- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]

The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was originally developed in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis.
He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993 for his pioneering work.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method involves in vitro replication of DNA, therefore it is also called as “genetic xeroxing” method.
Multiple copies of specific region of DNA are made by repeated cycles or heating and cooling.
Principle of PCR
The PCR technique is based on the enzymatic replication of DNA.
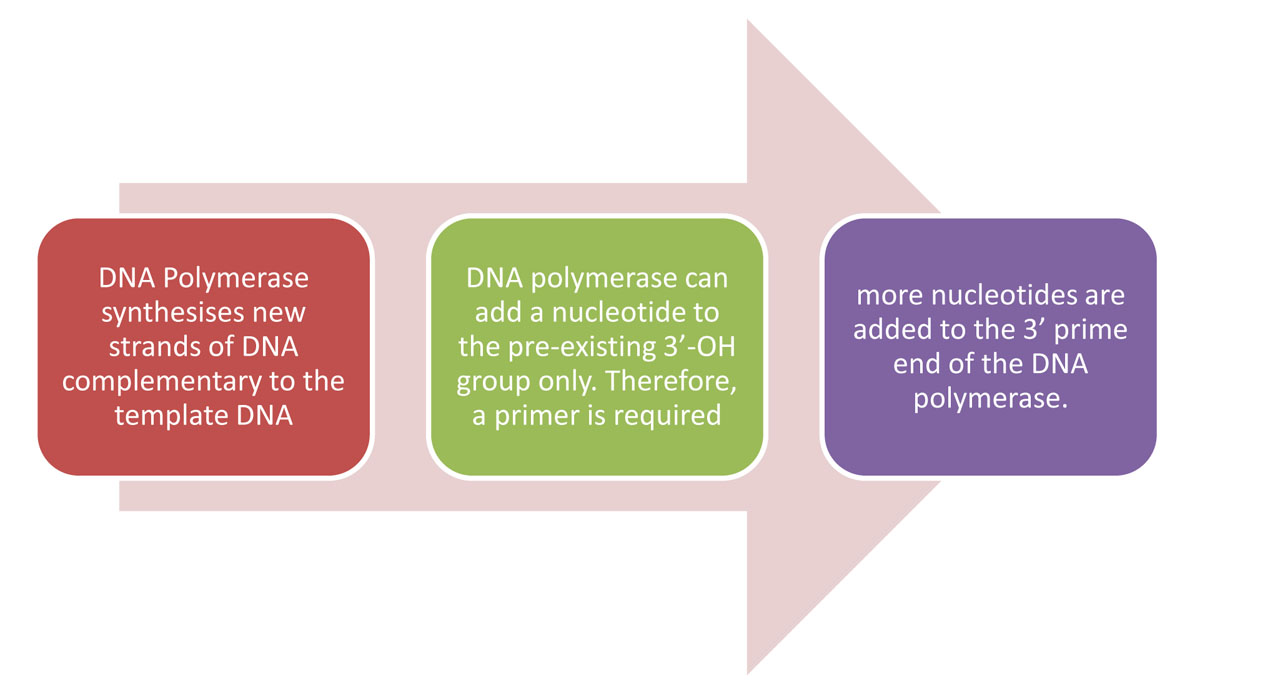
In PCR, a short segment of DNA is amplified using primer mediated enzymes.
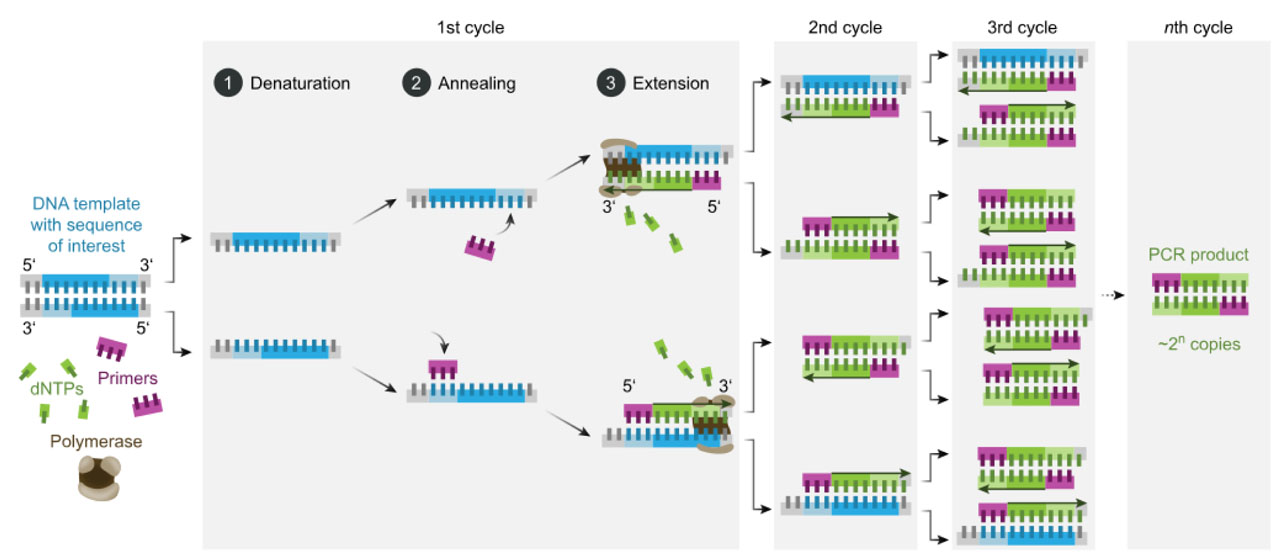
There are three main stages:
Denaturing – when the double-stranded template DNA is heated to separate it into two single strands.
Annealing – when the temperature is lowered to enable the DNA primers to attach to the template DNA.
Extending – when the temperature is raised and the new strand of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme.
How the process works?
- During a typical PCR, cycles of denaturation, annealing and extension are repeated to achieve exponential amplification of the target sequence.
- Denaturation consists of heating the samples up typically between 94- 98°C to cause denaturation of the template DNA, disrupting the hydrogen bonds and base stacking interactions that hold the DNA strands together.
- Once the strands are separated, the temperature is decreased to the annealing temperature to allow the primers to base pair (or anneal) to complementary regions of the template.
- The annealing temperature (typically between 48-72°C) is related to the melting temperature (Tm) of the primers and must be determined for each primer pair used in PCR.
- During the extension step (typically 68-72°C) the polymerase extends the primer to form a nascent DNA strand.
- This process is repeated multiple times (typically 25-35 cycles), and because each new strand can also serve as a template for the primers, the region of interest is amplified exponentially.
- The final step of the PCR is generally a longer, single temperature step (often 5-10 min at 68-72°C) that allows for the completion of any partial copies and the clearance of all replication machinery from the nascent DNA.
- Once the PCR is complete, the thermal cycler is set to 4°-10°C to maintain product integrity until such time as the tubes can be removed from the machine.
Advantages of PCR method
- PCR has remarkable sensitivity and specificity because each distinct microbial species has unique DNA sequences.
- PCR can be used to detect virtually all bacterial species in a sample.
- It is also used to investigate microbial diversity in a given environment. Clonal analysis of microorganisms can also be done by PCR method.
Disadvantages of PCR method
- Identify microorganisms qualitatively not quantitatively
- Detect only target microorganisms
- Difficult in microorganisms with thick wall like fungi
- Possibility of false positive and negative results.
NOTE
- RT-PCR (Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction) is a highly sensitive technique for the detection and quantitation of mRNA (messenger RNA). The technique consists of two parts:
- The synthesis of cDNA (complementary DNA) from RNA by reverse transcription (RT) and
- The amplification of a specific cDNA by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- RT-PCR has been used to measure viral load with HIV and may also be used with other RNA viruses such as measles, mumps, corona etc.


