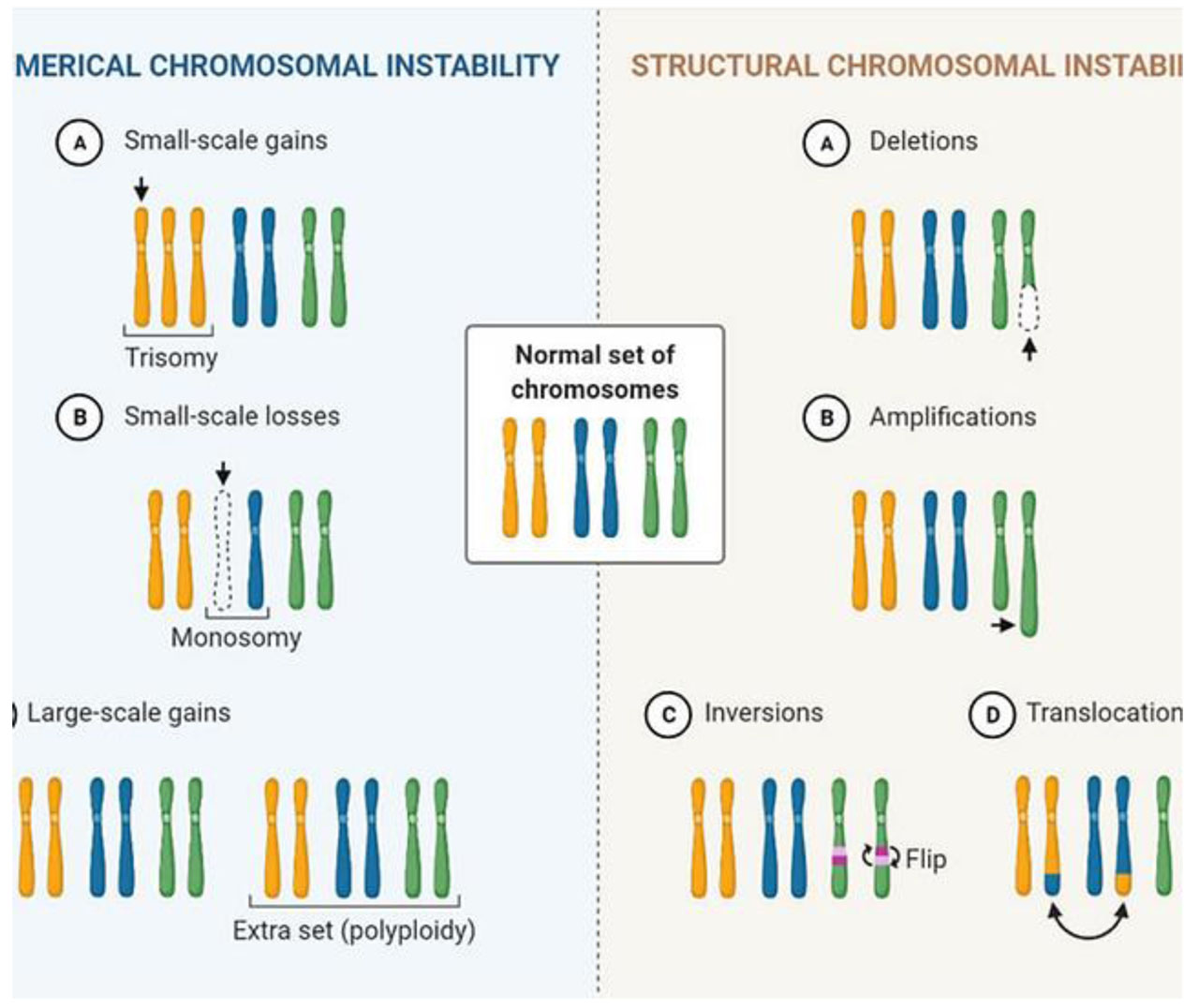
Numerical abnormalities
Polyploidy is the term used for the number of chromosomes which is a multiple of haploid number e.g. triploid or 3N (69 chromosomes), tetraploid or 4N (92 chromosomes).
Aneuploidy is the number of chromosomes which is not an exact multiple of haploid number e.g. hypodiploid or 2N-1 (45 chromosomes) monosomy, hyperdiploid or 2 N+1 (47 chromosomes) trisomy.
Examples
Most important
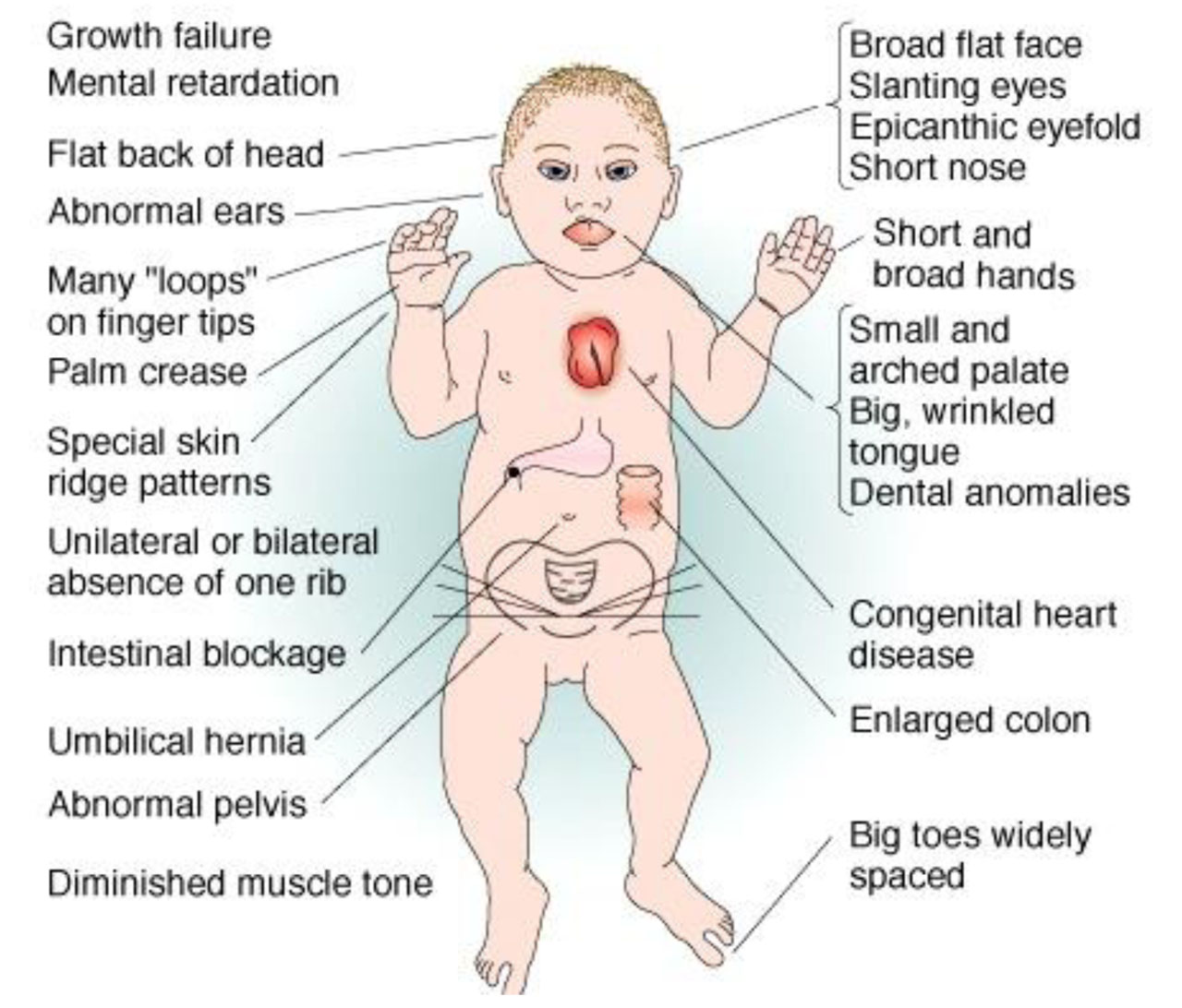
Down’s syndrome.
There is trisomy 21 in about 95% cases of Down’s syndrome due to nondisjunction during meiosis in one of the parents. Down’s syndrome is the most common chromosomal disorder and is the commonest cause of mental retardation. The incidence of producing offspring with Down’s syndrome rises in mothers over 35 years of age.
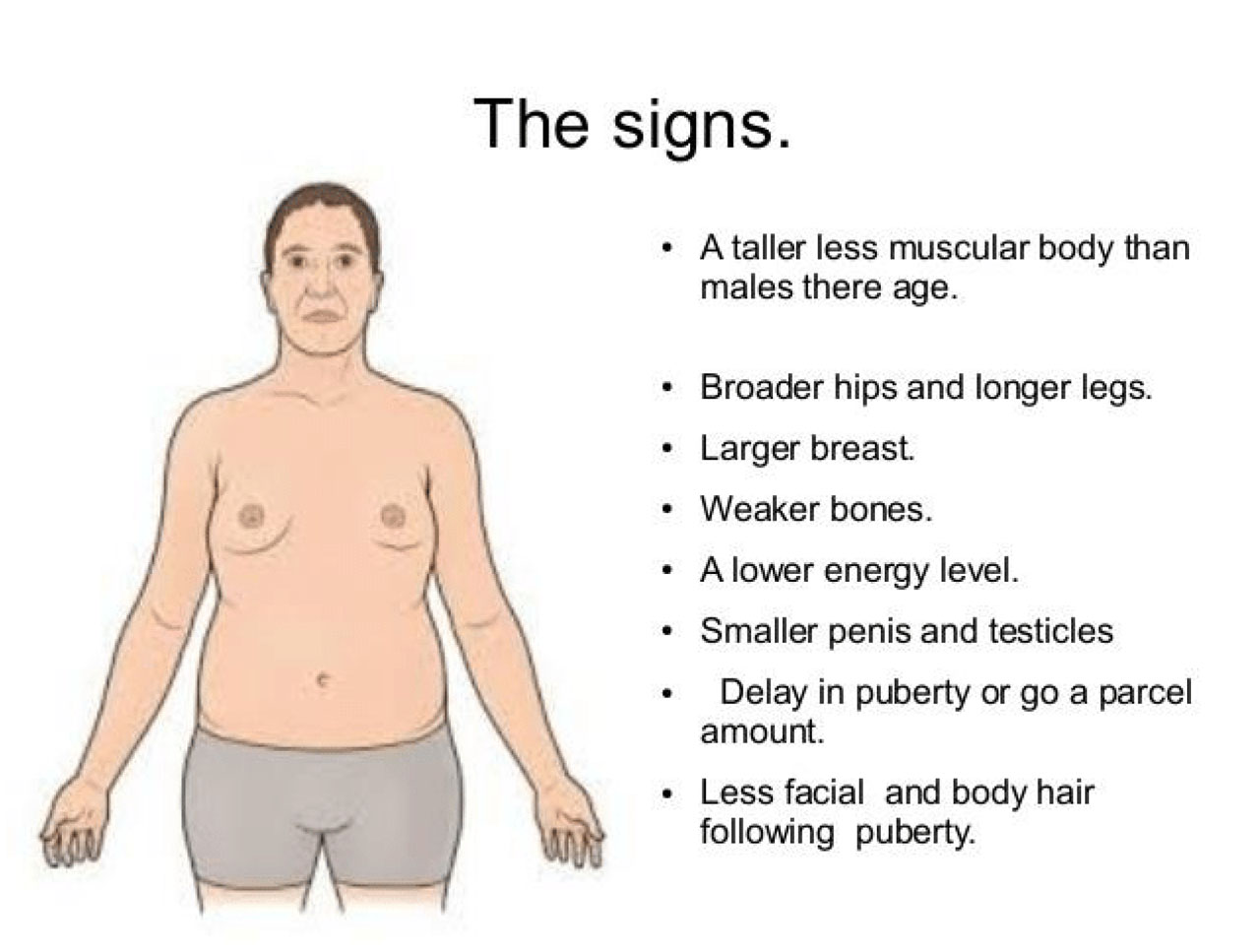
Klinefelter’s syndrome.
Klinefelter’s syndrome is the most important example of sex chromosome trisomy. About 80% cases have 47, XXY karyotype while others are mosaics. Typically, these patients have testicular dysgenesis. In general, sex chromosome trisomies are more common than trisomies of autosomes.
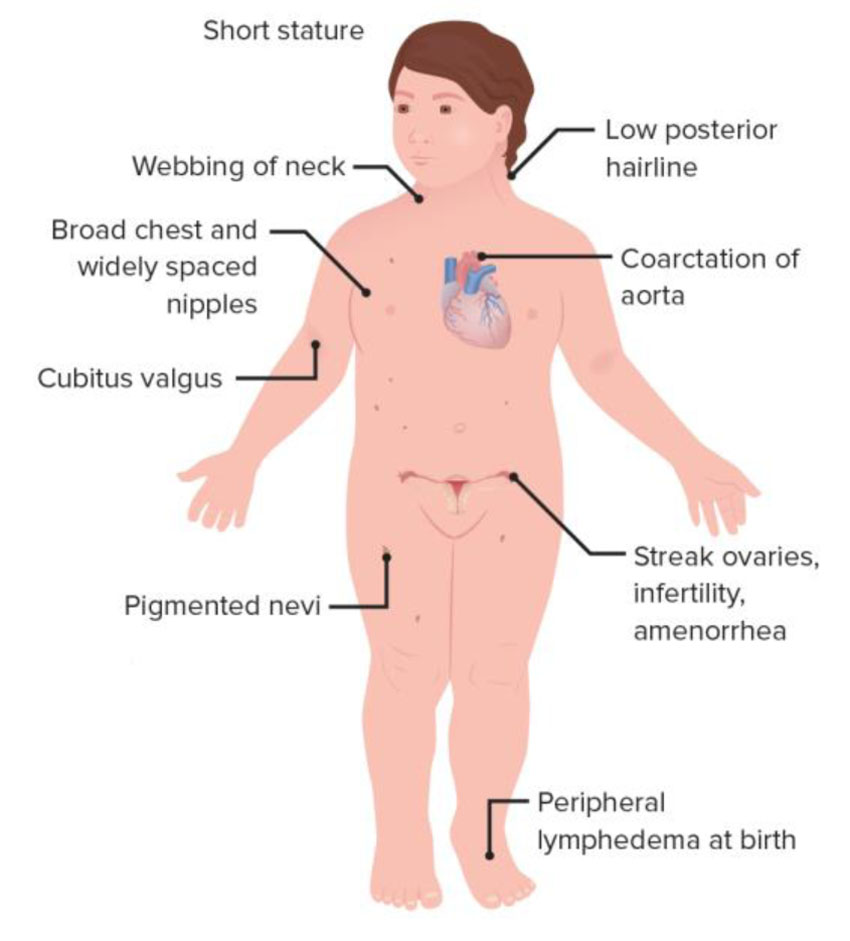
Turner’s syndrome.
Turner’s syndrome is an example of monosomy (45, X0) most often due to loss of X chromosome in paternal meiosis.
Structural Abnormalities
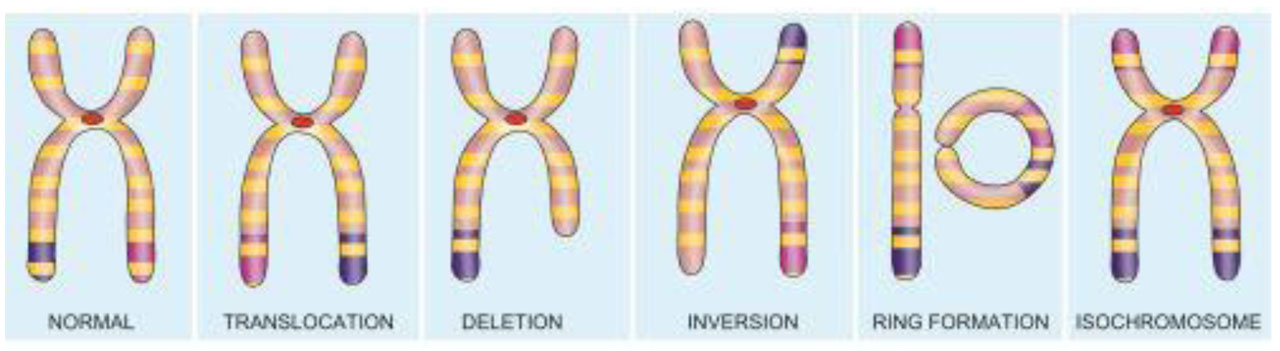
TRANSLOCATIONS means crossing over or exchange of fragment of chromosome which may occur between non-homologous or homologous chromosomes.
There are two main types of translocations: reciprocal in about two-third and Robertsonian in one-third cases.
DELETIONS. Loss of genetic material from the chromosome is called deletion.
INVERSION. Inversion is a form of rearrangement involving breaks of a single chromosome at two points.
RING CHROMOSOME. A ring of chromosome is formed by a break at both the telomeric (terminal) ends of a chromosome followed by deletion of the broken fragment and then end-to-end fusion.
ISOCHROMOSOME. When centromere, rather than dividing parallel to the long axis, instead divides transverse to the long axis of chromosome, it results in either two short arms only or two long arms only called isochromosomes.




