- NEED HELP? CALL US NOW
- +919995411505
- [email protected]
SPRING IN ORTHODONTICS

Springs are a part of the active components of removable orthodontic appliances
used to bring about tooth movement
- Those parts which deliver forces to the teeth and/or skeletal structures to
bring about changes in position. - To bring about tooth movement, always use light and continuous forces
- Heavy forces damage the periodontium, bring about root resorption etc
Removable appliance has 3 components
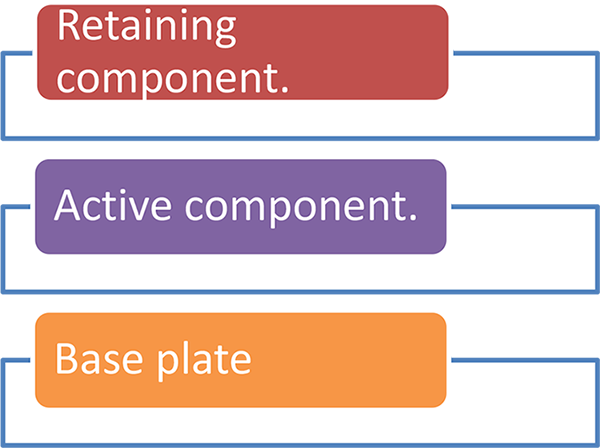
Spring is a part of active component
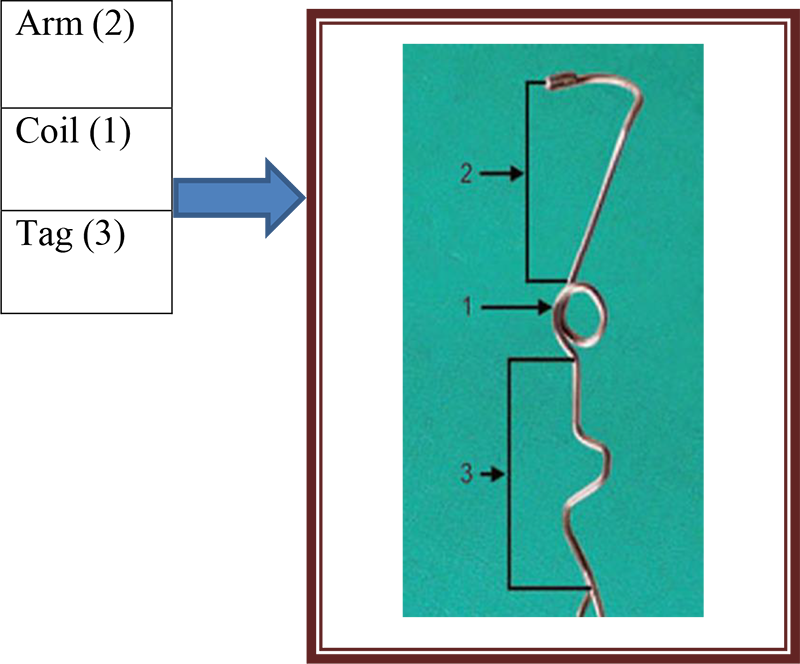
Components of a spring.
Classification of springs
(1) Based on the presence or absence of helix they can be classified as
- Simple –without helix
- Compound –with helix
(2) Based on the presence of loop or helix they can be classified as
- Helical springs – have a helix
- Looped springs – have a loop
(3) Based on the nature of stability of the springs they can be classified as:
- Self –supported spring = made of thicker gauge wire ,can support themselves
- Supported springs = made of thinner gauge wire and thus lack adequate stability, springs are encased in metallic tube to give adequate support .
Ideal requisites of a spring :-
- Simple to fabricate.
- Easily adjustable.
- Should fit into the avilable space with out discomfort to the patient.
- Easy to clean.
- Should apply force of required magnitude and direction.
- Should not slip or dislodge when placed over a sloping tooth surface
- It should remain active over a long period of time.
Factor to be considered in designing a spring
- Diameter of wire :- flexibility of the spring to a large extent depends upon
diameter of wire - The force (F) delivered by a spring is expressed by the formula F α dr4/l3
- F= force applied by spring D=diameter of wire L= length of wire
- Length of wire :- force can be decreased by increasing the length of wire .
- Thus springs that are longer are more flexible and remains active for long
duration of time . - By doubling the length of wire force can be reduced by eight times .
- Patient comfort :- spring should be comfortable to patient in design ,
shape , size or force generation . - Direction of tooth movement :- the direction of tooth movement is
determined by the point of contact between the spring and the tooth .
Palatally placed spring are used for labial and mesio – distal tooth
movement .buccally placed spring are used when the tooth is to be moved
palatally and in a mesio-distal direction .
FEW EXAMPLES OF SPRING ARE…
FINGER SPRING
- It is constructed using 0.5 mm SS wire .
- Parts Helix (2 mm) -Active arm -Retentive arm
- The helix is positioned opposite to the direction of intended tooth
movement. - It should also be placed along the long axis of the tooth to be moved and
perpendicular to the directon of tooth movement - INDICA TION – Mesio-distal movement of teeth e.g. closure of anterior
diastemas - Activation Opening the coil or moving the active arm towards the tooth to
be moved 2-3 mm of activation
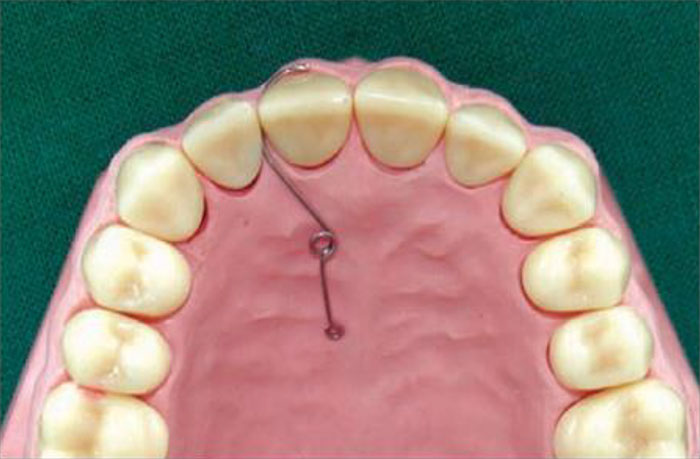
Z-SPRING (DOUBLE CANTILEVER ):
- A useful variation of the finger spring where a second limb is formed
with a second coil. - Construction: it consists of 2 helices of small diameter can be made for 1
or more incisors. - The spring is positioned perpendicular to the palatal surface of the tooth
with a long retentive arm. - The Z-spring needs to be boxed in wax prior to acrylization.
- INDICA TION: to move one or more teeth in the same direction E.g.
proclining 2 or more upper incisors for the correction of anterior tooth
crossbites. - To correct mild rotation if only one helix is activated.
- Activation: By opening both the helices up to 2 mm at a time.

CRANKED SINGLE CANTILEVER SPRING
- It is constructed with 0.5mm wire .
- The spring consist of coil , close to its emergence from base plate .
- The spring is cranked to keep it clear of the other teeth .it is used to move
teeth labially .
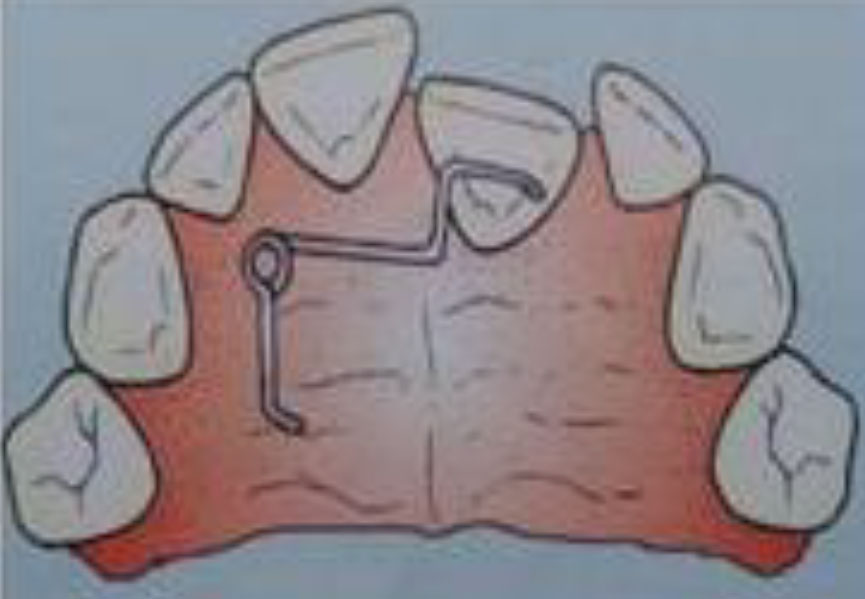
T SPRING
- It is made of 0.5 mm wire .
- The spring consist of t shaped arm whose arm are embedded in acrylic.
- It is used for buccal movement of premolar and some canine .
- It is activated by pulling the free end of the spring toward the intended
direction of tooth movement.
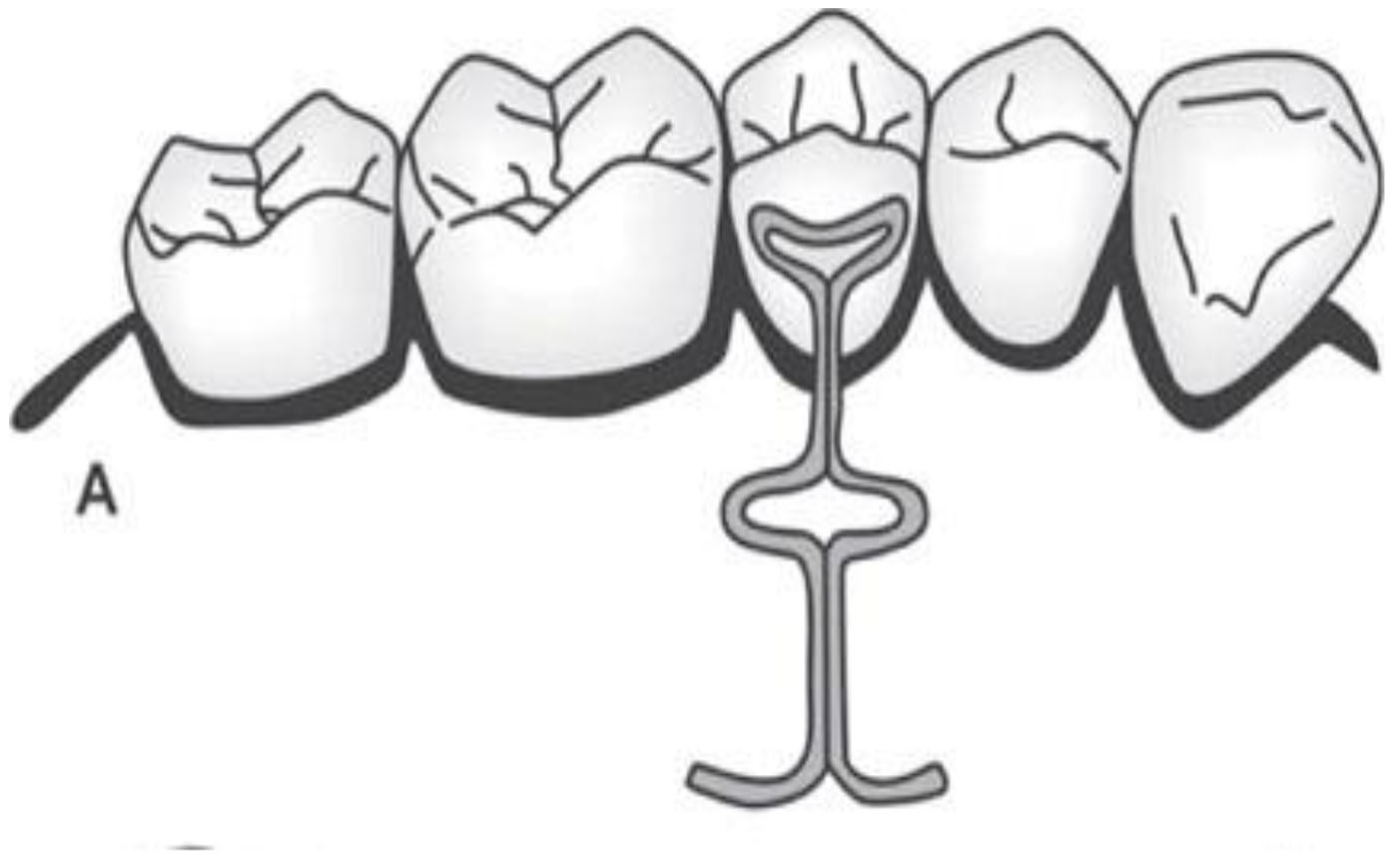
COFFIN SPRING
- It is made of 1.2mm wire .
- It consist of a u or omega shaped wire placed in the midpalatal region
with retentive arm incorporated in base plates . - It is retended by adams clasp in molar. It is used in slow dentoalveolar
arch expansion in patient with upper arch constriction or in unilateral
crossbite.

Related posts
April 10, 2025
April 9, 2025
April 4, 2025




