- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
1. Endotoxic shock is initiated by
a. Peripheral vasodilation
b. Injury to endothelial cells
c. Inadequate blood volume
d. Failure of myocardial pump
ANSWER b
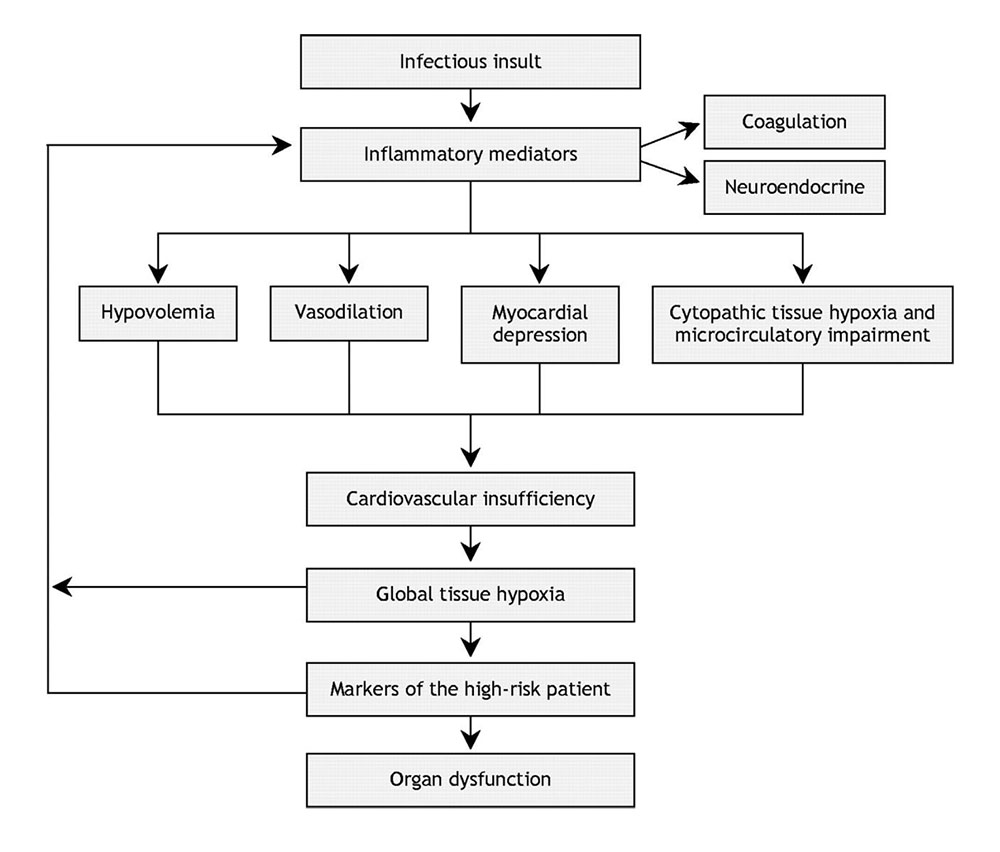
Endotoxic shock results from a severe, generalized inflammatory response induced by bloodstream infection with gram-negative bacteria.
Endotoxin on the surface of gram negative organisms stimulates the release of inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide resulting in smooth muscle relaxation, vasodilation, and increased vascular permeability.
Patients typically present with fever and hypotension, often refractory despite adequate fluid resuscitation.
A flowchart representation of pathogenesis of shock
2. Nephrotic syndrome causes of except
a. General edema
b. Hematuria
c. Hyperlipidemia
d. Hypercholesterolemia
ANSWER b
Nephrotic syndrome causes your kidneys to release too much protein in your urine. Causes include kidney diseases that affect the tiny filters inside your kidneys.
Common nephrotic syndrome symptoms include:
- Large amounts (greater than 3.5 grams) of the protein albumin in your pee (albuminuria).
- High fat and cholesterol levels in your blood (hyperlipidemia).
- Swelling (edema), usually in your legs, feet or ankles. Swelling may also occur in your hands or face.
- Low levels of albumin in your blood (hypoalbuminemia).
- Loss of appetite.
- Feeling unwell or sick.
- Abdominal pain (pain anywhere from your ribs to your pelvis).
- Foamy pee.
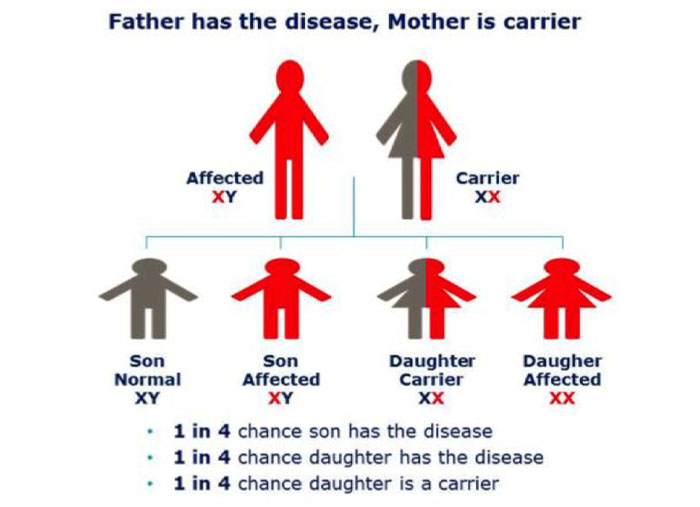
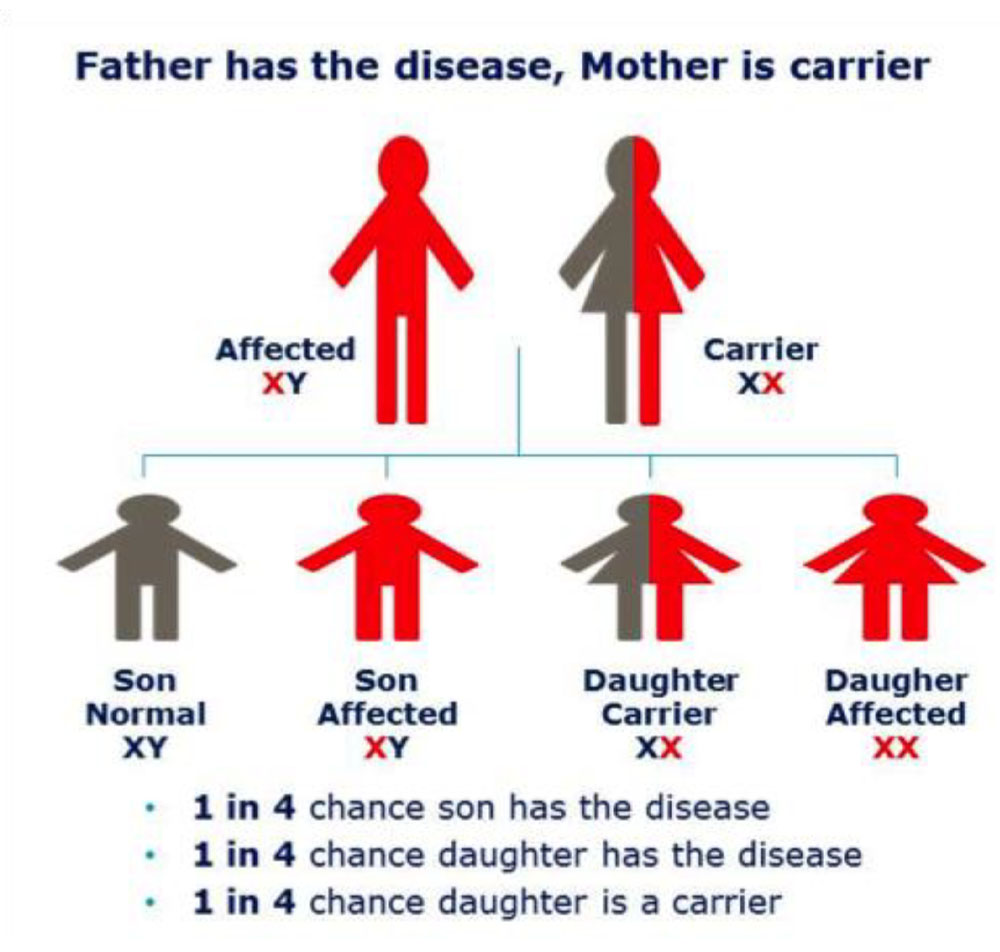
3. If father is hemophilic and mother is normal which of the following will be affected
a. 50% sons will be affected
b. All daughters are carries
c. All song are carriers
d. 50% of his daughter are carriers
ANSWER b
There are three possible scenarios for inheriting hemophilia, depending on whether a mother or father (or both) is affected:
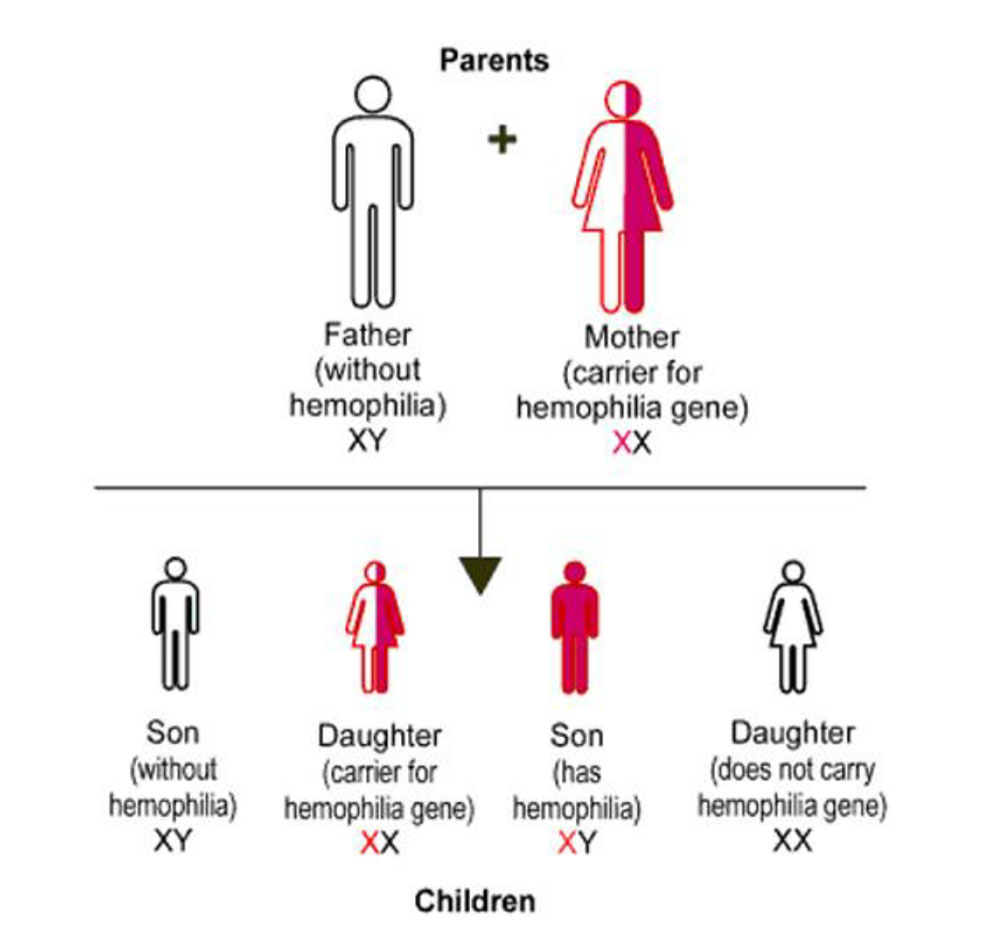
If the mother has one altered factor gene and the father does not have hemophilia, each son has a 50% chance of having hemophilia and each daughter has a 50% chance of having one altered factor gene, causing her to be a carrier or have hemophilia.
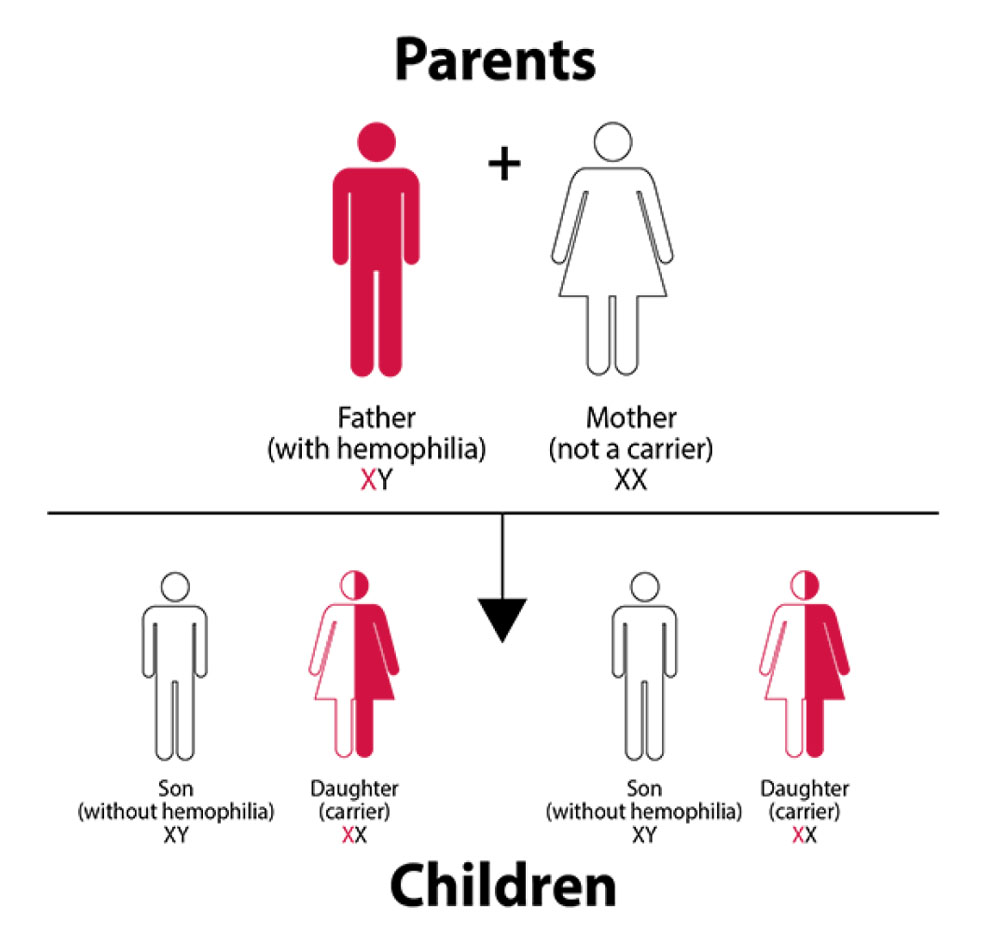
If the father has hemophilia, and the mother does not carry a hemophilia gene, then each son has a 0% chance of having hemophilia, and each daughter has a 100% chance of either being a carrier or having hemophilia.
If the father has hemophilia, and the mother is a carrier of the hemophilia gene, then each son has a 50% chance of having hemophilia, and each daughter has a 50% chance of having one altered factor gene causing her to be a carrier or have hemophilia, and a 50% chance of having two altered factor genes and having hemophilia.
4. A person aspirin will have
a. Increased PT
b. Increased CT
c. Increased BT
d. Thrombocytosis
ANSWER c
Aspirin influences the bleeding time, presumably through the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis and the resultant platelet secretion reaction. This can be measured by prolongation of the bleeding time and changes in platelet function results.
5. Not a market of new bone formation
a. Alkaline phosphates
b. Urine hydroxyproline
c. Osteocalcine
d. Procollagen peptide
ANSWER b
Evidence of bone formation is indicated by the presence of
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bone alkaline phosphatase (B-ALP),
- Osteocalcin (OC),
- C- and N-terminal propeptide of type 1 procollagen (PICP and PINP).
ALP is specific for bone formation, but only if the patient has no bile duct or liver disease




